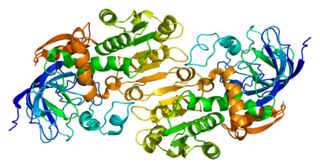
Alcohol dehydrogenases (ADH) (EC 1.1.1.1) are a group of dehydrogenase enzymes that occur in many organisms and facilitate the interconversion between alcohols and aldehydes or ketones with the reduction of nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NAD+) to NADH. In humans and many other animals, they serve to break down alcohols that are otherwise toxic, and they also participate in the generation of useful aldehyde, ketone, or alcohol groups during the biosynthesis of various metabolites. In yeast, plants, and many bacteria, some alcohol dehydrogenases catalyze the opposite reaction as part of fermentation to ensure a constant supply of NAD+.

Acetaldehyde dehydrogenases are dehydrogenase enzymes which catalyze the conversion of acetaldehyde into acetyl-CoA. This can be summarized as follows:
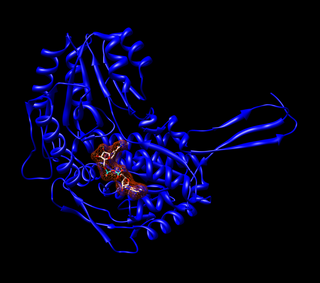
Aldehyde dehydrogenases are a group of enzymes that catalyse the oxidation of aldehydes. They convert aldehydes to carboxylic acids. The oxygen comes from a water molecule. To date, nineteen ALDH genes have been identified within the human genome. These genes participate in a wide variety of biological processes including the detoxification of exogenously and endogenously generated aldehydes.

Carotenoid oxygenases are a family of enzymes involved in the cleavage of carotenoids to produce, for example, retinol, commonly known as vitamin A. This family includes an enzyme known as RPE65 which is abundantly expressed in the retinal pigment epithelium where it catalyzed the formation of 11-cis-retinol from all-trans-retinyl esters.
3β-Hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase/Δ5-4 isomerase (3β-HSD) is an enzyme that catalyzes the biosynthesis of the steroid progesterone from pregnenolone, 17α-hydroxyprogesterone from 17α-hydroxypregnenolone, and androstenedione from dehydroepiandrosterone (DHEA) in the adrenal gland. It is the only enzyme in the adrenal pathway of corticosteroid synthesis that is not a member of the cytochrome P450 family. It is also present in other steroid-producing tissues, including the ovary, testis and placenta. In humans, there are two 3β-HSD isozymes encoded by the HSD3B1 and HSD3B2 genes.
Ethanol, an alcohol found in nature and in alcoholic drinks, is metabolized through a complex catabolic metabolic pathway. In humans, several enzymes are involved in processing ethanol first into acetaldehyde and further into acetic acid and acetyl-CoA. Once acetyl-CoA is formed, it becomes a substrate for the citric acid cycle ultimately producing cellular energy and releasing water and carbon dioxide. Due to differences in enzyme presence and availability, human adults and fetuses process ethanol through different pathways. Gene variation in these enzymes can lead to variation in catalytic efficiency between individuals. The liver is the major organ that metabolizes ethanol due to its high concentration of these enzymes.

Aldehyde dehydrogenase, mitochondrial is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the ALDH2 gene located on chromosome 12. This protein belongs to the aldehyde dehydrogenase family of enzymes. Aldehyde dehydrogenase is the second enzyme of the major oxidative pathway of alcohol metabolism. Two major liver isoforms of aldehyde dehydrogenase, cytosolic and mitochondrial, can be distinguished by their electrophoretic mobilities, kinetic properties, and subcellular localizations.

6-Phosphogluconate dehydrogenase (6PGD) is an enzyme in the pentose phosphate pathway. It forms ribulose 5-phosphate from 6-phosphogluconate:

In enzymology, a homoserine dehydrogenase (EC 1.1.1.3) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction

In enzymology, beta-carotene 15,15'-dioxygenase, (EC 1.13.11.63) is an enzyme with systematic name beta-carotene:oxygen 15,15'-dioxygenase (bond-cleaving). In human it is encoded by the BCDO2 gene. This enzyme catalyses the following chemical reaction
In enzymology, an aryl-aldehyde dehydrogenase (NADP+) (EC 1.2.1.30) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction

Alcohol dehydrogenase 1B is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the ADH1B gene.
Apo-beta-carotenoid-14',13'-dioxygenase (EC 1.13.11.67 is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction

Aldehyde dehydrogenase, dimeric NADP-preferring is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the ALDH3A1 gene.

Methylmalonate-semialdehyde dehydrogenase [acylating], mitochondrial (MMSDH) is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the ALDH6A1 gene.
Phytoene desaturase (3,4-didehydrolycopene-forming) is an enzyme with systematic name 15-cis-phytoene:acceptor oxidoreductase (3,4-didehydrolycopene-forming). This enzyme catalyses the following chemical reaction
Torulene dioxygenase (EC 1.13.11.59, CAO-2, CarT) is an enzyme with systematic name torulene:oxygen oxidoreductase. This enzyme catalyses the following chemical reaction
9-cis-beta-carotene 9',10'-cleaving dioxygenase (EC 1.13.11.68, CCD7 (gene), MAX3 (gene), NCED7 (gene)) is an enzyme with systematic name 9-cis-beta-carotene:O2 oxidoreductase (9',10'-cleaving). This enzyme catalyses the following chemical reaction
Carlactone synthase (EC 1.13.11.69, CCD8 (gene), MAX4 (gene), NCED8 (gene)) is an enzyme with systematic name 9-cis-10'-apo-beta-carotenal:O2 oxidoreductase (14,15-cleaving, carlactone-forming). This enzyme catalyses the following chemical reaction
All-trans-8'-apo-beta-carotenal 15,15'-oxygenase (EC 1.14.99.41, Diox1, ACO, 8'-apo-beta-carotenal 15,15'-oxygenase) is an enzyme with systematic name all-trans-8'-apo-beta-carotenal:oxygen 15,15'-oxidoreductase (bond-cleaving). This enzyme catalyses the following chemical reaction











