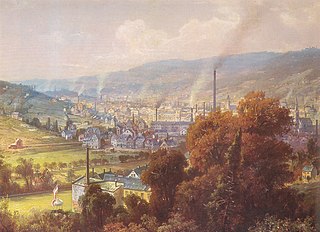Carding is a mechanical process that disentangles, cleans and intermixes fibres to produce a continuous web or sliver suitable for subsequent processing. This is achieved by passing the fibres between differentially moving surfaces covered with "card clothing", a firm flexible material embedded with metal pins. It breaks up locks and unorganised clumps of fibre and then aligns the individual fibres to be parallel with each other. In preparing wool fibre for spinning, carding is the step that comes after teasing.

The spinning jenny is a multi-spindle spinning frame, and was one of the key developments in the industrialization of textile manufacturing during the early Industrial Revolution. It was invented in 1764 or 1765 by James Hargreaves in Stanhill, Oswaldtwistle, Lancashire in England.

A cotton mill is a building that houses spinning or weaving machinery for the production of yarn or cloth from cotton, an important product during the Industrial Revolution in the development of the factory system.
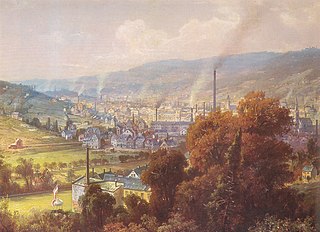
Textile manufacture during the British Industrial Revolution was centred in south Lancashire and the towns on both sides of the Pennines in the United Kingdom. The main drivers of the Industrial Revolution were textile manufacturing, iron founding, steam power, oil drilling, the discovery of electricity and its many industrial applications, the telegraph and many others. Railroads, steam boats, the telegraph and other innovations massively increased worker productivity and raised standards of living by greatly reducing time spent during travel, transportation and communications..

The spinning mule is a machine used to spin cotton and other fibres. They were used extensively from the late 18th to the early 20th century in the mills of Lancashire and elsewhere. Mules were worked in pairs by a minder, with the help of two boys: the little piecer and the big or side piecer. The carriage carried up to 1,320 spindles and could be 150 feet (46 m) long, and would move forward and back a distance of 5 feet (1.5 m) four times a minute. It was invented between 1775 and 1779 by Samuel Crompton. The self-acting (automatic) mule was patented by Richard Roberts in 1825. At its peak there were 50,000,000 mule spindles in Lancashire alone. Modern versions are still in niche production and are used to spin woollen yarns from noble fibres such as cashmere, ultra-fine merino and alpaca for the knitware market.

Murrays' Mills is a complex of former cotton mills on land between Jersey Street and the Rochdale Canal in the district of Ancoats, Manchester, England. The mills were built for brothers Adam and George Murray.

The Lancashire Cotton Corporation was a company set up by the Bank of England in 1929, to rescue the Lancashire spinning industry by means of horizontal rationalisation. In merged 105 companies, ending up in 1950 with 53 operating mills. It was bought up by Courtaulds in August 1964.

Ring spinning is a spindle-based method of spinning fibres, such as cotton, flax or wool, to make a yarn. The ring frame developed from the throstle frame, which in its turn was a descendant of Arkwright's water frame. Ring spinning is a continuous process, unlike mule spinning which uses an intermittent action. In ring spinning, the roving is first attenuated by using drawing rollers, then spun and wound around a rotating spindle which in its turn is contained within an independently rotating ring flyer. Traditionally ring frames could only be used for the coarser counts, but they could be attended by semi-skilled labour.

Texas Mill was a cotton spinning mill in the Whitelands district of Ashton-under-Lyne, Greater Manchester, in England. It was built between 1905 and 1907 for the Ashton Syndicate by Sydney Stott of Oldham. It was destroyed in a massive fire on 22–23 October 1971. It had been re-equipped as a ring mill for spinning artificial fibres when it was destroyed.
Curzon Mill, later known as Alger Mill was a cotton spinning mill in the Hurst district of Ashton-under-Lyne, Greater Manchester, in England. It was built between 1899 and 1902 for the Ashton Syndicate by Sydney Stott of Oldham. It was a sister mill to the Atlas Mill. It was sold to the Alger Spinning Co. Ltd in 1911, and closed in 1942. It was then used as a cigarette factory by the J.A. Pattreiouex company until 1966, and then sold to the Qualitex company for the production of artificial fibres. It was still spinning artificial fibres in the 1990s and was demolished in 1994; the site being used for a housing estate.

Trent Mill was a cotton spinning mill on Duchess Street in Shaw and Crompton, Greater Manchester, England. It was built by F.W. Dixon & Son in 1908. It closed and was taken over by the Lancashire Cotton Corporation in 1929 reopened in 1938 and closed again in 1962, and was demolished in 1967.

Fox Mill, Hollinwood is a cotton spinning mill in Hollinwood, Oldham, Greater Manchester. It was taken over by the Lancashire Cotton Corporation in the 1930s and passed to Courtaulds in 1964.

Heron Mill is a cotton spinning mill in Hollinwood, Oldham, Greater Manchester. It was designed by architect P. S. Stott and was constructed in 1905 by the Heron Mill Company Ltd next to Durban Mill. It was taken over by the Lancashire Cotton Corporation in the 1930s and passed to Courtaulds in 1964. Production ended in 1960, and it was used by Courtaulds for offices, warehousing, and some experimental fabric manufacture. Courtaulds occupation ended in 1994.

Kingston Mill, Stockport is a mid nineteenth century cotton spinning mill in Edgeley, Stockport, Greater Manchester, England. It was taken over by the Lancashire Cotton Corporation in the 1930s and passed to Courtaulds in 1964. Production finished, it was made over to multiple uses.

John Kennedy was a Scottish textile industrialist in Manchester.

McConnel & Kennedy Mills are a group of cotton mills on Redhill Street in Ancoats, Manchester, England. With the adjoining Murrays' Mills, they form a nationally important group.

Royal Mill, which is located on the corner of Redhill Street and Henry Street, Ancoats, in Manchester, England, is an early-twentieth-century cotton mill, one of the last of "an internationally important group of cotton-spinning mills" sited in East Manchester. Royal Mill was constructed in 1912 on part of the site of the earlier McConnel & Kennedy mills, established in 1798. It was originally called New Old Mill and was renamed following a royal visit by King George VI and Queen Elizabeth in 1942. A plaque commemorates the occasion. The Ancoats mills collectively comprise "the best and most-complete surviving examples of early large-scale factories concentrated in one area".

Pear New Mill is a former Edwardian cotton spinning mill on the northern bank of the River Goyt in Bredbury, Stockport, Greater Manchester, England. It is a Grade II* listed building.
Piece-rate lists were the ways of assessing a cotton operatives pay in Lancashire in the nineteenth and early twentieth centuries. They started as informal agreements made by one cotton master and their operatives then each cotton town developed their own list. Spinners merged all of these into two main lists which were used by all, while weavers used one 'unified' list.
Ormrod and Hardcastle spinning and manufacturing firm began in 1788, with the partnership of James Ormrod and Thomas Hardcastle, and the purchase of the Flash Street mills in Bolton, Greater Manchester. These two men have been identified amongst the fathers of the early cotton trade in North West England. Others named are Carlisles, Gray, Knowles, Bulling, Crook and Culling. These names often figured prominently in the political, judicial and economic life of Bolton during its great period of growth, but sadly these names have been largely forgotten in the history of the cotton trade. By the time of their closure, in 1960, Ormrod and Hardcastle owned six large successful cotton mills in Bolton.