
Withdrawal from the European Union is the legal and political process whereby an EU member state ceases to be a member of the Union. Article 50 of the Treaty on European Union (TEU) states that "Any Member State may decide to withdraw from the Union in accordance with its own constitutional requirements".

Relations between the European Union (EU) and the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland (UK) are governed, since 1 January 2021, by the EU–UK Trade and Cooperation Agreement (TCA).
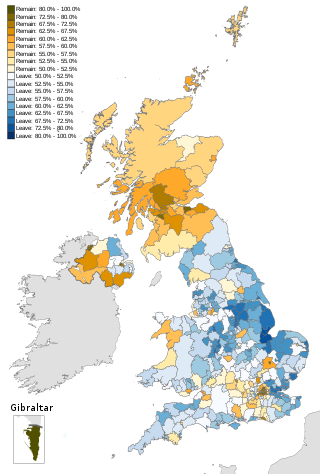
On 23 June 2016, a referendum, commonly referred to as the EU referendum or the Brexit referendum, took place in the United Kingdom (UK) and Gibraltar to ask the electorate whether the country should remain a member of, or leave, the European Union (EU). It was organised and facilitated through the European Union Referendum Act 2015 and the Political Parties, Elections and Referendums Act 2000. The referendum resulted in 51.9% of the votes cast being in favour of leaving the EU. Although the referendum was legally non-binding, the government of the time promised to implement the result.

Brexit was the withdrawal of the United Kingdom (UK) from the European Union (EU) at 23:00 GMT on 31 January 2020. The UK is the only sovereign country to have left the EU. The UK had been a member state of the EU or its predecessor the European Communities (EC), sometimes of both at the same time, since 1 January 1973. Following Brexit, EU law and the Court of Justice of the European Union no longer have primacy over British laws. The European Union (Withdrawal) Act 2018 retains relevant EU law as domestic law, which the UK can now amend or repeal.

The European Union Referendum Act 2015 was an Act of the Parliament of the United Kingdom that made legal provision for a consultative referendum to be held in the United Kingdom and Gibraltar, on whether it should remain a member state of the European Union or leave the bloc altogether. The Bill was introduced to the House of Commons by Philip Hammond, Foreign Secretary on 28 May 2015. Two weeks later, the second reading of the Bill was supported by MPs from all parties except the SNP; the Bill subsequently passed on its third reading in the Commons on 7 September 2015. It was approved by the House of Lords on 14 December 2015, and given Royal Assent on 17 December 2015. The Act came partly into force on the same day and came into full legal force on 1 February 2016.

A second referendum on independence from the United Kingdom (UK) has been proposed by the Scottish Government. An independence referendum was first held on 18 September 2014, with 55% voting "No" to independence. The Scottish Government stated in its white paper for independence that voting Yes was a "once in a generation opportunity to follow a different path, and choose a new and better direction for our nation". Following the "No" vote, the cross party Smith Commission proposed areas that could be devolved to the Scottish Parliament; this led to the passing of the Scotland Act 2016, formalising new devolved policy areas in time for the 2016 Scottish Parliament election campaign.
After the British EU membership referendum held on 23 June 2016, in which a majority voted to leave the European Union, the United Kingdom experienced political and economic upsets, with spillover effects across the rest of the European Union and the wider world. Prime Minister David Cameron, who had campaigned for Remain, announced his resignation on 24 June, triggering a Conservative leadership election, won by Home Secretary Theresa May. Following Leader of the Opposition Jeremy Corbyn's loss of a motion of no confidence among the Parliamentary Labour Party, he also faced a leadership challenge, which he won. Nigel Farage stepped down from leadership of the pro-Leave party UKIP in July. After the elected party leader resigned, Farage then became the party's interim leader on 5 October until Paul Nuttall was elected leader on 28 November.

On 29 March 2017, the United Kingdom (UK) invoked Article 50 of the Treaty on European Union (TEU) which began the member state's withdrawal, commonly known as Brexit, from the European Union (EU). In compliance with the TEU, the UK gave formal notice to the European Council of its intention to withdraw from the EU to allow withdrawal negotiations to begin.

The European Union (Withdrawal) Act 2018 is an Act of the Parliament of the United Kingdom that provides both for repeal of the European Communities Act 1972, and for parliamentary approval to be required for any withdrawal agreement negotiated between the Government of the United Kingdom and the European Union. The bill's passage through both Houses of Parliament was completed on 20 June 2018 and it became law by Royal Assent on 26 June.

R (Miller) v Secretary of State for Exiting the European Union is a United Kingdom constitutional law case decided by the United Kingdom Supreme Court on 24 January 2017, which ruled that the British Government might not initiate withdrawal from the European Union by formal notification to the Council of the European Union as prescribed by Article 50 of the Treaty on European Union without an Act of Parliament giving the government Parliament's permission to do so. Two days later, the government responded by bringing to Parliament the European Union Act 2017 for first reading in the House of Commons on 26 January 2017. The case is informally referred to as "the Miller case" or "Miller I".

The European Union Act 2017 was an Act of the Parliament of the United Kingdom to empower the Prime Minister to give to the Council of the European Union the formal notice – required by Article 50 of the Treaty on European Union – for starting negotiations for the United Kingdom's withdrawal from the European Union. It was passed following the result of the 2016 United Kingdom European Union membership referendum held on 23 June in which 51.9% of voters voted to leave the European Union.
Brexit and arrangements for science and technology refers to arrangements affecting scientific research, experimental development and innovation that are within the scope of the negotiations between the United Kingdom and the European Union on the terms of Britain's withdrawal from the European Union (EU).

Between 2017 and 2019, representatives of the United Kingdom and the European Union negotiated the terms for Brexit, the planned withdrawal of the UK from the EU. These negotiations arose following the decision of the Parliament of the United Kingdom to invoke Article 50 of the Treaty on European Union, following the UK's EU membership referendum on 23 June 2016.

The United Kingdom (UK) was a member of the European Economic Area (EEA) from 1 January 1994 to 31 December 2020, following the coming into force of the 1992 EEA Agreement. Membership of the EEA is a consequence of membership of the European Union (EU). The UK ceased to be a Contracting Party to the EEA Agreement after its withdrawal from the EU on 31 January 2020, as it was a member of the EEA by virtue of its EU membership, but retained EEA rights during the Brexit transition period, based on Article 126 of the withdrawal agreement between the EU and the UK. During the transition period, which ended on 31 December 2020, the UK and EU negotiated their future relationship.

The United Kingdom was a member state of the European Union (EU) and of its predecessor the European Communities (EC) – principally the European Economic Community (EEC) from 1 January 1973 until 31 January 2020. Since the foundation of the EEC, the UK had been an important neighbour and then leading member state, until Brexit ended 47 years of membership. During the UK's time as a member state two referendums were held on the issue of its membership, with the first being held on 5 June 1975, resulting in a vote to stay in the EC, and the second, held on 23 June 2016, which resulted in the vote to leave the EU.

The European Union Act 2020 is an act of the Parliament of the United Kingdom that makes legal provision for ratifying the Brexit Withdrawal Agreement and incorporating it into the domestic law of the United Kingdom. It is the most significant constitutional piece of legislation to be passed by Parliament of the Second Johnson ministry. The Withdrawal Agreement was the result of Brexit negotiations.

The Brexit withdrawal agreement, officially titled Agreement on the withdrawal of the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland from the European Union and the European Atomic Energy Community, is a treaty between the European Union (EU), Euratom, and the United Kingdom (UK), signed on 24 January 2020, setting the terms of the withdrawal of the UK from the EU and Euratom. The text of the treaty was published on 17 October 2019, and is a renegotiated version of an agreement published half a year earlier. The earlier version of the withdrawal agreement was rejected by the House of Commons on three occasions, leading to the resignation of Theresa May as Prime Minister and the appointment of Boris Johnson as the new prime minister on 24 July 2019.
Brexit was the withdrawal of the UK from the EU at 23:00 GMT on 31 January 2020. As of 2020, the UK is the only sovereign country to have left the EU. Britain's membership of the EU began on 1 January 1973, when it entered the European Communities (EC), the predecessor to the EU. Following this, Eurosceptic groups formed in the UK, opposing aspects of both the EC and the EU. In January 2013, Prime Minister David Cameron delivered a speech at Bloomberg London, in which he called for reform of the EU and promised an in–out referendum on the UK's membership if the Conservative Party won a majority at the 2015 general election. The Conservatives won 330 seats at the election, giving Cameron a majority of 12, and a bill to hold a referendum was introduced to Parliament that month.
In the wake of the referendum held in the United Kingdom on 23 June 2016, many new pieces of Brexit-related jargon entered popular use.
The Brexit withdrawal agreement Bill plan, officially known as Legislating for the Withdrawal Agreement between the United Kingdom and the European Union , was a UK Government white paper setting out the Governments proposals for ratifying and implementing the Brexit withdrawal agreement in legislation.









