Related Research Articles

A cotton mill is a building that houses spinning or weaving machinery for the production of yarn or cloth from cotton, an important product during the Industrial Revolution in the development of the factory system.
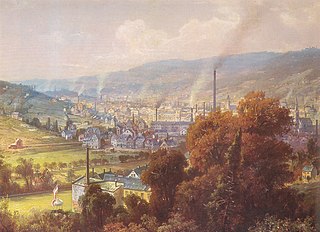
Textile manufacture during the Industrial Revolution in Britain was centred in south Lancashire and the towns on both sides of the Pennines. In Germany it was concentrated in the Wupper Valley, Ruhr Region and Upper Silesia, in Spain it was concentrated in Catalonia while in the United States it was in New England. The main key drivers of the Industrial Revolution were textile manufacturing, iron founding, steam power, oil drilling, the discovery of electricity and its many industrial applications, the telegraph and many others. Railroads, steam boats, the telegraph and other innovations massively increased worker productivity and raised standards of living by greatly reducing time spent during travel, transportation and communications.
B. Hick and Sons, subsequently Hick, Hargreaves & Co, was a British engineering company based at the Soho Ironworks in Bolton, England. Benjamin Hick, a partner in Rothwell, Hick and Rothwell, later Rothwell, Hick & Co., set up the company in partnership with two of his sons, John (1815–1894) and Benjamin (1818–1845) in 1833.

Bolton Steam Museum is a museum in Bolton, Greater Manchester, England, which houses a variety of preserved steam engines. Based in the cotton store of the former Atlas Mill in Mornington Road, it is owned and run by the Northern Mill Engine Society (NMES).
Shudehill Mill or Simpson's Mill was a very early cotton mill in Manchester city centre, England. It was built in 1782 by for Richard Arkwright and his partners and destroyed by fire in 1854. It was rebuilt and finally destroyed during the Manchester Blitz in 1940. One of Arkwright's larger mills, it was built three years before his patent lapsed. The mill had a 30 feet diameter water wheel and a Newcomen atmospheric engine was installed. Doubts remain as to why the engine was installed, whether it was a failed attempt to power a mill directly by steam or was modified to assist the wheel. It is possible that this engine, constructed by Hunt, could have been one of the 13 engines installed in Manchester mills by Joshua Wrigley. Water from the upper storage pond turned the water wheel to drive the mill. The steam engine recycled water from the lower storage pond to the upper storage pond. Three more Boulton and Watt engines were installed to power the increasing number of spindles.

George Saxon & Co was an English engineering company that manufactured stationary steam engines. It was based in the Openshaw district of Manchester. The company produced large steam-driven engines for power stations and later for textile mills in Lancashire and elsewhere.

Stalybridge Mill, Stalybridge is a cotton spinning mill in Stalybridge, Tameside, Greater Manchester, England. It was built in 1868, and the engine reconfigured in around 1925. It was taken over by the Lancashire Cotton Corporation in the 1930s and passed to Courtaulds in 1964.

Mons Mill, Todmorden, is a former cotton spinning mill in Todmorden, Calderdale, West Yorkshire, England built for the Hare Spinning Company Limited. It was built in 1907, but ran into financial difficulties. It passed over to the Mons Mill (1919) Co Ltd and then was taken over by the Lancashire Cotton Corporation in 1930 and passed to Courtaulds in 1964 and production stopped in 1968. It was used into the 1990s by Ward & Goldstone Ltd. The site was cleared in 2000.
Alexander Petrie and Co was a company that manufactured stationary steam engines. It was based in Rochdale, Greater Manchester in England. The company did general millwrighting, producing some steam engines during the 19th century. Around 1845, their superintendent, William McNaught, was producing large steam-driven beam engines for textile mills in Rochdale.

Soulé Steam Feed Works is a historic business founded in Meridian, Mississippi in 1891 by George Soulé. The complex was listed as a contributing property to Union Station Historic District, which was placed on the National Register of Historic Places in 1979 under the Meridian Multiple Resource Area (MRA). It was listed as a Mississippi Landmark in 2003. The business, known for its many patented innovations in steam engine technology, reached its height around the turn of the century, producing products that were sold around the world.

McConnel & Kennedy Mills are a group of cotton mills on Redhill Street in Ancoats, Manchester, England. With the adjoining Murrays' Mills, they form a nationally important group.

Ellenroad Mill was a cotton spinning mill in Newhey, Milnrow, Rochdale, Greater Manchester, England. It was built as a mule spinning mill in 1890 by Stott and Sons and extended in 1899. It was destroyed by fire on 19 January 1916. When it was rebuilt, it was designed and equipped as a ring spinning mill.

Coventry Corporation Tramways operated a tramway service in Coventry, England, between 1912 and 1940.
Kirkcaldy Corporation Tramways operated a tramway service in Kirkcaldy between 1903 and 1931.

Huddersfield Corporation Tramways operated a tramway service in Huddersfield, England, between 1883 and 1940. It initially used steam locomotives pulling unpowered tramcars, but as the system was expanded, a decision was taken to change to electric traction in 1900, and the first electric trams began operating in February 1901. The system was built to the unusual gauge of 4 ft 7+3⁄4 in, in the hope that coal wagon from neighbouring coal tramways, which used that gauge, could be moved around the system. This did not occur, but two coal trams were used to delivered coal to three mills.

William Roberts and Company of Phoenix Foundry in Nelson, Lancashire, England, produced many of the steam engines that powered cotton weaving and spinning mills of Pendle and neighbouring districts. Industrial historian Mike Rothwell has called Phoenix foundry “Nelson’s most significant engineering site”.

Bancroft Shed was a weaving shed in Barnoldswick, Lancashire, England, situated on the road to Skipton. Construction was started in 1914 and the shed was commissioned in 1920 for James Nutter & Sons Limited. The mill closed on 22 December 1978 and was demolished. The engine house, chimneys and boilers have been preserved and maintained as a working steam museum. The mill was the last steam-driven weaving shed to be constructed and the last to close.

Kearsley Mill is a 240,000 sq ft (22,000 m2), late period cotton mill located in the small village of Prestolee in Kearsley, Greater Manchester. A near complete example of Edwardian mill architecture, the building now functions as headquarters for a number of businesses and is still used in the continued manufacturing and distribution of textiles by Richard Haworth Ltd Est (1876), part of the Ruia Group. The mill is a Grade II listed building.
Aberystwyth power station supplied electricity to the town of Aberystwyth from 1895 to the 1970s. The oil-engine station was operated by a succession of private and public owners including Aberystwyth Corporation prior to the nationalisation of the electricity industry in 1948. The power station, with an ultimate capacity of 5 MW, was redeveloped as demand for electricity grew and old plant was replaced.
