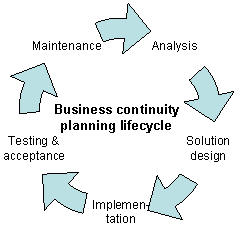
Any event that could negatively impact operations should be included in the plan, such as supply chain interruption, loss of or damage to critical infrastructure (major machinery or computing/network resource). As such, BCP is a subset of risk management. [8] In the U.S., government entities refer to the process as continuity of operations planning (COOP). [9] A business continuity plan [10] outlines a range of disaster scenarios and the steps the business will take in any particular scenario to return to regular trade. BCP's are written ahead of time and can also include precautions to be put in place. Usually created with the input of key staff as well as stakeholders, a BCP is a set of contingencies to minimize potential harm to businesses during adverse scenarios. [11]
Resilience
A 2005 analysis of how disruptions can adversely affect the operations of corporations and how investments in resilience can give a competitive advantage over entities not prepared for various contingencies [12] extended then-common business continuity planning practices. Business organizations such as the Council on Competitiveness embraced this resilience goal. [13]
Adapting to change in an apparently slower, more evolutionary manner - sometimes over many years or decades - has been described as being more resilient, [14] and the term "strategic resilience" is now used to go beyond resisting a one-time crisis, but rather continuously anticipating and adjusting, "before the case for change becomes desperately obvious".
This approach is sometimes summarized as: preparedness, [15] protection, response and recovery. [16]
Resilience Theory can be related to the field of Public Relations. Resilience is a communicative process that is constructed by citizens, families, media system, organizations and governments through everyday talk and mediated conversation. [17]
The theory is based on the work of Patrice M. Buzzanell, a professor at the Brian Lamb School of Communication at Purdue University. In her 2010 article, "Resilience: Talking, Resisting, and Imagining New Normalcies Into Being" [18] Buzzanell discussed the ability for organizations to thrive after having a crisis through building resistance. Buzzanell notes that there are five different processes that individuals use when trying to maintain resilience- crafting normalcy, affirming identity anchors, maintaining and using communication networks, putting alternative logics to work and downplaying negative feelings while foregrounding positive emotions.
While resilience theory and crisis communication theory share similarities, they are not the same. The crisis communication theory is based on the reputation of the company, but the resilience theory is based on the process of recovery of the company. There are five main components of resilience: crafting normalcy, affirming identity anchors, maintaining and using communication networks, putting alternative logics to work, and downplaying negative feelings while foregrounding negative emotions. [19] Each of these processes can be applicable to businesses in crisis times, making resilience an important factor for companies to focus on while training.
There are three main groups that are affected by a crisis. They are micro (individual), meso (group or organization) and macro (national or interorganizational). There are also two main types of resilience, which are proactive and post resilience. Proactive resilience is preparing for a crisis and creating a solid foundation for the company. Post resilience includes continuing to maintain communication and check in with employees. [20] Proactive resilience is dealing with issues at hand before they cause a possible shift in the work environment and post resilience maintaining communication and accepting changes after an incident has happened. Resilience can be applied to any organization. In New Zealand, the Canterbury University Resilient Organisations programme developed an assessment tool for benchmarking the Resilience of Organisations. [21] It covers 11 categories, each having 5 to 7 questions. A Resilience Ratio summarizes this evaluation. [22]