Related Research Articles

The Baltic Shield is a segment of the Earth's crust belonging to the East European Craton, representing a large part of Fennoscandia, northwestern Russia and the northern Baltic Sea. It is composed mostly of Archean and Proterozoic gneisses and greenstone which have undergone numerous deformations through tectonic activity. It contains the oldest rocks of the European continent with a thickness of 250–300 km.

Coesite is a form (polymorph) of silicon dioxide (SiO2) that is formed when very high pressure (2–3 gigapascals), and moderately high temperature (700 °C, 1,300 °F), are applied to quartz. Coesite was first synthesized by Loring Coes, Jr., a chemist at the Norton Company, in 1953.

Baltica is a paleocontinent that formed in the Paleoproterozoic and now constitutes northwestern Eurasia, or Europe north of the Trans-European Suture Zone and west of the Ural Mountains. The thick core of Baltica, the East European Craton, is more than three billion years old and formed part of the Rodinia supercontinent at c. 1 Ga.
In geology, a terrane is a crust fragment formed on a tectonic plate and accreted or "sutured" to crust lying on another plate. The crustal block or fragment preserves its distinctive geologic history, which is different from the surrounding areas—hence the term "exotic" terrane. The suture zone between a terrane and the crust it attaches to is usually identifiable as a fault. A sedimentary deposit that buries the contact of the terrane with adjacent rock is called an overlap formation. An igneous intrusion that has intruded and obscured the contact of a terrane with adjacent rock is called a stitching pluton.

The Caledonian orogeny was a mountain-building cycle recorded in the northern parts of the British Isles, the Scandinavian Caledonides, Svalbard, eastern Greenland and parts of north-central Europe. The Caledonian orogeny encompasses events that occurred from the Ordovician to Early Devonian, roughly 490–390 million years ago (Ma). It was caused by the closure of the Iapetus Ocean when the Laurentia and Baltica continents and the Avalonia microcontinent collided.

The geology of Norway encompasses the history of Earth that can be interpreted by rock types found in Norway, and the associated sedimentological history of soils and rock types.

The Lewisian complex or Lewisian gneiss is a suite of Precambrian metamorphic rocks that outcrop in the northwestern part of Scotland, forming part of the Hebridean Terrane and the North Atlantic Craton. These rocks are of Archaean and Paleoproterozoic age, ranging from 3.0–1.7 billion years (Ga). They form the basement on which the Stoer Group, Wester Ross Supergroup and probably the Loch Ness Supergroup sediments were deposited. The Lewisian consists mainly of granitic gneisses with a minor amount of supracrustal rocks. Rocks of the Lewisian complex were caught up in the Caledonian orogeny, appearing in the hanging walls of many of the thrust faults formed during the late stages of this tectonic event.

The Scandinavian Mountains or the Scandes is a mountain range that runs through the Scandinavian Peninsula. The western sides of the mountains drop precipitously into the North Sea and Norwegian Sea, forming the fjords of Norway, whereas to the northeast they gradually curve towards Finland. To the north they form the border between Norway and Sweden, reaching 2,000 metres (6,600 ft) high at the Arctic Circle. The mountain range just touches northwesternmost Finland but are scarcely more than hills at their northernmost extension at the North Cape.
Ultra-high-pressure metamorphism refers to metamorphic processes at pressures high enough to stabilize coesite, the high-pressure polymorph of SiO2. It is important because the processes that form and exhume ultra-high-pressure (UHP) metamorphic rocks may strongly affect plate tectonics, the composition and evolution of Earth's crust. The discovery of UHP metamorphic rocks in 1984 revolutionized our understanding of plate tectonics. Prior to 1984 there was little suspicion that continental rocks could reach such high pressures.
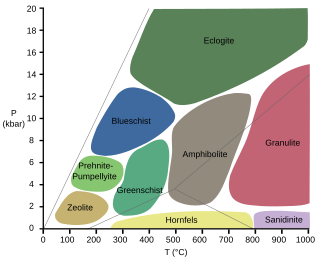
Eclogitization is the tectonic process in which the high-pressure, metamorphic facies, eclogite, is formed. This leads to an increase in the density of regions of Earth's crust, which leads to changes in plate motion at convergent boundaries.

The Nordfjord—Sogn Detachment (NSD) is a major extensional shear zone in Norway up to 6 km in thickness, which extends about 120 km along strike from Nordfjord to Sognefjord, bringing Devonian continental coarse clastic sedimentary rocks into close contact with eclogite facies metamorphic rocks of the Western Gneiss Region. It formed towards the end of the Caledonian Orogeny and was mainly active during the Devonian. It has an estimated displacement of at least 70 km and possibly as much as 110 km. It was reactivated during the Mesozoic and may have influenced the development of fault structures in the North Sea rift basin.

The Sveconorwegian orogeny was an orogenic system active 1140 to 960 million years ago and currently exposed as the Sveconorwegian orogenic belt in southwestern Sweden and southern Norway. In Norway the orogenic belt is exposed southeast of the front of the Caledonian nappe system and in nappe windows. The Sveconorwegian orogen is commonly grouped within the Grenvillian Mesoproterozoic orogens. Contrary to many other known orogenic belts the Sveconorwegian orogens eastern border does not have any known suture zone with ophiolites.

The Famatinian orogeny is an orogeny that predates the rise of the Andes and that took place in what is now western South America during the Paleozoic, leading to the formation of the Famatinian orogen also known as the Famatinian belt. The Famatinian orogeny lasted from the Late Cambrian to at least the Late Devonian and possibly the Early Carboniferous, with orogenic activity peaking about 490 to 460 million years ago. The orogeny involved metamorphism and deformation in the crust and the eruption and intrusion of magma along a Famatinian magmatic arc that formed a chain of volcanoes. The igneous rocks of the Famatinian magmatic arc are of calc-alkaline character and include gabbros, tonalites, granodiorites and trondhjemites. The youngest igneous rocks of the arc are granites.
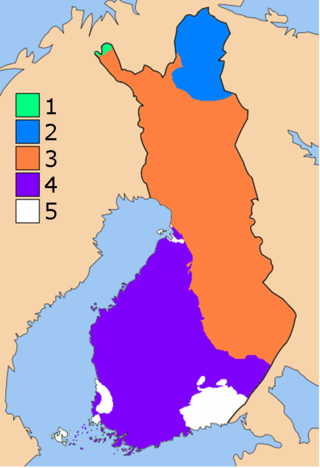
The geology of Finland is made up of a mix of geologically very young and very old materials. Common rock types are orthogneiss, granite, metavolcanics and metasedimentary rocks. On top of these lies a widespread thin layer of unconsolidated deposits formed in connection to the Quaternary ice ages, for example eskers, till and marine clay. The topographic relief is rather subdued because mountain massifs were worn down to a peneplain long ago.

The Scandinavian Caledonides are the vestiges of an ancient, today deeply eroded orogenic belt formed during the Silurian–Devonian continental collision of Baltica and Laurentia, which is referred to as the Scandian phase of the Caledonian orogeny. The size of the Scandinavian Caledonides at the time of their formation can be compared with the size of the Himalayas. The area east of the Scandinavian Caledonides, including parts of Finland, developed into a foreland basin where old rocks and surfaces were covered by sediments. Today, the Scandinavian Caledonides underlie most of the western and northern Scandinavian Peninsula, whereas other parts of the Caledonides can be traced into West and Central Europe as well as parts of Greenland and eastern North America.

The geology of Sweden is the regional study of rocks, minerals, tectonics, natural resources and groundwater in the country. The oldest rocks in Sweden date to more than 2.5 billion years ago in the Precambrian. Complex orogeny mountain building events and other tectonic occurrences built up extensive metamorphic crystalline basement rock that often contains valuable metal deposits throughout much of the country. Metamorphism continued into the Paleozoic after the Snowball Earth glaciation as the continent Baltica collided with an island arc and then the continent Laurentia. Sedimentary rocks are most common in southern Sweden with thick sequences from the last 250 million years underlying Malmö and older marine sedimentary rocks forming the surface of Gotland.

The geology of North Macedonia includes the study of rocks dating to the Precambrian and a wide array of volcanic, sedimentary and metamorphic rocks formed in the last 539 million years.
The geology of Venezuela includes ancient Precambrian igneous and metamorphic basement rocks, layered with sedimentary rocks from the Paleozoic and Mesozoic and thick geologically recent Cenozoic sediments with extensive oil and gas.

The Hornelen Basin is a sedimentary basin in Vestland, Norway, containing an estimated 25 km stratigraphic thickness of coarse clastic sedimentary rocks of Devonian age. It forms part of a group of basins of similar age along the west coast of Norway between Sognefjord and Nordfjord, related to movement on the Nordfjord-Sogn Detachment. It formed as a result of extensional tectonics as part of the post-orogenic collapse of crust that was thickened during the Caledonian Orogeny towards the end of the Silurian period. It is named for the mountain Hornelen on the northern margin of the basin.
Davidsmithite is a Ca-bearing nepheline-group mineral with the formula (Ca,◻)2Na6Al8Si8O32, with the "◻" being a vacancy in the formula. It is a feldspathoid mineral that occurs as a rock forming in the Liset eclogite pod (Norwegian Caledonides). Commonly found alongside lisetite, davidsmithite is found overgrowing this other mineral in corona textures.
References
- 1 2 Askheim, Svein. "Gneisregionen". In Helle, Knut (ed.). Store norske leksikon (in Norwegian). Oslo: Kunnskapsforlaget.
- 1 2 Cuthbert, S.J.; Carswell, D.A.; Krogh-Ravna, E.J.; Wain, A. (2000). "Eclogites and eclogites in the Western Gneiss Region, Norwegian Caledonides". Lithos . 52 (1–4): 165–195. doi:10.1016/s0024-4937(99)00090-0.
- 1 2 3 4 Austrheim, Håkon; Corfu, Fernando; Bryhni, Inge; Andersen, Torgeir B. (2003). "The Proterozoic Hustad igneous complex: a low strain enclave with a key to the history of the Western Gneiss Region of Norway" (PDF). Precambrian Research . 120: 149–175. doi:10.1016/s0301-9268(02)00167-5.
- ↑ Steltenpohl, Mark G.; Hames, Willis E.; Andresen, Arild (2004). "The Silurian to Permian history of a metamorphic core complex in Lofoten, northern Scandinavian Caledonides". Tectonics. 23 (1). doi: 10.1029/2003TC001522 .
- ↑ DesOrmeau, Joel W.; Gordon, Stacia M.; Kylander-Clark, Andrew R.C.; Hacker, Bradley R.; Bowring, Samuel A.; Schoene, Blair; Samperton, Kyle M. (2015). "Insights into (U)HP metamorphism of the Western Gneiss Region, Norway: A high-spatial resolution and high-precision zircon study". Chemical Geology. 414: 138–155. doi: 10.1016/j.chemgeo.2015.08.004 .