Related Research Articles

Bornholm is a Danish island in the Baltic Sea, to the east of the rest of Denmark, south of Sweden, northeast of Germany and north of Poland.

Skåneland or Skånelandene (Danish) is a region on the southern Scandinavian peninsula. It includes the Swedish provinces of Blekinge, Halland, and Scania. The Danish island of Bornholm is traditionally also included. Skåneland has no official recognition or function and the term is not in common usage. Equivalent terms in English and Latin are "the Scanian Provinces" and "Terrae Scaniae" respectively. The term is mostly used in historical contexts and not in daily speech. In Danish, Skånelandene is used more often. The terms have no political implications as the region is not a political entity but a cultural region, without officially established administrative borders.

The Treaty of Roskilde was negotiated at Høje Taastrup Church and signed (NS) during the Second Northern War between Frederick III of Denmark–Norway and Karl X Gustav of Sweden in the Danish city of Roskilde. After a devastating defeat, Denmark–Norway was forced to give up a third of its territory to save the rest, the ceded lands comprising Blekinge, Bornholm, Bohuslän (Båhuslen), Scania (Skåne) and Trøndelag, as well as her claims to Halland.

A shield is a large area of exposed Precambrian crystalline igneous and high-grade metamorphic rocks that form tectonically stable areas. These rocks are older than 570 million years and sometimes date back to around 2 to 3.5 billion years. They have been little affected by tectonic events following the end of the Precambrian, and are relatively flat regions where mountain building, faulting, and other tectonic processes are minor, compared with the activity at their margins and between tectonic plates. Shields occur on all continents.

Fennoscandia, or the Fennoscandian Peninsula, is the geographical peninsula in Europe which includes the Scandinavian and Kola peninsulas, mainland Finland, and Karelia. Administratively, this roughly encompasses the mainlands of Finland, Norway and Sweden, as well as Murmansk Oblast, much of the Republic of Karelia, and parts of northern Leningrad Oblast in Russia.
The Treaty of Copenhagen was signed on 27 May 1660, and marked the conclusion of the Second Northern War between the Swedish Empire and the alliance of Denmark-Norway and the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth. This treaty was a smaller follow-up treaty to that of the Treaty of Roskilde, which decisively delineated the mutually recognized boundaries of Denmark, Sweden, and Norway; boundaries which are almost exactly the same to this day.

The Diocese of Lund is a diocese within the Church of Sweden which corresponds to the provinces of Blekinge and Skåne. There are 217 parishes within the diocese, the most significant number in any of the dioceses of the Church of Sweden. The present bishop of Lund, Johan Tyrberg, succeeded Antje Jackelén in 2014.
Bornholmsk is an East Danish dialect spoken on the island of Bornholm in the Baltic Sea. It was originally part of the East Danish dialect continuum, which includes the dialects of southern Sweden, but became isolated in the Danish dialect landscape after 1658, when Sweden annexed the eastern Danish provinces of Scania (Skåne), Halland and Blekinge.

The Dano-Swedish War of 1657–1658, known in Denmark as the First Karl Gustav War in Norway as Krabbes Feud and in Sweden as Karl Gustav's First Danish War, was a conflict between Sweden and Denmark–Norway during the Second Northern War. In 1657, Charles X of Sweden and his Swedish army were bogged down in Poland. Frederick III of Denmark-Norway saw an opportunity to recover the territories lost in 1645 and attacked Sweden. The outbreak of war with Denmark provided Charles with an excuse to withdraw from the Polish campaign and move against Denmark.

The Danish language has a number of regional and local dialect varieties. These can be divided into the traditional dialects, which differ from modern Standard Danish in both phonology and grammar, and the Danish accents, which are local varieties of the standard language distinguished mostly by pronunciation and local vocabulary colored by traditional dialects. Traditional dialects are now mostly extinct in Denmark, with only the oldest generations still speaking them.
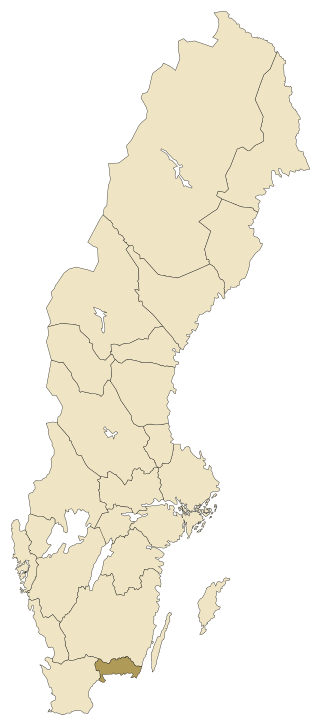
Blekinge (Swedish pronunciation:[ˈblêːkɪŋɛ], is one of the traditional Swedish provinces, situated in the southern coast of the geographic region of Götaland, in southern Sweden. It borders Småland, Scania and the Baltic Sea. It is the country's second-smallest province by area, and the smallest province located on the mainland.

Joachim Gersdorff was a Danish politician, from 1650 to 1660 Steward of the Danish Realm. It was Gersdorff who negotiated the Treaty of Roskilde on Denmark's part during the Second Northern War, a war he had himself been in favour of entering. Through this treaty, which was concluded in Roskilde on 8 March 1658 (NS), the eastern Danish provinces of Scania, Halland, Blekinge and Bornholm were ceded to Sweden.
Events from the year 1658 in Denmark.

The Sveconorwegian orogeny was an orogenic system active 1140 to 960 million years ago and currently exposed as the Sveconorwegian orogenic belt in southwestern Sweden and southern Norway. In Norway the orogenic belt is exposed southeast of the front of the Caledonian nappe system and in nappe windows. The Sveconorwegian orogen is commonly grouped within the Grenvillian Mesoproterozoic orogens. Contrary to many other known orogenic belts the Sveconorwegian orogens eastern border does not have any known suture zone with ophiolites.

The Svecofennian orogeny is a series of related orogenies that resulted in the formation of much of the continental crust in what is today Sweden and Finland plus some minor parts of Russia. The orogenies lasted from about 2000 to 1800 million years ago during the Paleoproterozoic Era. The resulting orogen is known as the Svecofennian orogen or Svecofennides. To the west and southwest the Svecofennian orogen limits with the generally younger Transscandinavian Igneous Belt. It is assumed that the westernmost fringes of the Svecofennian orogen have been reworked by the Sveconorwegian orogeny just as the western parts of the Transscandinavian Igneous Belt has. The Svecofennian orogeny involved the accretion of numerous island arcs in such manner that the pre-existing craton grew with this new material from what is today northeast to the southwest. The accretion of the island arcs was also related to two other processes that occurred in the same period; the formation of magma that then cooled to form igneous rocks and the metamorphism of rocks.
The geology of Finland is made up of a mix of geologically very young and very old materials. Common rock types are orthogneiss, granite, metavolcanics and metasedimentary rocks. On top of these lies a widespread thin layer of unconsolidated deposits formed in connection to the Quaternary ice ages, for example eskers, till and marine clay. The topographic relief is rather subdued because mountain massifs were worn down to a peneplain long ago.

The Sub-Mesozoic hilly peneplains or Sub-Mesozoic hilly relief is a landscape in Scandinavia made up of undulating hills and joint valleys and occasional kaolinized bedrock in valley bottoms. The landscape formed in the Mesozoic Era and was eventually drowned by the sea during the Campanian transgression and covered by a thick cover of Cretaceous sedimentary rocks. Later erosion of the cover rocks partly re-exposed this landscape. During the Quaternary epoch the re-exposed Mesozoic hilly relief escaped major glacier erosion being only surficially scoured in parts.
The Ljusdal Batholith is a group of plutons in central Sweden formed during the Svecofennian orogeny. The batholith occupies a NW-SE elongated area of c. 130 x 100 km covering most of Hälsingland. The Ljusdal Bathoilith is mostly made up of granitoids with lesser amounts of mafic intrusions.

The geology of Sweden is the regional study of rocks, minerals, tectonics, natural resources and groundwater in the country. The oldest rocks in Sweden date to more than 2.5 billion years ago in the Precambrian. Complex orogeny mountain building events and other tectonic occurrences built up extensive metamorphic crystalline basement rock that often contains valuable metal deposits throughout much of the country. Metamorphism continued into the Paleozoic after the Snowball Earth glaciation as the continent Baltica collided with an island arc and then the continent Laurentia. Sedimentary rocks are most common in southern Sweden with thick sequences from the last 250 million years underlying Malmö and older marine sedimentary rocks forming the surface of Gotland.
The geology of Denmark includes 12 kilometers of unmetamorphosed sediments lying atop the Precambrian Fennoscandian Shield, the Norwegian-Scottish Caledonides and buried North German-Polish Caledonides. The stable Fennoscandian Shield formed from 1.45 billion years ago to 850 million years ago in the Proterozoic. The Fennoscandian Border Zone is a large fault, bounding the deep basement rock of the Danish Basin—a trough between the Border Zone and the Ringkobing-Fyn High. The Sorgenfrei-Tornquist Zone is a fault-bounded area displaying Cretaceous-Cenozoic inversion.
References
- ↑ Zariņš, K.; Johansson, Å. (2009). "U–Pb geochronology of gneisses and granitoids from the Danish island of Bornholm: new evidence for 1.47–1.45 Ga magmatism at the southwestern margin of the East European Craton." International Journal of Earth Sciences . 98 (7): 1561–1580.
- ↑ Johansson, Åke; Bogdanova, Svetlana; Čečys, Audius (2006). "A revised geochronology for the Blekinge Province, southern Sweden". GFF . 128 (4): 287–302. Bibcode:2006GFF...128..287J. doi:10.1080/11035890601284287. S2CID 129372111.