Terminology is the study of terms and their use. Terms are words and compound words or multi-word expressions that in specific contexts are given specific meanings—these may deviate from the meanings the same words have in other contexts and in everyday language. Terminology is a discipline that studies, among other things, the development of such terms and their interrelationships within a specialized domain. Terminology differs from lexicography, as it involves the study of concepts, conceptual systems and their labels (terms), whereas lexicography studies words and their meanings.
ISO/IEC/IEEE 12207Systems and software engineering – Software life cycle processes is an international standard for software lifecycle processes. First introduced in 1995, it aims to be a primary standard that defines all the processes required for developing and maintaining software systems, including the outcomes and/or activities of each process.
In sociolinguistics, a register is a variety of language used for a particular purpose or in a particular communicative situation. For example, when speaking officially or in a public setting, an English speaker may be more likely to follow prescriptive norms for formal usage than in a casual setting; examples might include pronouncing words ending in -ing with a velar nasal instead of an alveolar nasal, choosing words that are considered more "formal", and refraining from using words considered nonstandard, such as ain't.
ISO/IEC 11179 is an international standard for representing metadata for an organization in a metadata registry.
SNOMED CT or SNOMED Clinical Terms is a systematically organized computer processable collection of medical terms providing codes, terms, synonyms and definitions used in clinical documentation and reporting. SNOMED CT is considered to be the most comprehensive, multilingual clinical healthcare terminology in the world. The primary purpose of SNOMED CT is to encode the meanings that are used in health information and to support the effective clinical recording of data with the aim of improving patient care. SNOMED CT provides the core general terminology for electronic health records. SNOMED CT comprehensive coverage includes: clinical findings, symptoms, diagnoses, procedures, body structures, organisms and other etiologies, substances, pharmaceuticals, devices and specimens.
The ISO 15926 is a standard for data integration, sharing, exchange, and hand-over between computer systems.
IEEE 1471 is a superseded IEEE Standard for describing the architecture of a "software-intensive system", also known as software architecture.
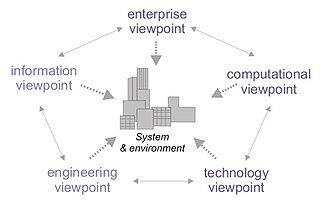
Reference Model of Open Distributed Processing (RM-ODP) is a reference model in computer science, which provides a co-ordinating framework for the standardization of open distributed processing (ODP). It supports distribution, interworking, platform and technology independence, and portability, together with an enterprise architecture framework for the specification of ODP systems.
Gellish is a formal language that is natural language independent, although its concepts have 'names' and definitions in various natural languages. Any natural language variant, such as Gellish Formal English is a controlled natural language. Information and knowledge can be expressed in such a way that it is computer-interpretable, as well as system-independent and natural language independent. Each natural language variant is a structured subset of that natural language and is suitable for information modeling and knowledge representation in that particular language. All expressions, concepts and individual things are represented in Gellish by (numeric) unique identifiers. This enables software to translate expressions from one formal natural language to any other formal natural language.
Terminology planning is a planning activity for developing domain communication largely according to the needs and requirements of knowledge representation. Domain-specific conventions of knowledge representation — depending on the domain as such or text within a domain, may comprise not only linguistic representation of concepts (i.e.terms), but also all kinds of non-linguistic representations. Therefore, to different degrees depending on the particular domain, terminology planning may have to take into account these non-linguistic representations as well.

ISO/TC 37 is a technical committee within the International Organization for Standardization (ISO) that prepares standards and other documents concerning methodology and principles for terminology and language resources.
ISO/IEC/IEEE 42010Systems and software engineering — Architecture description is an international standard for architecture descriptions of systems and software.
Like any supplier of goods or services, a translator potentially bears ethical and legal obligations toward his patron or employer. This has turned to be of enormous importance with the development of the language industry at global scale. For the protection of both parties, standards have been developed that seek to spell out their mutual duties.
A specification often refers to a set of documented requirements to be satisfied by a material, design, product, or service. A specification is often a type of technical standard.
In software engineering, a software development process is the process of dividing software development work into distinct phases to improve design, product management, and project management. It is also known as a software development life cycle. The methodology may include the pre-definition of specific deliverables and artifacts that are created and completed by a project team to develop or maintain an application.
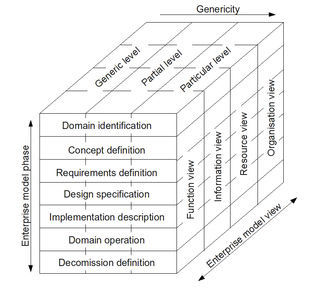
ISO 19439:2006 Enterprise integration—Framework for enterprise modelling, is an international standard for enterprise modelling and enterprise integration developed by the International Organization for Standardization, based on CIMOSA and GERAM.
ISO 25964 is the international standard for thesauri, published in two parts as follows:
ISO 25964 Information and documentation - Thesauri and interoperability with other vocabulariesPart 1: Thesauri for information retrieval [published August 2011] Part 2: Interoperability with other vocabularies [published March 2013]
In computing, a data definition specification (DDS) is a guideline to ensure comprehensive and consistent data definition. It represents the attributes required to quantify data definition. A comprehensive data definition specification encompasses enterprise data, the hierarchy of data management, prescribed guidance enforcement and criteria to determine compliance.
ISO/IEC JTC 1/SC 37 Biometrics is a standardization subcommittee in the Joint Technical Committee ISO/IEC JTC 1 of the International Organization for Standardization (ISO) and the International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC), which develops and facilitates standards within the field of biometrics. The international secretariat of ISO/IEC JTC 1/SC 37 is the American National Standards Institute (ANSI), located in the United States.
NPU terminology is a patient centered clinical laboratory terminology for use in the clinical laboratory sciences. Its function is to enable results of clinical laboratory examinations to be used safely across technology, time and geography. To achieve this, the NPU terminology supplies:



