
The astronomical unit is a unit of length defined to be exactly equal to 149,597,870,700 m. Historically, the astronomical unit was conceived as the average Earth-Sun distance, before its modern redefinition in 2012.

ISO 8601 is an international standard covering the worldwide exchange and communication of date and time-related data. It is maintained by the International Organization for Standardization (ISO) and was first published in 1988, with updates in 1991, 2000, 2004, and 2019, and an amendment in 2022. The standard provides a well-defined, unambiguous method of representing calendar dates and times in worldwide communications, especially to avoid misinterpreting numeric dates and times when such data is transferred between countries with different conventions for writing numeric dates and times.

A physical quantity is a property of a material or system that can be quantified by measurement. A physical quantity can be expressed as a value, which is the algebraic multiplication of a numerical value and a unit of measurement. For example, the physical quantity mass, symbol m, can be quantified as m=n kg, where n is the numerical value and kg is the unit symbol. Quantities that are vectors have, besides numerical value and unit, direction or orientation in space.
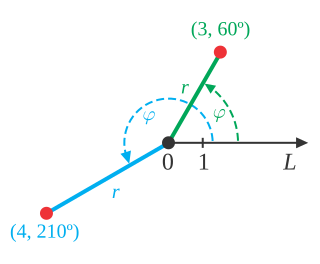
The angular displacement – also called angle of rotation, rotational displacement, or rotary displacement – of a physical body is the angle through which the body rotates around a centre or axis of rotation. Angular displacement may be signed, indicating the sense of rotation ; it may also be greater than a full turn.
Million years ago, abbreviated as Mya, Myr (megayear) or Ma (megaannum), is a unit of time equal to 1,000,000 years (i.e. 1×106 years), or approximately 31.6 teraseconds.
IEC 60027 is a technical international standard for letter symbols published by the International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC), comprising the following parts:
ISO 31 is a superseded international standard concerning physical quantities, units of measurement, their interrelationships and their presentation. It was revised and replaced by ISO/IEC 80000.

Rotational frequency, also known as rotational speed or rate of rotation, is the frequency of rotation of an object around an axis. Its SI unit is the reciprocal seconds (s−1); other common units of measurement include the hertz (Hz), cycles per second (cps), and revolutions per minute (rpm).
International standard ISO 1000 is the ISO standard describing the International System of Units (SI).
ISO 31-0 is the introductory part of international standard ISO 31 on quantities and units. It provides guidelines for using physical quantities, quantity and unit symbols, and coherent unit systems, especially the SI. It was intended for use in all fields of science and technology and is augmented by more specialized conventions defined in other parts of the ISO 31 standard. ISO 31-0 was withdrawn on 17 November 2009. It is superseded by ISO 80000-1. Other parts of ISO 31 have also been withdrawn and replaced by parts of ISO 80000.
ISO 31-3 is the part of international standard ISO 31 that defines names and symbols for quantities and units related to mechanics. It is superseded by ISO 80000-4.
ISO 31-4 is the part of international standard ISO 31 that defines names and symbols for quantities and units related to heat. It is superseded by ISO 80000-5.
ISO 31-6 is the part of international standard ISO 31 that defines names and symbols for quantities and units related to light and related electromagnetic radiations. It is superseded by ISO 80000-7.
ISO 31-7 is the part of international standard ISO 31 that defines names and symbols for quantities and units related to acoustics. It is superseded by ISO 80000-8.
ISO 31-11:1992 was the part of international standard ISO 31 that defines mathematical signs and symbols for use in physical sciences and technology. It was superseded in 2009 by ISO 80000-2:2009 and subsequently revised in 2019 as ISO-80000-2:2019.
ISO/IEC 80000, Quantities and units, is an international standard describing the International System of Quantities (ISQ). It was developed and promulgated jointly by the International Organization for Standardization (ISO) and the International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC). It serves as a style guide for using physical quantities and units of measurement, formulas involving them, and their corresponding units, in scientific and educational documents for worldwide use. The ISO/IEC 80000 family of standards was completed with the publication of the first edition of Part 1 in November 2009.

The International System of Quantities (ISQ) is a standard system of quantities used in physics and in modern science in general. It includes basic quantities such as length and mass and the relationships between those quantities. This system underlies the International System of Units (SI) but does not itself determine the units of measurement used for the quantities.
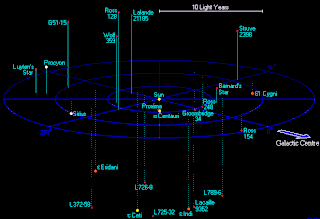
A light-year, alternatively spelled light year, is a unit of length used to express astronomical distances and is equal to exactly 9460730472580.8 km, which is approximately 5.88 trillion mi. As defined by the International Astronomical Union (IAU), a light-year is the distance that light travels in vacuum in one Julian year. Despite its inclusion of the word "year", the term should not be misinterpreted as a unit of time.
In science and engineering, a power level and a field level are logarithmic magnitudes of certain quantities referenced to a standard reference value of the same type.
A power quantity is a power or a quantity directly proportional to power, e.g., energy density, acoustic intensity, and luminous intensity. Energy quantities may also be labelled as power quantities in this context.








