
The Ohio River is a 981-mile-long (1,579 km) river in the United States. It is located at the boundary of the Midwestern and Southern United States, flowing in a southwesterly direction from western Pennsylvania to its mouth on the Mississippi River at the southern tip of Illinois. It is the third largest river by discharge volume in the United States and the largest tributary by volume of the north-south flowing Mississippi River, which divides the eastern from western United States. It is also the 6th oldest river on the North American continent. The river flows through or along the border of six states, and its drainage basin includes parts of 14 states. Through its largest tributary, the Tennessee River, the basin includes several states of the southeastern U.S. It is the source of drinking water for five million people.

Braxton County is a county in the central part of the U.S. state of West Virginia. As of the 2020 census, the population was 12,447. The county seat is Sutton. The county was formed in 1836 from parts of Lewis, Kanawha, and Nicholas counties and named for Carter Braxton, a Virginia statesman and signer of the Declaration of Independence.

Brownsville is a borough in Fayette County, Pennsylvania, United States, first settled in 1785 as the site of a trading post a few years after the defeat of the Iroquois enabled a resumption of westward migration after the Revolutionary War. The trading post soon became a tavern and inn and was receiving emigrants heading west, as it was located above the cut bank overlooking the first ford that could be reached to those descending from the Allegheny Mountains. Brownsville is located 40 miles (64 km) south of Pittsburgh along the east bank of the Monongahela River.

Lord Dunmore's War, also known as Dunmore's War, was a brief conflict in fall 1774 between the British Colony of Virginia and the Shawnee and Mingo in the trans-Appalachian region of the colony south of the Ohio River. Broadly, the war included events between May and October 1774. The governor of Virginia during the conflict was John Murray, 4th Earl of Dunmore, who in May 1774, asked the House of Burgesses to declare a state of war with the Indians and call out the Virginia militia.

The Kanawha River is a tributary of the Ohio River, approximately 97 mi (156 km) long, in the U.S. state of West Virginia. The largest inland waterway in West Virginia, its watershed has been a significant industrial region of the state since early in the 19th century.

The Little Kanawha River is a tributary of the Ohio River, 169 mi (269 km) long, in western West Virginia in the United States. Via the Ohio, it is part of the watershed of the Mississippi River, draining an area of 2,320 mi2 (6,009 km2) on the unglaciated portion of the Allegheny Plateau. It served as an important commercial water route in the early history of West Virginia, particularly in the logging and petroleum industries.

The Ohio Company, formally known as the Ohio Company of Virginia, was a land speculation company organized for the settlement by Virginians of the Ohio Country and to trade with the Native Americans. The company had a land grant from Britain and a treaty with Indians, but France also claimed the area, and the conflict helped provoke the outbreak of the French and Indian War.

The Cheat River is a 78.3-mile-long (126.0 km) tributary of the Monongahela River in eastern West Virginia and southwestern Pennsylvania in the United States. Via the Ohio River, the Cheat and Monongahela are part of the Mississippi River watershed. Owing to the ruggedness of the surrounding Allegheny Mountains, the Cheat remains largely remote with few settlements or developments along its banks. Its headwaters are in the Cheat-Potomac Ranger District of the Monongahela National Forest.
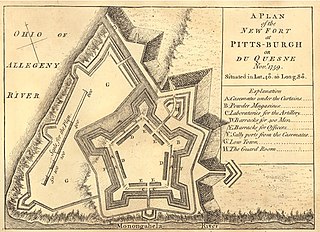
Fort Pitt was a fort built by British forces between 1759 and 1761 during the French and Indian War at the confluence of the Monongahela and Allegheny rivers, where the Ohio River is formed in western Pennsylvania. It was near the site of Fort Duquesne, a French colonial fort built in 1754 as tensions increased between Great Britain and France in both Europe and North America. The French destroyed Fort Duquesne in 1758 when they retreated under British attack.
Redstone Old Fort — or Redstone Fort or Fort Burd — on the Nemacolin Trail, was the name of the French and Indian War-era wooden fort built in 1759 by Pennsylvania militia colonel James Burd to guard the ancient Indian trail's river ford on a mound overlooking the eastern shore of the Monongahela River in what is now Fayette County, Pennsylvania, near, or on the banks of Dunlap's Creek at the confluence. The site is unlikely to be the same as an earlier fort the French document as Hangard dated to 1754 and which was confusedly, likely located on the nearby stream called Redstone Creek. Red sandstones predominate the deposited rock column of the entire region.

Burnsville Lake is both a recreational and flood control reservoir on Little Kanawha River located southeast of Burnsville in Braxton County, West Virginia. Burnsville Lake was authorized by the U.S. Congress in the Flood Control Act of 1938.

Orlando is an unincorporated community located in Braxton and Lewis counties, West Virginia, United States. It is located on Oil Creek, a tributary of the Little Kanawha River.
Kanuksusy or Kos Showeyha was a member of the Seneca tribe and son of Seneca chieftain Queen Alliquippa. He acted as a liaison between the Ohio Seneca and the Pennsylvania Colony during the French and Indian War as well as an intermediary and messenger for the Six Nations among other Native American tribes during the early part of the 18th century.
The Prehistory of West Virginia spans ancient times until the arrival of Europeans in the early 17th century. Hunters ventured into West Virginia's mountain valleys and made temporary camp villages since the Archaic period in the Americas. Many ancient human-made earthen mounds from various mound builder cultures survive, especially in the areas of Moundsville, South Charleston, and Romney. The artifacts uncovered in these areas give evidence of a village society with a tribal trade system culture that included limited cold worked copper. As of 2009, over 12,500 archaeological sites have been documented in West Virginia.

Teedyuscung was known as "King of the Delawares". He worked to establish a permanent Lenape (Delaware) home in eastern Pennsylvania in the Lehigh, Susquehanna, and Delaware River valleys. Teedyuscung participated in the Treaty of Easton, which resulted in the surrender of Lenape claims to all lands in Pennsylvania. Following the treaty, the Lenape were forced to live under the control of the Iroquois in the Wyoming Valley near modern-day Wilkes-Barre. Teedyuscung was murdered by arsonists in the night of April 19, 1763. This marked the beginning of the end of the Lenape presence in Pennsylvania. Teedyuscung's son Chief Bull conducted a raid on the Wyoming Valley that was part of a greater Indian uprising. As a result, the Lenape were forced to move west of the Appalachian Mountains by the Royal Proclamation of 1763.

The western part of Virginia which became West Virginia was settled in two directions, north to south from Pennsylvania, Maryland and New Jersey and from east to west from eastern Virginia and North Carolina. The earliest arrival of enslaved people was in the counties of the Shenandoah Valley, where prominent Virginia families built houses and plantations. The earliest recorded slave presence was about 1748 in Hampshire County on the estate of Thomas Fairfax, 6th Lord Fairfax of Cameron, which included 150 enslaved people. By the early 19th century, slavery had spread to the Ohio River up to the northern panhandle.

The protohistoric period of the state of West Virginia in the United States began in the mid-sixteenth century with the arrival of European trade goods. Explorers and colonists brought these goods to the eastern and southern coasts of North America and were brought inland by native trade routes. This was a period characterized by increased intertribal strife, rapid population decline, the abandonment of traditional life styles, and the extinction and migrations of many Native American groups.
Redstone Creek is a historically important widemouthed canoe and river boat-navigable brook-sized tributary stream of the Monongahela River in Fayette County, Pennsylvania. The creek is 28.4 miles (45.7 km) long, running from headwaters on Chestnut Ridge north through the city of Uniontown and reaching the Monongahela at Brownsville. Located in a 1/4-mile-wide valley with low streambanks, the site was ideal for ship building in a region geologically most often characterized by steep-plunging relatively inaccessible banks — wide enough to launch and float several large boats, and indeed steamboats after 1811, and slow-moving enough to provide good docks and parking places while craft were outfitting.
Bull, often known as Captain Bull, was a son of the Lenape chief Teedyuscung.
















