| Brown violetear | |
|---|---|
| in Panama | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Chordata |
| Class: | Aves |
| Clade: | Strisores |
| Order: | Apodiformes |
| Family: | Trochilidae |
| Genus: | Colibri |
| Species: | C. delphinae |
| Binomial name | |
| Colibri delphinae | |
 | |
| Synonyms | |
Ornismya Delphinae (protonym) | |
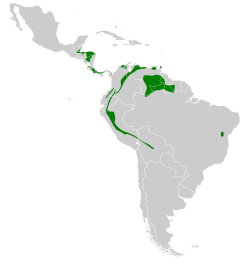
The brown violetear (Colibri delphinae) is a large hummingbird that breeds at middle elevations in the mountains in Central America, and western and northern South America (primarily the Andes and the tepuis) with isolated populations on Trinidad and in the Brazilian state Bahia.
The breeding habitat is forest at altitudes between 400 and 1600 m, but the brown Violet-ear will spread widely into the lowlands when not nesting. It is replaced at higher altitudes by its relative, the lesser violetear (C. cyanotus), but their ranges overlap widely.
The brown violetear is typically found high in the canopy of the rainforest, tall second growth and coffee plantations, but it will feed at lower levels at edges and clearings. The nest is a small cup of plant down saddled on a twig 1–3 m. high in a bush, into which two white eggs are laid.
The 11.5 cm long, 6.5-7 g weight brown violetear is unmistakable; it is mainly dull brown, with a rufous rump and greyer underparts. There is a violet patch running back and down from the eye, a hermit-like malar stripe, and a glittering green and blue throat stripe. The bill is relatively short and almost straight.
The female is similar to the male, but has a smaller throat patch. Immature bird have rufous fringes to the upperpart plumage, and little or no violet behind the eyes. The song is a vigorous repetition of the chit call, and is delivered by up to several dozen breeding males in loose leks.
The brown violetear feeds on nectar from small flowers of trees, shrubs [4] and epiphytes. It also takes insects, often caught in flight (hawking), as an essential source of protein. Although not particularly territorial, this species is highly aggressive, and at feeders seems to spend far more time attacking other hummingbirds than actually feeding.
- showing green gorget
- showing violet auricular



