
Adonis is a genus of about 20–30 species of flowering plants of the crowfoot family, Ranunculaceae, native to Europe and Asia.

Boehmeria is a genus of 47 species of flowering plants in the nettle family Urticaceae. Of the species, 33 are indigenous to the Old World and 14 to the New World; no species is indigenous to both the Old and New Worlds. The species include herbaceous perennials, shrubs and small trees. Although related to the similar-looking species of the stinging nettles of genus Urtica, species of Boehmeria do not have stinging hairs. Because of the similarity in appearance, some species are commonly called "false nettles".

Drosera peltata, commonly called the shield sundew or pale sundew, is a climbing or scrambling perennial tuberous species in the carnivorous plant genus Drosera. Among the tuberous sundews, D. peltata has the largest distribution, which includes eastern and western Australia, New Zealand, India, and most of Southeast Asia including the Philippines. The specific epithet is Latin for "shield shaped", a reference to the shape of the cauline leaves. It is either a single extremely variable species, or a complex of several closely related species of uncertain taxonomic boundaries. In Australia at least four forms have had or still have specific taxonomic recognition: Drosera peltata subsp. peltata, D. peltata subsp. auriculata, D. foliosa and D. gracilis.

Ulmus davidiana var. japonica, the Japanese elm, is one of the larger and more graceful Asiatic elms, endemic to much of continental northeast Asia and Japan, where it grows in swamp forest on young alluvial soils, although much of this habitat has now been lost to intensive rice cultivation.

Ulmus laciniata var. nikkoensisRehder, the Nikko elm, was discovered as a seedling near Lake Chūzenji, near Nikkō, Japan, and obtained by the Arnold Arboretum in 1905. The taxonomy of the tree remains a matter of contention, and has been considered possibly a hybrid of U. laciniata and U. davidiana var. japonica. However, in crossability experiments at the Arnold Arboretum in the 1970s, U. laciniata, a protogynous species, was found to be incompatible with U. davidiana var. japonica, which is protandrous.

Tsuga chinensis, commonly referred to as the Taiwan or Chinese hemlock, or in Chinese as tieshan, is a coniferous tree species native to China, Taiwan, Tibet and Vietnam. The tree is quite variable and has many recognised varieties, though some are also maintained to be separate species by certain authorities. The tree was recently discovered in the mountains of northern Vietnam, making that the southernmost extension of its range.

Harfordia macroptera is a woody perennial in the family Polygonaceae commonly known as rabbit's purse. It is the sole species in the genus Harfordia, which is endemic to the Baja California Peninsula. This plant is characterized by a unique, conspicuous bladder embellished with red to purple veins that surround the fruit. The sac-like structure is actually a dramatically modified bract, and assists in dispersal of the seeds through the wind.

Pouzolzia is a genus of flowering plants in the nettle family. There are about 35 species distributed throughout the tropical world. Most are shrubs, and some are herbs. The genus was named for French botanist and plant collector Pierre Marie Casimir de Pouzolz (1785–1858).

Angelica acutiloba is a perennial herb from the family Apiaceae or Umbelliferous. It is predominately in Japan and perhaps endemic (unique). It is now distributed widely and cultivated in Jilin, China, Korea, Taiwan and Indonesia.
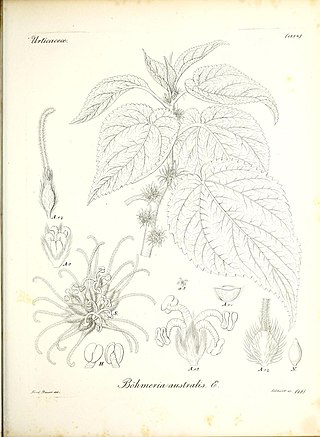
Pouzolzia australis, synonyms including Boehmeria australis and Boehmeria calophleba, is a species of large shrub or small tree in the plant family Urticaceae. It is endemic to small islands belonging to Australia and New Zealand – Norfolk Island, Lord Howe Island, and the Kermadec Islands. The population on Norfolk island, sometimes treated as a distinct subspecies, is critically endangered. In the Kermadec Islands, it was described in 2018 as "threatened – nationally endangered".
Strobilanthes japonica is a flowering herbaceous perennial plant from Asia, one of around 350 plants of the genus Strobilanthes. The 20–50 cm ornamental plant is cultivated in Japan and China, and blooms in autumn with 1.5 cm purple to white funnel-shaped flowers.

Boehmeria cylindrica, with common names false nettle and bog hemp, is an herb in the family Urticaceae. It is widespread in eastern North America and the Great Plains from New Brunswick to Florida to Texas to Nebraska, with scattered reports of isolated populations in New Mexico, Arizona, and Utah, as well as in Bermuda, Mexico, Central America, the West Indies, and South America.

Hakea rhombales, commonly known as walukara, is a shrub in the family Proteacea. It has red, pink or purple flowers and is endemic to Western Australia and the Northern Territory.

Acroglochin persicarioides is a species of flowering plants in the plant family Amaranthaceae. It is distributed from the Himalayas to China. The systematic position of the genus Acroglochin in subfamily Betoideae is still uncertain.

Hypericum denticulatum, the coppery St. John's Wort, is a perennial herb in the flowering plant family Hypericaceae. It is native to the Eastern United States. The species has two varieties, H. denticulatum var. recognitum and H. denticulatum var. acutifolium. The herb has a diploid number of 24 or 48.

Passiflora bogotensis is a climbing plant native to Colombia, in the genus Passiflora. It can also be found in Venezuela.

Symphyotrichum ontarionis is a species of flowering plant in the family Asteraceae native to eastern North America. Commonly known as Ontario aster and bottomland aster, it is a perennial, herbaceous plant that may reach heights of 120 centimeters. Each flower head has many tiny florets put together into what appear as one.

Aporosa octandra is a species of plant in the family Phyllanthaceae found from Queensland and New Guinea to Indonesia, Zhōngguó/China and India. It is a highly variable plant with 4 named varieties. Its wood is used in construction and to make implements, its fruit is edible. The Karbi people of Assam use the plant for dyeing, textile colours have quite some significance in their culture.
Gutenbergia rueppellii is an African species of flowering plant in the family Asteraceae.

Gambelia juncea is a species of flowering shrub in the plantain family commonly known as the Baja California bush snapdragon or Baja bush snapdragon. Gambelia juncea is a highly variable woody perennial to 1 m (3.3 ft) characterized by long, arching, reed-like stems and showy, bright red, two-lipped tubular flowers. Native to the Baja California peninsula and coastal Sonora, this species is widespread in the region across numerous habitats and has several varieties. It was formerly placed in the primarily South American genus Galvezia, but taxonomic studies have supported the reclassification of the two North American species into Gambelia. This species, with a number of cultivars, is widely used as an ornamental shrub for xeriscaping, erosion control, native plant gardens, and wildlife gardens.




















