
The following is an alphabetical list of topics related to the British Overseas Territory of the Bermuda Islands .

The following is an alphabetical list of topics related to the British Overseas Territory of the Bermuda Islands .




Bermuda is a British Overseas Territory in the North Atlantic Ocean. The closest land outside the territory is in the American state of North Carolina, approximately 1,035 km (643 mi) to the west-northwest.

Bermuda was first documented by a European in 1503 by Spanish explorer Juan de Bermúdez. In 1609, the English Virginia Company, which had established Jamestown in Virginia two years earlier, permanently settled Bermuda in the aftermath of a hurricane, when the crew and passengers of Sea Venture steered the ship onto the surrounding reef to prevent it from sinking, then landed ashore. Bermuda's first capital, St. George's, was established in 1612.

Bermuda is an overseas territory of the United Kingdom in the North Atlantic Ocean. Located off the east coast of the United States, it is situated around 1,770 km (1,100 mi) northeast of Miami, Florida, and 1,350 km (840 mi) south of Halifax, Nova Scotia, west of Portugal, northwest of Brazil, 1,759 km (1,093 mi) north of Havana, Cuba and north-northeast of San Juan, Puerto Rico. The nearest landmass is Cape Hatteras, North Carolina, about 1,030 km (640 mi) west-northwest, followed by Cape Sable Island, Nova Scotia, Canada 1,236 km northward. Although commonly referred to in the singular, the territory consists of approximately 138 islands, with a total area of 57 km2 (22 sq mi).

While the defence of Bermuda remains the responsibility of the government of the United Kingdom, rather than of the local Bermudian Government, the island still maintains a militia for the purpose of defence.

The City of Hamilton, in Pembroke Parish, is the territorial capital of the British Overseas Territory of Bermuda. It is the territory's financial centre and a major port and tourist destination. Its population of 854 (2016) is one of the smallest of any capital city.

St. George's, located on the island and within the parish of the same names, settled in 1612, is the first permanent English settlement on the islands of Bermuda. It is often described as the third permanent British settlement in the Americas, after Jamestown, Virginia (1607), and Cupids, Newfoundland (1610), and the oldest continuously-inhabited British town in the New World, since the other two settlements were seasonal for a number of years.

Kindley Air Force Base was a United States Air Force base in Bermuda from 1948–1970, having been operated from 1943 to 1948 by the United States Army Air Forces as Kindley Field.
A variety of sports are played in British Overseas Territory of Bermuda, from those brought by British and International relations, and sail racing). Some sports and events have greater historical and cultural significance whilst others are played for entertainment or competition.
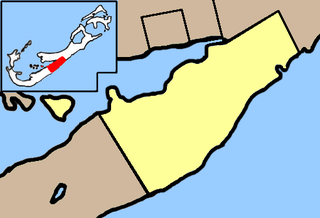
Paget Parish is one of the nine parishes of Bermuda. It is named for William Paget, 4th Baron Paget de Beaudesert (1572–1629).
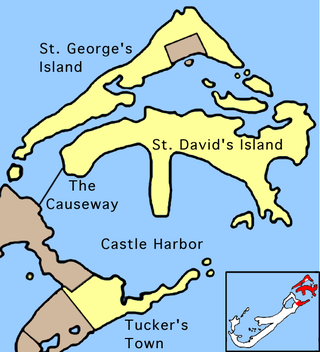
St. George's Parish is one of the nine parishes of Bermuda. It is named after the founder of the Bermuda colony, Admiral Sir George Somers.

St. David's Island is one of the main islands of the British Overseas Territory of Bermuda. It is located in the far north of the territory, one of the two similarly sized islands that make up the majority of St. George's Parish.

The Royal Air Force (RAF) operated from two locations in the Imperial fortress colony of Bermuda during the Second World War. Bermuda's location had made it an important naval station since US independence, and, with the advent of the aeroplane, had made it as important to trans-Atlantic aviation in the decades before the Jet Age. The limited, hilly land mass had prevented the construction of an airfield, but, with most large airliners in the 1930s being flying boats, this was not initially a limitation.
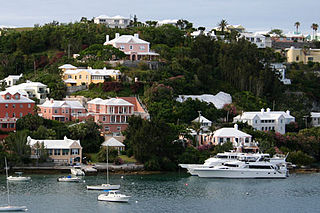
The architecture of Bermuda has developed over the past four centuries. The archipelago's isolation, environment, climate, and scarce resources have been key driving points, though inspiration from Europe, the Caribbean and the Americas is evident. Distinctive elements appeared with initial settlement in the early 17th century, and by the second half of that century features that remain common today began to appear.

Naval Air Station Bermuda, was located on St. David's Island in the British Colony of Bermuda from 1970 to 1995, on the former site of Kindley Air Force Base. It is currently the site of Bermuda International Airport.
The following is an alphabetical list of topics related to the nation of Jamaica.

The following outline is provided as an overview of and topical guide to Bermuda:

The Bermuda Garrison was the military establishment maintained on the British Overseas Territory and Imperial fortress of Bermuda by the regular British Army and its local militia and voluntary reserves from 1701 to 1957. The garrison evolved from an independent company, to a company of Royal Garrison Battalion during the American War of Independence, and a steadily growing and diversifying force of artillery and infantry with various supporting corps from the French Revolution onwards. During the American War of Independence, the garrison in Bermuda fell under the military Commander-in-Chief of America. Subsequently, it was part of the Nova Scotia Command until 1868, and was an independent Bermuda Command from then until its closure in 1957.

HMS Castle Harbour was a civilian harbour vessel of 730 tons that was taken-up from trade (TUFT) during the Second World War by the Royal Naval Dockyard in Bermuda for use by the Royal Naval Examination Service and later armed and commissioned as a warship, providing harbour defence from submarines.

Imperial fortress was the designation given in the British Empire to four colonies that were located in strategic positions from each of which Royal Navy squadrons could control the surrounding regions and, between them, much of the planet.