
Bletia is a genus of about 30 species of orchids, almost all of which are terrestrial; some are occasionally lithophytic or epiphytic. It is named after Spanish botanist and pharmacist Don Luis Blet. The genus is widespread across Florida, Mexico, Central America, the West Indies, and South America as far south as Argentina.

Epidendrum microphyllum is a species of tropical orchid in the genus Epidendrum with non-resupinate flowers.

Bletia purpurata is a species of orchid widespread across much of Mexico and Central America, from Nicaragua to Tamaulipas, Sinaloa and Baja California Sur.

Brassavola cucullata, common name daddy long-legs orchid, is a species of orchid native to Mexico, Belize, Central America, the West Indies and northern South America.

Brassia caudata is a species of orchid. It is found widespread across the warmer parts of the Western Hemisphere, reported from southern Mexico, Central America, southern Florida, Greater Antilles, Trinidad, northern South America. It is also known by the common names tailed Brassia, spider orchid and cricket orchid.

Cycnoches haagii is a species of orchid native to tropical South America.

Epidendrum rigidum is an epiphytic reed-stemmed Epidendrum orchid common throughout the Neotropical lowlands, below 600 m (2,000 ft).
Epidendrum parviflorum is a small-flowered reed-stemmed Epidendrum orchid found in the montane tropical wet forests of Bolivia, Ecuador, and Amazonas, Peru.
Epidendrum spruceanum is an epiphytic reed-stemmed Epidendrum orchid native to the Tropical rainforest of Peru, Bolivia, and Brazil.

Triphora is a genus of flowering plants from the orchid family, Orchidaceae. It is native to South America, Central America, southern Mexico, the West Indies and eastern North America as far north as Ontario. Noddingcaps is a common name for plants in this genus.
- Triphora amazonicaSchltr. - Florida, Caribbean, south to Brazil
- Triphora carnosula(Rchb.f.) Schltr. - Brazil
- Triphora craigheadiiLuer - Florida
- Triphora debilis(Schltr.) Schltr. - southern Mexico, Costa Rica, Guatemala, Panama
- Triphora duckeiSchltr. - Brazil
- Triphora foldatsiiCarnevali - Venezuela
- Triphora gentianoides(Sw.) Nutt. ex Ames & Schltr. - Florida, Southern Mexico, Costa Rica, Veenzuela, Colombia, Ecuador, Bahamas, Greater Antilles
- Triphora hassleriana(Cogn. ex Chodat & Hassl.) Schltr. - from Mexico to Argentina
- Triphora heringeriPabst - Brazil
- Triphora miserrima(Cogn.) Acuña - Cuba, Hispaniola
- Triphora nitida(Schltr.) Schltr. - Costa Rica
- Triphora pusilla(Rchb.f. & Warm.) Schltr. - Brazil
- Triphora ravenii(L.O.Williams) Garay - Costa Rica, Panama
- Triphora santamariensisPortalet - Brazil
- Triphora surinamensis(Lindl. ex Benth.) Britton - West Indies south to Brazil
- Triphora trianthophoros(Sw.) Rydb. Ontario, Eastern United States, much of Mexico
- Triphora unifloraA.W.C.Ferreira, Baptista & Pansarin - Brazil
- Triphora wagneriSchltr. - from Mexico to Ecuador
- Triphora yucatanensisAmes - Florida and the Yucatán Peninsula

Trichoceros is a genus of flowering plants from the orchid family, Orchidaceae. The genus is endemic to South America.

Pelexia is a genus of flowering plants from the orchid family, Orchidaceae. It has about 60-70 accepted species, native to Latin America, the West Indies and Florida.

Sacoila is a genus of flowering plants from the orchid family, Orchidaceae, native to the Western Hemisphere. It occurs in Mexico, Central America, South America, the West Indies and Florida.

Sarcoglottis is a genus of flowering plants from the orchid family, Orchidaceae. It is widespread across much of Latin America from Mexico to Argentina, with one species extending northward into Trinidad and the Windward Islands.
Suarezia is a monotypic genus of flowering plants from the orchid family, Orchidaceae. The sole species is Suarezia ecuadorana, endemic to Ecuador and classified as vulnerable.

Yucca aloifolia is the type species for the genus Yucca. Common names include aloe yucca, dagger plant, and Spanish bayonet. It grows in sandy soils, especially on sand dunes along the coast.
Tropidia polystachya, the young palm orchid, is a species of orchid native to Mexico, Central America, Greater Antilles, Bahamas, Cayman Islands, Florida, Colombia, Venezuela, and Ecuador.

Ionopsis utricularioides, the delicate violet orchid, is an epiphytic orchid native to the warmer parts of the Americas. It is reported from Florida, Mexico, Central America, much of the West Indies including the Cayman Islands, South America as far south as Paraguay, and the Galápagos.
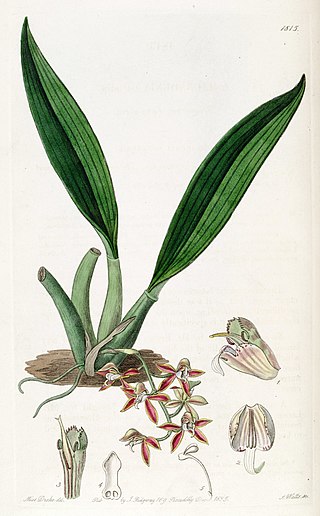
Macradenia lutescens is a species of epiphytic orchid known by the common name longgland orchid. It is native to South America, the West Indies, and southern Florida.

Heterotaxis sessilis is an epiphytic orchid widespread across the West Indies, Central America, southern Mexico, Florida and northern South America. Hidden orchid is a common name.
















