
→

Diamantina is a Brazilian municipality in the state of Minas Gerais. Its estimated population in 2020 was 47,825 in a total area of 3,870 km2.

Águas Vermelhas is a city in the northeast of the Brazilian state of Minas Gerais. In 2020 its population was estimated to be 13,599 in a total area of 1,258 km².

Araçuaí is a Brazilian municipality located in the northeast of the state of Minas Gerais in the Jequitinhonha River valley. The Araçuaí River, a tributary of the Jequitinhonha, flows through it. Its population as of 2020 was estimated to be 36,712 people living in a total area of 2,235 km2. The city belongs to the mesoregion of Jequitinhonha and the microregion of Araçuaí. The city is the seat of the Roman Catholic Diocese of Araçuaí. The elevation of the municipal seat is 307 meters. It became a municipality in 1870.

Olhos-d'Água is a Brazilian municipality located in the north of the state of Minas Gerais. Its population as of 2020 was 6,171 people living in a total area of 2,086 km2. The city belongs to the mesoregion of North of Minas and to the microregion of Bocaiúva. It became a municipality in 1997.
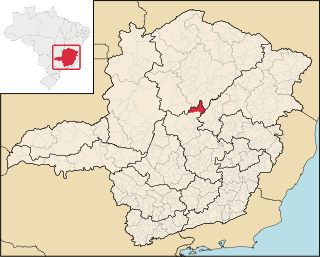
Buenópolis is a Brazilian municipality located in the northeast of the state of Minas Gerais. Its population as of 2020 was 10,353 living in a total area of 1,610 km2. The city belongs to the statistical mesoregion of Central Mineira and to the statistical microregion of Curvelo. It became a municipality in 1938.

Joaquim Felício is a Brazilian municipality located in the northeast of the state of Minas Gerais. Its population as of 2020 was 4,727 living in a total area of 791 km2. The city belongs to the statistical mesoregion of Central Mineira and to the statistical microregion of Curvelo. It became a municipality in 1962.

Itinga is a Brazilian municipality located in the northeast of the state of Minas Gerais in the Jequitinhonha River valley. As of 2020 the population was 15,022 in a total area of 1,641 km2. The city belongs to the mesoregion of Jequitinhonha and to the microregion of Araçuaí. The elevation of the municipal seat is 269 meters. It became a municipality in 1943. Between the municipalities of Araçuaí and Itinga is located the largest lithium mine in Brazil, explored and extracted by Sigma Lithium Resources.

Itacambira is a Brazilian municipality located in the north of the state of Minas Gerais. In 2020 the population was 5,417 in a total area of 1,788 km². It became a municipality in 1962.

Josenópolis is a Brazilian municipality located in the north of the state of Minas Gerais. In 2020 the population was 4,889 in a total area of 536 km2. It became a municipality in 1997.
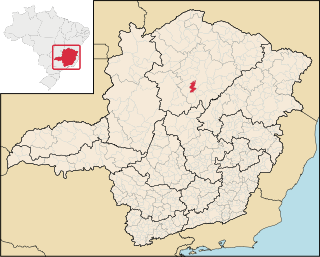
Claro dos Poções is a Brazilian municipality located in the north of the state of Minas Gerais. In 2020 the population was 7,514 in a total area of 706 km². It became a municipality in 1962.
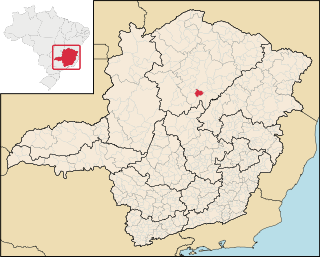
Engenheiro Navarro is a Brazilian municipality located in the north of the state of Minas Gerais. Its population as of 2020 was 7,241 people living in a total area of 632 km2. The city belongs to the mesoregion of North of Minas and to the microregion of Bocaiúva. It became a municipality in 1962.

Francisco Dumont is a Brazilian municipality located in the north of the state of Minas Gerais. Its population as of 2020 was 5,242 people living in a total area of 1,553 km². The city belongs to the mesoregion of North of Minas and to the microregion of Bocaiúva. It became a municipality in 1962.
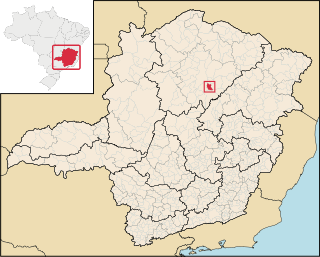
Guaraciama is a Brazilian municipality located in the north of the state of Minas Gerais. Its population as of 2020 was 4,989 people living in a total area of 392 km2. The city belongs to the mesoregion of North of Minas and to the microregion of Bocaiúva. It became a municipality in 1997.
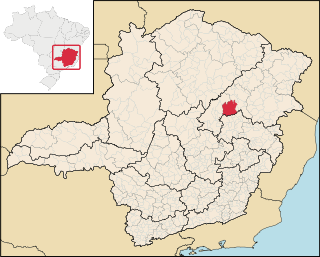
Itamarandiba is a Brazilian municipality located in the north-center of the state of Minas Gerais. Its population as of 2020 was 34,936 living in a total area of 2,736 km2.
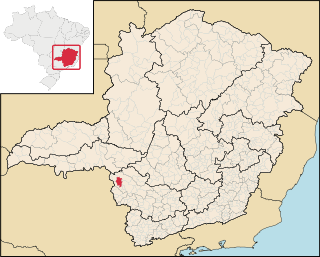
Cássia is a Brazilian municipality located in the center of the state of Minas Gerais. Its population as of 2020 was 17,740 people living in a total area of 643 km². The city belongs to the meso-region of Sul e Sudoeste de Minas and to the micro-region of Passos. It became a municipality in 1890.

Pingo-d'Água is a municipality in the state of Minas Gerais in the Southeast region of Brazil.
Engenheiro Caldas is a municipality in the state of Minas Gerais in the Southeast region of Brazil.

The Espinhaço: Alto Jequitinhonha – Serra do Cabral Mosaic, or simply Espinhaço Mosaic, is a protected area mosaic in the state of Minas Gerais, Brazil.

The Immediate Geographic Region of Montes Claros is one of the 7 immediate geographic regions in the Intermediate Geographic Region of Montes Claros, one of the 70 immediate geographic regions in the Brazilian state of Minas Gerais and one of the 509 of Brazil, created by the National Institute of Geography and Statistics (IBGE) in 2017.
























