A modeling language is any artificial language that can be used to express information or knowledge or systems in a structure that is defined by a consistent set of rules. The rules are used for interpretation of the meaning of components in the structure.
ISO/IEC 15504Information technology – Process assessment, also termed Software Process Improvement and Capability Determination (SPICE), is a set of technical standards documents for the computer software development process and related business management functions. It is one of the joint International Organization for Standardization (ISO) and International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC) standards, which was developed by the ISO and IEC joint subcommittee, ISO/IEC JTC 1/SC 7.
ISO 10303 is an ISO standard for the computer-interpretable representation and exchange of product manufacturing information. Its official title is: Automation systems and integration — Product data representation and exchange. It is known informally as "STEP", which stands for "Standard for the Exchange of Product model data". ISO 10303 can represent 3D objects in Computer-aided design (CAD) and related information.

Computer-integrated manufacturing (CIM) is the manufacturing approach of using computers to control the entire production process. This integration allows individual processes to exchange information with each other and initiate actions. Although manufacturing can be faster and less error-prone by the integration of computers, the main advantage is the ability to create automated manufacturing processes. Typically CIM relies on closed-loop control processes, based on real-time input from sensors. It is also known as flexible design and manufacturing.

The Department of Defense Architecture Framework (DoDAF) is an architecture framework for the United States Department of Defense (DoD) that provides visualization infrastructure for specific stakeholders concerns through viewpoints organized by various views. These views are artifacts for visualizing, understanding, and assimilating the broad scope and complexities of an architecture description through tabular, structural, behavioral, ontological, pictorial, temporal, graphical, probabilistic, or alternative conceptual means.
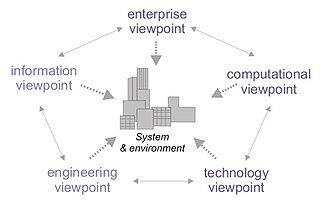
Reference Model of Open Distributed Processing (RM-ODP) is a reference model in computer science, which provides a co-ordinating framework for the standardization of open distributed processing (ODP). It supports distribution, interworking, platform and technology independence, and portability, together with an enterprise architecture framework for the specification of ODP systems.
ISO/IEC/IEEE 42010Systems and software engineering — Architecture description is an international standard for architecture descriptions of systems and software.
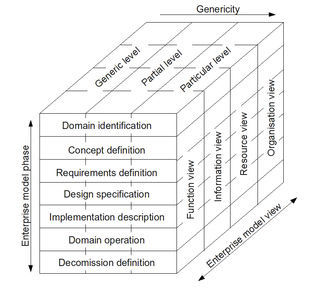
Enterprise engineering is defined as the body of knowledge, principles, and practices to design all or part of an enterprise. An enterprise is a complex, socio-technical system that comprises interdependent resources of people, information, and technology that must interact with each other and their environment in support of a common mission. According to Kosanke, Vernadat and Zelm, enterprise engineering is an enterprise life-cycle oriented discipline for the identification, design, and implementation of enterprises and their continuous evolution, supported by enterprise modelling. Enterprise engineering is a subdiscipline of industrial engineering / systems engineering. The discipline examines each aspect of the enterprise, including business processes, information flows, material flows, and organizational structure. Enterprise engineering may focus on the design of the enterprise as a whole, or on the design and integration of certain business components.

Enterprise life cycle (ELC) in enterprise architecture is the dynamic, iterative process of changing the enterprise over time by incorporating new business processes, new technology, and new capabilities, as well as maintenance, disposition and disposal of existing elements of the enterprise.

A view model or viewpoints framework in systems engineering, software engineering, and enterprise engineering is a framework which defines a coherent set of views to be used in the construction of a system architecture, software architecture, or enterprise architecture. A view is a representation of a whole system from the perspective of a related set of concerns.

Treasury Enterprise Architecture Framework (TEAF) was an Enterprise architecture framework for treasury, based on the Zachman Framework. It was developed by the US Department of the Treasury and published in July 2000. May 2012 this framework has been subsumed by evolving Federal Enterprise Architecture Policy as documented in "The Common Approach to Federal Enterprise Architecture".
In software engineering, a software development process is the process of dividing software development work into distinct phases to improve design, product management, and project management. It is also known as a software development life cycle. The methodology may include the pre-definition of specific deliverables and artifacts that are created and completed by a project team to develop or maintain an application.
Enterprise interoperability is the ability of an enterprise—a company or other large organization—to functionally link activities, such as product design, supply chains, manufacturing, in an efficient and competitive way.
Model Driven Interoperability (MDI) is a methodological framework, which provides a conceptual and technical support to make interoperable enterprises using ontologies and semantic annotations, following model driven development (MDD) principles.