Related Research Articles
ANSI C, ISO C, and Standard C are successive standards for the C programming language published by the American National Standards Institute (ANSI) and ISO/IEC JTC 1/SC 22/WG 14 of the International Organization for Standardization (ISO) and the International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC). Historically, the names referred specifically to the original and best-supported version of the standard. Software developers writing in C are encouraged to conform to the standards, as doing so helps portability between compilers.

The International Organization for Standardization is an independent, non-governmental, international standard development organization composed of representatives from the national standards organizations of member countries. Membership requirements are given in Article 3 of the ISO Statutes.

Vulcanization is a range of processes for hardening rubbers. The term originally referred exclusively to the treatment of natural rubber with sulfur, which remains the most common practice. It has also grown to include the hardening of other (synthetic) rubbers via various means. Examples include silicone rubber via room temperature vulcanizing and chloroprene rubber (neoprene) using metal oxides.
ISO 3166-2:IN is part of the ISO 3166 standardization codes published by the International Organization for Standardization (ISO) for India. It is part of the ISO 3166-2, which defines codes for the names of the principal subdivisions of all countries coded in ISO 3166-1. ISO 3166-2 codes are defined for 28 states and 8 union territories of India.

Ebonite is a brand name for a material generically known as hard rubber or vulcanite, obtained via vulcanizing natural rubber for prolonged periods. Ebonite may contain from 25% to 80% sulfur and linseed oil. Its name comes from its intended use as an artificial substitute for ebony wood. The material has also been called vulcanite, although that name formally refers to the mineral vulcanite.
ISO 10962, known as Classification of Financial Instruments (CFI), is a six-letter-code used in the financial services industry to classify and describe the structure and function of a financial instrument as part of the instrument reference data. It is an international standard approved by the International Organization for Standardization (ISO). CFI have been required since 1 July 2017.
ISO 31 is a superseded international standard concerning physical quantities, units of measurement, their interrelationships and their presentation. It was revised and replaced by ISO/IEC 80000.
ISO/IEC 9529 is a standard published by the International Organization for Standardization which defines the data format used on 3.5 inch floppy disks. It is also known as ECMA-125.

The International Standard Atmosphere (ISA) is a static atmospheric model of how the pressure, temperature, density, and viscosity of the Earth's atmosphere change over a wide range of altitudes or elevations. It has been established to provide a common reference for temperature and pressure and consists of tables of values at various altitudes, plus some formulas by which those values were derived. The International Organization for Standardization (ISO) publishes the ISA as an international standard, ISO 2533:1975. Other standards organizations, such as the International Civil Aviation Organization (ICAO) and the United States Government, publish extensions or subsets of the same atmospheric model under their own standards-making authority.
Spin casting, also known as centrifugal rubber mold casting (CRMC), is a method of utilizing inertia to produce castings from a rubber mold. Typically, a disc-shaped mold is spun along its central axis at a set speed. The casting material, usually molten metal or liquid thermoset plastic, is then poured in through an opening at the top-center of the mold. The filled mold then continues to spin as the metal solidifies.

Pneumatic tires are manufactured according to relatively standardized processes and machinery, in around 455 tire factories in the world. With over 1 billion tires manufactured worldwide annually, the tire industry is a major consumer of natural rubber. Tire factories start with bulk raw materials such as synthetic rubber, carbon black, and chemicals and produce numerous specialized components that are assembled and cured.
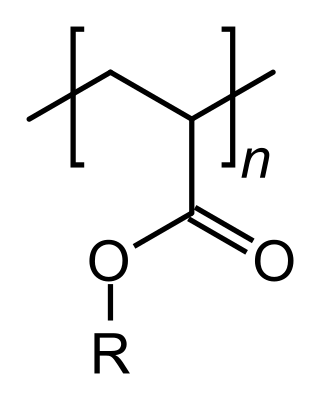
An acrylate polymer is any of a group of polymers prepared from acrylate monomers. These plastics are noted for their transparency, resistance to breakage, and elasticity.
ISO/IEC 80000, Quantities and units, is an international standard describing the International System of Quantities (ISQ). It was developed and promulgated jointly by the International Organization for Standardization (ISO) and the International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC). It serves as a style guide for using physical quantities and units of measurement, formulas involving them, and their corresponding units, in scientific and educational documents for worldwide use. The ISO/IEC 80000 family of standards was completed with the publication of the first edition of Part 1 in November 2009.
ISO 1 is an international standard set by the International Organization for Standardization that specifies the standard reference temperature for geometrical product specification and verification. The temperature is fixed at 20 degrees Celsius (°C), which exactly equals both 293.15 kelvin (K) and 68 degrees Fahrenheit (°F).

Abrasion is the process of scuffing, scratching, wearing down, marring, or rubbing away. It can be intentionally imposed in a controlled process using an abrasive. Abrasion can be an undesirable effect of exposure to normal use or exposure to the elements.
ISO 6943 is a specification created by the International Organization for Standardization for a method in determining the tension fatigue of vulcanised rubber.
MPEG-H is a group of international standards under development by the ISO/IEC Moving Picture Experts Group (MPEG). It has various "parts" – each of which can be considered a separate standard. These include a media transport protocol standard, a video compression standard, an audio compression standard, a digital file format container standard, three reference software packages, three conformance testing standards, and related technologies and technical reports. The group of standards is formally known as ISO/IEC 23008 – High efficiency coding and media delivery in heterogeneous environments. Development of the standards began around 2010, and the first fully approved standard in the group was published in 2013. Most of the standards in the group have been revised or amended several times to add additional extended features since their first edition.
References
- 1 2 "ISO 2921:2011". International Organization for Standardization. 2011. Retrieved October 21, 2011.
- ↑ ISO 2921:2019 Rubber, vulcanized — Determination of low-temperature characteristics — Temperature-retraction procedure (TR test) (6 ed.). ISO. 2019. pp. 1–2.