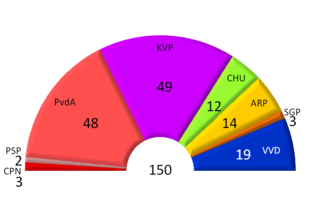
General elections were held in the Netherlands on 12 March 1959. The Catholic People's Party emerged as the largest party, winning 49 of the 150 seats in the House of Representatives.

Parliamentary elections were held in Austria on 10 May 1959. Although the Social Democratic Party received the most votes, the Austrian People's Party retained a bare one-seat plurality. The Communist Party of Austria lost its remaining three seats and has not returned to the National Council since. Voter turnout was 94.2%. The grand coalition that had governed the country since 1945 remained in office, with People's Party leader Julius Raab as Chancellor and Socialist leader Bruno Pittermann as Vice-Chancellor.
General elections were held in Luxembourg on 1 February 1959. The Christian Social People's Party remained the largest party, winning 21 of the 52 seats in the Chamber of Deputies.

Parliamentary elections were held in Iceland on 28 June 1959. The Independence Party and the Progressive Party both won 13 seats in the Lower House of the Althing. Following the tie, electoral reforms were introduced and early elections were held in October.

Early parliamentary elections were held in Iceland on 25 and 26 October 1959. Following the electoral reforms made after the June elections, the Independence Party won 16 of the 40 seats in the Lower House of the Althing.
Federal elections were held in Switzerland on 25 October 1959. The Social Democratic Party and the Free Democratic Party emerged as the largest parties in the National Council, each winning 51 of the 196 seats.

Parliamentary elections were held in Guatemala on 16 December 1959, in order to elect half the seats in Congress. Voter turnout was just 44.91%.
General elections were held in Tanganyika in September 1958 and February 1959. Elections were held in five constituencies on 8 and 12 September 1958, and in the other five on 9 and 15 February 1959. The Tanganyika African National Union (TANU) won 28 of the 30 elected seats in the Legislative Council, whilst the remaining 34 members were appointed.

General elections were held in Turkey on 21 July 1946, the first multi-party elections in the country's history. The multiple non-transferable vote electoral system was used. The result was a victory for the Republican People's Party, which won 395 of the 465 seats.

General elections were held in Liberia in May 1959. In the presidential election, William Tubman of the True Whig Party was re-elected for a fourth term, defeating independent candidate William O. Davies Bright, who won just 55 votes.

Parliamentary elections were held in Senegal on 22 March 1959. The result was a victory for the Senegalese Progressive Union. Voter turnout was 74.5%.

Parliamentary elections were held in British Cameroons on 24 January 1959. The result was a victory for the Kamerun National Democratic Party, which won 14 of the 26 seats in the House of Assembly.

General elections were held in Nepal on 18 February 1959. 109 members were elected using the single-member plurality system. The result was a victory for the Nepali Congress, which won 74 of the 109 seats. Voter turnout was 42.0%.
The Republican Party was a political party in Jamaica. It first contested national elections in 1955, but received only 108 votes and failed to win a seat. It did not take part in elections in 1959 or 1962, but returned for the 1967 elections, in which it received only 45 votes. After failing to participate in the 1972, 1976 and 1980 elections it contested the 1983 elections, but received only 257 votes, again failing to win a seat. It did not contest any further elections.
The Independent Labour Party was a political party in Jamaica. It first contested national elections in 1959, but received only 0.8% of the vote and failed to win a seat. It did not contest any further elections.
The Convention Independent Party was a political party in Jamaica. It first contested national elections in 1959, when it received fewer than 305 votes and failed to win a seat. It did not contest any further elections.
The Jamaica Independent Party was a political party in Jamaica. It first contested national elections in 1959, when it received fewer than 305 votes and failed to win a seat. It did not contest any further elections.

Presidential elections were held in Cyprus for the first time on 13 December 1959. Only two candidates contested the election; Makarios III, who was backed by EOKA and Ioannis Clerides, a member of the Democratic Union, who was also supported by AKEL. The result was a victory for Makarios III, who won 66.8% of the vote, although he did not take office until 16 August 1960. Voter turnout was 91.2%.

General elections were held in San Marino on 13 September 1959. The Sammarinese Christian Democratic Party remained the largest party, winning 27 of the 60 seats in the Grand and General Council.
Two referendums were held in Switzerland in 1959. The first was held on 1 February on the introduction of women's suffrage at the federal level, but was rejected by 67% of voters. The second was held on 24 May on adding article 22bis to the federal constitution, which concerned civil protection. It was approved by 62% of voters.













