
In astronomy, declination is one of the two angles that locate a point on the celestial sphere in the equatorial coordinate system, the other being hour angle. The declination angle is measured north (positive) or south (negative) of the celestial equator, along the hour circle passing through the point in question.

The ecliptic or ecliptic plane is the orbital plane of Earth around the Sun. From the perspective of an observer on Earth, the Sun's movement around the celestial sphere over the course of a year traces out a path along the ecliptic against the background of stars. The ecliptic is an important reference plane and is the basis of the ecliptic coordinate system.
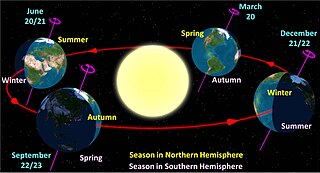
A solar equinox is a moment in time when the Sun crosses the Earth's equator, which is to say, appears directly above the equator, rather than north or south of the equator. On the day of the equinox, the Sun appears to rise "due east" and set "due west". This occurs twice each year, around 20 March and 23 September.

A lunar phase or Moon phase is the apparent shape of the Moon's directly sunlit portion as viewed from the Earth. In common usage, the four major phases are the new moon, the first quarter, the full moon and the last quarter; the four minor phases are waxing crescent, waxing gibbous, waning gibbous, and waning crescent. A lunar month is the time between successive recurrences of the same phase: due to the eccentricity of the Moon's orbit, this duration is not perfectly constant but averages about 29.5 days.

The zodiac is a belt-shaped region of the sky that extends approximately 8° north and south of the ecliptic, the apparent path of the Sun across the celestial sphere over the course of the year. Within this zodiac belt appear the Moon and the brightest planets, along their orbital planes. The zodiac is divided along the ecliptic into 12 equal parts, called "signs", each occupying 30° of celestial longitude. These signs roughly correspond to the astronomical constellations with the following modern names: Aries, Taurus, Gemini, Cancer, Leo, Virgo, Libra, Scorpio, Sagittarius, Capricorn, Aquarius, and Pisces.

In astronomy, axial precession is a gravity-induced, slow, and continuous change in the orientation of an astronomical body's rotational axis. In the absence of precession, the astronomical body's orbit would show axial parallelism. In particular, axial precession can refer to the gradual shift in the orientation of Earth's axis of rotation in a cycle of approximately 26,000 years. This is similar to the precession of a spinning top, with the axis tracing out a pair of cones joined at their apices. The term "precession" typically refers only to this largest part of the motion; other changes in the alignment of Earth's axis—nutation and polar motion—are much smaller in magnitude.

In astronomy, an analemma is a diagram showing the position of the Sun in the sky as seen from a fixed location on Earth at the same mean solar time, as that position varies over the course of a year. The diagram resembles a figure eight. Globes of the Earth often display an analemma as a two-dimensional figure of equation of time vs. declination of the Sun.

A lunar node is either of the two orbital nodes of the Moon, that is, the two points at which the orbit of the Moon intersects the ecliptic. The ascending node is where the Moon moves into the northern ecliptic hemisphere, while the descending node is where the Moon enters the southern ecliptic hemisphere.
Earth orbits the Sun at an average distance of 149.60 million km (92.96 million mi), or 8.317 light-minutes, in a counterclockwise direction as viewed from above the Northern Hemisphere. One complete orbit takes 365.256 days, during which time Earth has traveled 940 million km (584 million mi). Ignoring the influence of other Solar System bodies, Earth's orbit, also called Earth's revolution, is an ellipse with the Earth–Sun barycenter as one focus with a current eccentricity of 0.0167. Since this value is close to zero, the center of the orbit is relatively close to the center of the Sun.

The September equinox is the moment when the Sun appears to cross the celestial equator, heading southward. Because of differences between the calendar year and the tropical year, the September equinox may occur from September 21 to 24.

The March equinox or northward equinox is the equinox on the Earth when the subsolar point appears to leave the Southern Hemisphere and cross the celestial equator, heading northward as seen from Earth. The March equinox is known as the vernal equinox in the Northern Hemisphere and as the autumnal equinox in the Southern Hemisphere.

Many astronomical phenomena viewed from the planet Mars are the same as or similar to those seen from Earth; but some are quite different. For example, because the atmosphere of Mars does not contain an ozone layer, it is also possible to make UV observations from the surface of Mars.

A lunar standstill or lunistice is when the Moon reaches its furthest north or furthest south point during the course of a month. The declination at lunar standstill varies in a cycle 18.6 years long between 18.134° and 28.725°, due to lunar precession. These extremes are called the minor and major lunar standstills.

Daytime or day as observed on Earth is the period of the day during which a given location experiences natural illumination from direct sunlight. Daytime occurs when the Sun appears above the local horizon, that is, anywhere on the globe's hemisphere facing the Sun. In direct sunlight the movement of the sun can be recorded and observed using a sundial that casts a shadow that slowly moves during the day. Other planets and natural satellites that rotate relative to a luminous primary body, such as a local star, also experience daytime, but this article primarily discusses daytime on Earth.

The summer solstice or estival solstice occurs when one of Earth's poles has its maximum tilt toward the Sun. It happens twice yearly, once in each hemisphere. For that hemisphere, the summer solstice is the day with the longest period of daylight and shortest night of the year, when the Sun is at its highest position in the sky. At either pole there is continuous daylight at the time of its summer solstice. The opposite event is the winter solstice.

Sun path, sometimes also called day arc, refers to the daily and seasonal arc-like path that the Sun appears to follow across the sky as the Earth rotates and orbits the Sun. The Sun's path affects the length of daytime experienced and amount of daylight received along a certain latitude during a given season.
The equator is a circle of latitude that divides a spheroid, such as Earth, into the Northern and Southern hemispheres. On Earth, the Equator is an imaginary line located at 0 degrees latitude, about 40,075 km (24,901 mi) in circumference, halfway between the North and South poles. The term can also be used for any other celestial body that is roughly spherical.
A season is a division of the year based on changes in weather, ecology, and the number of daylight hours in a given region. On Earth, seasons are the result of the axial parallelism of Earth's tilted orbit around the Sun. In temperate and polar regions, the seasons are marked by changes in the intensity of sunlight that reaches the Earth's surface, variations of which may cause animals to undergo hibernation or to migrate, and plants to be dormant. Various cultures define the number and nature of seasons based on regional variations, and as such there are a number of both modern and historical definitions of the seasons.

The position of the Sun in the sky is a function of both the time and the geographic location of observation on Earth's surface. As Earth orbits the Sun over the course of a year, the Sun appears to move with respect to the fixed stars on the celestial sphere, along a circular path called the ecliptic.
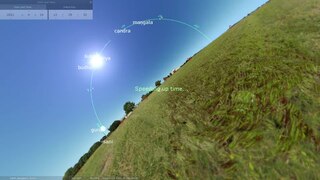
The Hindu calendar is based on a geocentric model of the Solar System. A geocentric model describes the Solar System as seen by an observer on the surface of the Earth.






























