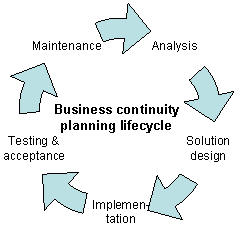
Business continuity planning is the process of creating systems of prevention and recovery to deal with potential threats to a company. In addition to prevention, the goal is to enable ongoing operations before and during execution of disaster recovery.
ISO 14000 is a family of standards related to environmental management that exists to help organizations (a) minimize how their operations negatively affect the environment ; (b) comply with applicable laws, regulations, and other environmentally oriented requirements; and (c) continually improve in the above.
Facility management is a professional management discipline focused on the efficient and effective delivery of support services for the organizations that it serves. The International Organization for Standardization (ISO) defines facility management as the "organizational function which integrates people, place, and process within the built environment with the purpose of improving the quality of life of people and the productivity of the core business."
Total cost of ownership (TCO) is a financial estimate intended to help buyers and owners determine the direct and indirect costs of a product or service. It is a management accounting concept that can be used in full cost accounting or even ecological economics where it includes social costs.

Life-cycle assessment or LCA is a methodology for assessing environmental impacts associated with all the stages of the life-cycle of a commercial product, process, or service. For instance, in the case of a manufactured product, environmental impacts are assessed from raw material extraction and processing (cradle), through the product's manufacture, distribution and use, to the recycling or final disposal of the materials composing it (grave).
Software maintenance in software engineering is the modification of a software product after delivery to correct faults, to improve performance or other attributes.
ISO 10303 is an ISO standard for the computer-interpretable representation and exchange of product manufacturing information. Its official title is: Automation systems and integration — Product data representation and exchange. It is known informally as "STEP", which stands for "Standard for the Exchange of Product model data". ISO 10303 can represent 3D objects in Computer-aided design (CAD) and related information.

Green building refers to both a structure and the application of processes that are environmentally responsible and resource-efficient throughout a building's life-cycle: from planning to design, construction, operation, maintenance, renovation, and demolition. This requires close cooperation of the contractor, the architects, the engineers, and the client at all project stages. The Green Building practice expands and complements the classical building design concerns of economy, utility, durability, and comfort. In doing so, the three dimensions of sustainability, i.e., planet, people and profit across the entire supply chain need to be considered.

Future-proofing is the process of anticipating the future and developing methods of minimizing the effects of shocks and stresses of future events. Future-proofing is used in industries such as electronics, medical industry, industrial design, and more recently, in design for climate change. The principles of future-proofing are extracted from other industries and codified as a system for approaching an intervention in an historic building.
ISO/IEC 20000 is the first international standard for service management. It was developed in 2005 by ISO/IEC JTC1/SC7 and revised in 2011 and 2018. It was originally based on the earlier BS 15000 that was developed by BSI Group.
Building information modeling (BIM) is a process supported by various tools, technologies and contracts involving the generation and management of digital representations of physical and functional characteristics of places. Building information models (BIMs) are computer files which can be extracted, exchanged or networked to support decision-making regarding a built asset. BIM software is used by individuals, businesses and government agencies who plan, design, construct, operate and maintain buildings and diverse physical infrastructures, such as water, refuse, electricity, gas, communication utilities, roads, railways, bridges, ports and tunnels.
Asset management refers to a systematic approach to the governance and realization of value from the things that a group or entity is responsible for, over their whole life cycles. It may apply both to tangible assets and to intangible assets. Asset management is a systematic process of developing, operating, maintaining, upgrading, and disposing of assets in the most cost-effective manner.
Whole-life cost is the total cost of ownership over the life of an asset. The concept is also known as life-cycle cost (LCC) or lifetime cost, and is commonly referred to as "cradle to grave" or "womb to tomb" costs. Costs considered include the financial cost which is relatively simple to calculate and also the environmental and social costs which are more difficult to quantify and assign numerical values. Typical areas of expenditure which are included in calculating the whole-life cost include planning, design, construction and acquisition, operations, maintenance, renewal and rehabilitation, depreciation and cost of finance and replacement or disposal.
ISO 55000 is an international standard covering management of assets of any kind. Before it, a Publicly Available Specification was published by the British Standards Institution in 2004 for physical assets. The ISO 55000 series of Asset Management standards was launched in January 2014.
Performance-Based Building Design is an approach to the design of any complexity of building, from single-detached homes up to and including high-rise apartments and office buildings. A building constructed in this way is required to meet certain measurable or predictable performance requirements, such as energy efficiency or seismic load, without a specific prescribed method by which to attain those requirements. This is in contrast to traditional prescribed building codes, which mandate specific construction practises, such as stud size and distance between studs in wooden frame construction. Such an approach provides the freedom to develop tools and methods to evaluate the entire life cycle of the building process, from the business dealings, to procurement, through construction and the evaluation of results.

Infrastructure asset management is the integrated, multidisciplinary set of strategies in sustaining public infrastructure assets such as water treatment facilities, sewer lines, roads, utility grids, bridges, and railways. Generally, the process focuses on the later stages of a facility's life cycle, specifically maintenance, rehabilitation, and replacement. Asset management specifically uses software tools to organize and implement these strategies with the fundamental goal to preserve and extend the service life of long-term infrastructure assets which are vital underlying components in maintaining the quality of life in society and efficiency in the economy. In the 21st century, climate change adaptation has become an important part of infrastructure asset management competence.

IT Risk Management is the application of risk management methods to information technology in order to manage IT risk, i.e.:
ISO 50001Energy management systems - Requirements with guidance for use, is an international standard created by the International Organization for Standardization (ISO). The standard specifies the requirements for establishing, implementing, maintaining and improving an energy management system, whose purpose is to enable an organization to follow a systematic approach in achieving continual improvement of energy performance, including energy efficiency, energy security, energy use and consumption.
ISO/IEC 27001 is an international standard on how to manage information security. The standard was originally published jointly by the International Organization for Standardization (ISO) and the International Electrotechnical Commission(IEC) in 2005 and then revised in 2013. It details requirements for establishing, implementing, maintaining and continually improving an information security management system (ISMS) – the aim of which is to help organizations make the information assets they hold more secure. A European update of the standard was published in 2017. Organizations that meet the standard's requirements can choose to be certified by an accredited certification body following successful completion of an audit.
ISO/IEC JTC 1/SC 7 Software and systems engineering is a standardization subcommittee of the Joint Technical Committee ISO/IEC JTC 1 of the International Organization for Standardization (ISO) and the International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC), that develops and facilitates standards within the field of engineering of software products and systems. The international secretariat of ISO/IEC JTC 1/SC 7 is the Bureau of Indian Standards (BIS) located in India.





