ISO/IEC 8859 is a joint ISO and IEC series of standards for 8-bit character encodings. The series of standards consists of numbered parts, such as ISO/IEC 8859-1, ISO/IEC 8859-2, etc. There are 15 parts, excluding the abandoned ISO/IEC 8859-12. The ISO working group maintaining this series of standards has been disbanded.
ISO/IEC 8859-15:1999, Information technology — 8-bit single-byte coded graphic character sets — Part 15: Latin alphabet No. 9, is part of the ISO/IEC 8859 series of ASCII-based standard character encodings, first edition published in 1999. It is informally referred to as Latin-9. It is similar to ISO 8859-1, and thus also intended for “Western European” languages, but replaces some less common symbols with the euro sign and some letters that were deemed necessary.
ISO/IEC 8859-5:1999, Information technology — 8-bit single-byte coded graphic character sets — Part 5: Latin/Cyrillic alphabet, is part of the ISO/IEC 8859 series of ASCII-based standard character encodings, first edition published in 1988. It is informally referred to as Latin/Cyrillic.
ISO/IEC 2022Information technology—Character code structure and extension techniques, is an ISO/IEC standard in the field of character encoding. It is equivalent to the ECMA standard ECMA-35, the ANSI standard ANSI X3.41 and the Japanese Industrial Standard JIS X 0202. Originating in 1971, it was most recently revised in 1994.
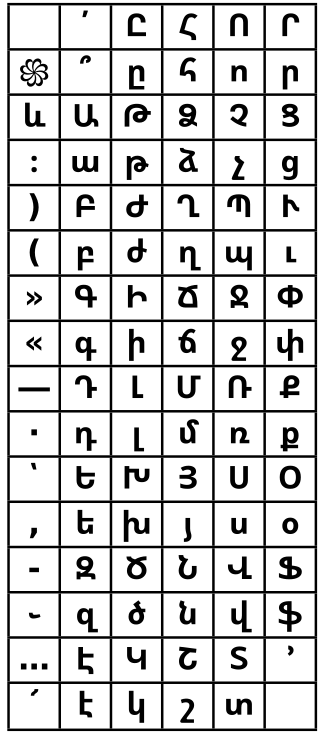
ArmSCII or ARMSCII is a set of obsolete single-byte character encodings for the Armenian alphabet defined by Armenian national standard 166–9. ArmSCII is an acronym for Armenian Standard Code for Information Interchange, similar to ASCII for the American standard. It has been superseded by the Unicode standard.
ISO 15924, Codes for the representation of names of scripts, is an international standard defining codes for writing systems or scripts. Each script is given both a four-letter code and a numeric code.
T.61 is an ITU-T Recommendation for a Teletex character set. T.61 predated Unicode, and was the primary character set in ASN.1 used in early versions of X.500 and X.509 for encoding strings containing characters used in Western European languages. It is also used by older versions of LDAP. While T.61 continues to be supported in modern versions of X.500 and X.509, it has been deprecated in favor of Unicode. It is also called Code page 1036, CP1036, or IBM 01036.

Kra is a glyph formerly used to write the Kalaallisut language of Greenland and is now only found in Inuttitut, a distinct Inuktitut dialect. It is visually similar to a Latin small capital letter K, a Greek letter Kappa: κ, or a Cyrillic small letter Ka: к.
The C0 and C1 control code or control character sets define control codes for use in text by computer systems that use ASCII and derivatives of ASCII. The codes represent additional information about the text, such as the position of a cursor, an instruction to start a new line, or a message that the text has been received.
UTF-1 is an obsolete method of transforming ISO/IEC 10646/Unicode into a stream of bytes. Its design does not provide self-synchronization, which makes searching for substrings and error recovery difficult. It reuses the ASCII printing characters for multi-byte encodings, making it unsuited for some uses. UTF-1 is also slow to encode or decode due to its use of division and multiplication by a number which is not a power of 2. Due to these issues, it did not gain acceptance and was quickly replaced by UTF-8.

〒 is the service mark of Japan Post and its successor, Japan Post Holdings, the postal operator in Japan. It is also used as a Japanese postal code mark since the introduction of the latter in 1968. Historically, it was used by the Ministry of Communications, which operated the postal service. The mark is a stylized katakana syllable te (テ), from the word teishin. The mark was introduced on February 8, 1887.
T.51 / ISO/IEC 6937:2001, Information technology — Coded graphic character set for text communication — Latin alphabet, is a multibyte extension of ASCII, or more precisely ISO/IEC 646-IRV. It was developed in common with ITU-T for telematic services under the name of T.51, and first became an ISO standard in 1983. Certain byte codes are used as lead bytes for letters with diacritics. The value of the lead byte often indicates which diacritic that the letter has, and the follow byte then has the ASCII-value for the letter that the diacritic is on.

A signature mark, in traditional bookbinding, is a letter, number or combination of either or both, which is printed at the bottom of the first page, or leaf, of a section.
ISO 6438:1983, Documentation — African coded character set for bibliographic information interchange, is an ISO standard for an 8-bit character encoding for African languages. Developed separately from the African reference alphabet but apparently based on the same data sets, it has had little use; its forms are retained Unicode. FreeDOS calls this Code Page 65504.
KPS 9566 is a North Korean standard specifying a character encoding for the Chosŏn'gŭl (Hangul) writing system used for the Korean language. The edition of 1997 specified an ISO 2022-compliant 94×94 two-byte coded character set. Subsequent editions have added additional encoded characters outside of the 94×94 plane, in a manner comparable to UHC or GBK.
The Universal Coded Character Set is a standard set of characters defined by the international standard ISO/IEC 10646, Information technology — Universal Coded Character Set (UCS), which is the basis of many character encodings, improving as characters from previously unrepresented writing systems are added.
ISO/IEC JTC 1/SC 2 Coded character sets is a standardization subcommittee of the Joint Technical Committee ISO/IEC JTC 1 of the International Organization for Standardization (ISO) and the International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC), that develops and facilitates standards within the field of coded character sets. The international secretariat of ISO/IEC JTC 1/SC 2 is the Japanese Industrial Standards Committee (JISC), located in Japan. SC 2 is responsible for the development of the Universal Coded Character Set standard, which is the international standard corresponding to the Unicode Standard.
ISO/IEC 10367:1991 is a standard developed by ISO/IEC JTC 1/SC 2, defining graphical character sets for use in character encodings implementing levels 2 and 3 of ISO/IEC 4873.
ISO-IR-197 is an 8-bit, single-byte character encoding which was designed for the Sámi languages. It is a modification of ISO 8859-1, replacing certain punctuation and symbol characters with additional letters used in certain Sámi orthographies. FreeDOS calls it code page 59187.



