Related Research Articles
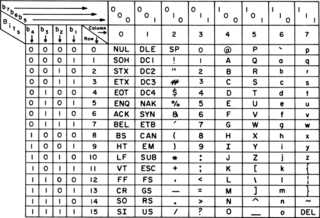
ASCII, abbreviated from American Standard Code for Information Interchange, is a character encoding standard for electronic communication. ASCII codes represent text in computers, telecommunications equipment, and other devices. Most modern character-encoding schemes are based on ASCII, although most of those support many additional characters.

ISO/IEC 8859-1:1998, Information technology — 8-bit single-byte coded graphic character sets — Part 1: Latin alphabet No. 1, is part of the ISO/IEC 8859 series of ASCII-based standard character encodings, first edition published in 1987. ISO/IEC 8859-1 encodes what it refers to as "Latin alphabet no. 1", consisting of 191 characters from the Latin script. This character-encoding scheme is used throughout the Americas, Western Europe, Oceania, and much of Africa. It is the basis for some popular 8-bit character sets and the first two blocks of characters in Unicode.

A vehicle identification number (VIN) is a unique code, including a serial number, used by the automotive industry to identify individual motor vehicles, towed vehicles, motorcycles, scooters and mopeds, as defined by the International Organization for Standardization in ISO 3779 and ISO 4030.
ISO/IEC 646 is the name of a set of ISO/IEC standards, described as Information technology — ISO 7-bit coded character set for information interchange and developed in cooperation with ASCII at least since 1964. Since its first edition in 1967 it has specified a 7-bit character code from which several national standards are derived.
The tilde˜ or ~, is a grapheme with several uses. The name of the character came into English from Spanish and Portuguese, which in turn came from the Latin titulus, meaning "title" or "superscription". Its primary use is as a diacritic (accent) in combination with a base letter; but for historical reasons, it is also used in standalone form within a variety of contexts.
ISO/IEC 8859-5:1999, Information technology — 8-bit single-byte coded graphic character sets — Part 5: Latin/Cyrillic alphabet, is part of the ISO/IEC 8859 series of ASCII-based standard character encodings, first edition published in 1988. It is informally referred to as Latin/Cyrillic. It was designed to cover languages using a Cyrillic alphabet such as Bulgarian, Belarusian, Russian, Serbian and Macedonian but was never widely used. It would also have been usable for Ukrainian in the Soviet Union from 1933 to 1990, but it is missing the Ukrainian letter ge, ґ, which is required in Ukrainian orthography before and since, and during that period outside Soviet Ukraine. As a result, IBM created Code page 1124.
ISO/IEC 8859-16:2001, Information technology — 8-bit single-byte coded graphic character sets — Part 16: Latin alphabet No. 10, is part of the ISO/IEC 8859 series of ASCII-based standard character encodings, first edition published in 2001. The same encoding was defined as Romanian Standard SR 14111 in 1998, named the "Romanian Character Set for Information Interchange". It is informally referred to as Latin-10 or South-Eastern European. It was designed to cover Albanian, Croatian, Hungarian, Polish, Romanian, Serbian and Slovenian, but also French, German, Italian and Irish Gaelic.

The general prohibition sign, also known informally as the no symbol, 'do not' sign, circle-backslash symbol, nay, interdictory circle, prohibited symbol, don't do it symbol, or universal no, is a red circle with a 45-degree diagonal line inside the circle from upper-left to lower-right. It is overlaid on a pictogram to warn that an activity is not permitted, or has accompanying text to describe what is prohibited.

ArmSCII or ARMSCII is a set of obsolete single-byte character encodings for the Armenian alphabet defined by Armenian national standard 166–9. ArmSCII is an acronym for Armenian Standard Code for Information Interchange, similar to ASCII for the American standard. It has been superseded by the Unicode standard.
ISO 15924, Codes for the representation of names of scripts, is an international standard defining codes for writing systems or scripts. Each script is given both a four-letter code and a numeric code.
International Standard Musical Work Code (ISWC) is a unique identifier for musical works, similar to ISBN for books. It is adopted as international standard ISO 15707. The ISO subcommittee with responsibility for the standard is TC 46/SC 9.
The C0 and C1 control code or control character sets define control codes for use in text by computer systems that use ASCII and derivatives of ASCII. The codes represent additional information about the text, such as the position of a cursor, an instruction to start a new line, or a message that the text has been received.
ISO 2709 is an ISO standard for bibliographic descriptions, titled Information and documentation—Format for information exchange.
ISO 6438:1983, Documentation — African coded character set for bibliographic information interchange, is an ISO standard for an 8-bit character encoding for African languages. It has had little use. In practice it is now superseded by Unicode.
ISO 3166-2:TD is the entry for Chad in ISO 3166-2, part of the ISO 3166 standard published by the International Organization for Standardization (ISO), which defines codes for the names of the principal subdivisions of all countries coded in ISO 3166-1.

OCR-A is a font created in 1968, in the early days of computer optical character recognition, when there was a need for a font that could be recognized not only by the computers of that day, but also by humans. OCR-A uses simple, thick strokes to form recognizable characters. The font is monospaced (fixed-width), with the printer required to place glyphs 0.254 cm apart, and the reader required to accept any spacing between 0.2286 cm and 0.4572 cm.
In mathematics, the radical sign, radical symbol, root symbol, radix, or surd is a symbol for the square root or higher-order root of a number. The square root of a number is written as
ISO 5428:1984, Greek alphabet coded character set for bibliographic information interchange, is an ISO standard for an 8-bit character encoding for the modern Greek language. It contains a set of 73 graphic characters and is available through UNIMARC. In practice it is now superseded by Unicode.
ISO 5426 is a character set developed by ISO, similar to ISO/IEC 6937. It was first published in 1983.
ISO-IR-153 is an 8-bit character set that covers the Russian and Bulgarian alphabets. Unlike the KOI encodings, this encoding lists the Cyrillic letters in their correct traditional order. This has become the basis for ISO/IEC 8859-5 and the Cyrillic Unicode block.
References
- ↑ https://www.iso.org/obp/ui/#iso:std:iso:6862:ed-1:v1:en [ bare URL ]
- ↑ "Mathematical coded character set for bibliographic information interchange, part 1" (PDF).
- ↑ "Mathematical coded character set for bibliographic information interchange, part 2" (PDF).
- ↑ https://www.unicode.org/Public/MAPPINGS/OBSOLETE/UNI2SGML.TXT [ bare URL plain text file ]