
Risk management is the identification, evaluation, and prioritization of risks followed by coordinated and economical application of resources to minimize, monitor, and control the probability or impact of unfortunate events or to maximize the realization of opportunities.
Security management is the identification of an organization's assets, followed by the development, documentation, and implementation of policies and procedures for protecting assets.
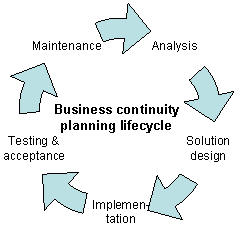
Business continuity may be defined as "the capability of an organization to continue the delivery of products or services at pre-defined acceptable levels following a disruptive incident", and business continuity planning is the process of creating systems of prevention and recovery to deal with potential threats to a company. In addition to prevention, the goal is to enable ongoing operations before and during execution of disaster recovery. Business continuity is the intended outcome of proper execution of both business continuity planning and disaster recovery.
A management system is a set of policies, processes and procedures used by an organization to ensure that it can fulfill the tasks required to achieve its objectives. These objectives cover many aspects of the organization's operations. For instance, an environmental management system enables organizations to improve their environmental performance, and an occupational safety and health management system enables an organization to control its occupational health and safety risks.

Critical infrastructure, or critical national infrastructure (CNI) in the UK, describes infrastructure considered essential by governments for the functioning of a society and economy and deserving of special protection for national security.
Disaster recovery is the process of maintaining or reestablishing vital infrastructure and systems following a natural or human-induced disaster, such as a storm or battle. It employs policies, tools, and procedures. Disaster recovery focuses on the information technology (IT) or technology systems supporting critical business functions as opposed to business continuity. This involves keeping all essential aspects of a business functioning despite significant disruptive events; it can therefore be considered a subset of business continuity. Disaster recovery assumes that the primary site is not immediately recoverable and restores data and services to a secondary site.
An incident is an event that could lead to loss of, or disruption to, an organization's operations, services or functions. Incident management (IcM) is a term describing the activities of an organization to identify, analyze, and correct hazards to prevent a future re-occurrence. These incidents within a structured organization are normally dealt with by either an incident response team (IRT), an incident management team (IMT), or Incident Command System (ICS). Without effective incident management, an incident can disrupt business operations, information security, IT systems, employees, customers, or other vital business functions.
Information assurance (IA) is the practice of assuring information and managing risks related to the use, processing, storage, and transmission of information. Information assurance includes protection of the integrity, availability, authenticity, non-repudiation and confidentiality of user data. IA encompasses not only digital protections but also physical techniques. These protections apply to data in transit, both physical and electronic forms, as well as data at rest. IA is best thought of as a superset of information security, and as the business outcome of information risk management.
In the United States, the hospital incident command system (HICS) is an incident command system (ICS) designed for hospitals and intended for use in both emergency and non-emergency situations. It provides hospitals of all sizes with tools needed to advance their emergency preparedness and response capability—both individually and as members of the broader response community.
ISO/TC 223 Societal security was a technical committee of the International Organization for Standardization formed in 2001 to develop standards in the area of societal security: i.e. protection of society from and response to incidents, emergencies, and disasters caused by intentional and unintentional human acts, natural hazards, and technical failures.
Information technology risk, IT risk, IT-related risk, or cyber risk is any risk relating to information technology. While information has long been appreciated as a valuable and important asset, the rise of the knowledge economy and the Digital Revolution has led to organizations becoming increasingly dependent on information, information processing and especially IT. Various events or incidents that compromise IT in some way can therefore cause adverse impacts on the organization's business processes or mission, ranging from inconsequential to catastrophic in scale.

Supply chain risk management (SCRM) is "the implementation of strategies to manage both everyday and exceptional risks along the supply chain based on continuous risk assessment with the objective of reducing vulnerability and ensuring continuity".
ISO 26262, titled "Road vehicles – Functional safety", is an international standard for functional safety of electrical and/or electronic systems that are installed in serial production road vehicles, defined by the International Organization for Standardization (ISO) in 2011, and revised in 2018.

IT risk management is the application of risk management methods to information technology in order to manage IT risk, i.e.:
ISO/IEC 27040 is part of a growing family of International Standards published by the International Organization for Standardization (ISO) and the International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC) in the area of security techniques; the standard is being developed by Subcommitee 27 (SC27) - IT Security techniques of the first Joint Technical Committee 1 of the ISO/IEC. A major element of SC27's program of work includes International Standards for information security management systems (ISMS), often referred to as the 'ISO/IEC 27000-series'.
Storage security is a specialty area of security that is concerned with securing data storage systems and ecosystems and the data that resides on these systems.

ISO/TC 292 Security and resilience is a technical committee of the International Organization for Standardization formed in 2015 to develop standards in the area of security and resilience.
ISO 22322:2022 is an international standard developed by the ISO/TC 292 Security and Resilience committee. It was published by the International Organization for Standardization (ISO) in 2015.
ISO 22381:2018 Security and resilience – Authenticity, integrity and trust for products and documents – Guidelines for establishing interoperability among object identification systems to deter counterfeiting and illicit trade, is an international standard developed by ISO/TC 292 Security and resilience and published by the International Organization for Standardization in 2018. ISO 22381 is a guidance document that provides various of recommendations for establishing interoperability among independently functioning product identification and related authentication systems, as described in ISO 16678.





