Related Research Articles
ISO/IEC 8859-3:1999, Information technology — 8-bit single-byte coded graphic character sets — Part 3: Latin alphabet No. 3, is part of the ISO/IEC 8859 series of ASCII-based standard character encodings, first edition published in 1988. It is informally referred to as Latin-3 or South European. It was designed to cover Turkish, Maltese and Esperanto, though the introduction of ISO/IEC 8859-9 superseded it for Turkish. The encoding was popular for users of Esperanto, but fell out of use as application support for Unicode became more common.
ISO/IEC 646 is a set of ISO/IEC standards, described as Information technology — ISO 7-bit coded character set for information interchange, and developed in cooperation with ASCII at least since 1964. Since its first edition in 1967 it has specified a 7-bit character code from which several national standards are derived.
ISO/IEC 8859-11:2001, Information technology — 8-bit single-byte coded graphic character sets — Part 11: Latin/Thai alphabet, is part of the ISO/IEC 8859 series of ASCII-based standard character encodings, first edition published in 2001. It is informally referred to as Latin/Thai. It is nearly identical to the national Thai standard TIS-620 (1990). The sole difference is that ISO/IEC 8859-11 allocates non-breaking space to code 0xA0, while TIS-620 leaves it undefined.
ISO/IEC 8859-4:1998, Information technology — 8-bit single-byte coded graphic character sets — Part 4: Latin alphabet No. 4, is part of the ISO/IEC 8859 series of ASCII-based standard character encodings, first edition published in 1988. It is informally referred to as Latin-4 or North European. It was designed to cover Estonian, Latvian, Lithuanian, Greenlandic, and Sámi. It has been largely superseded by ISO/IEC 8859-10 and Unicode. Microsoft has assigned code page 28594 a.k.a. Windows-28594 to ISO-8859-4 in Windows. IBM has assigned code page 914 to ISO 8859-4.
ISO/IEC 8859-5:1999, Information technology — 8-bit single-byte coded graphic character sets — Part 5: Latin/Cyrillic alphabet, is part of the ISO/IEC 8859 series of ASCII-based standard character encodings, first edition published in 1988. It is informally referred to as Latin/Cyrillic.
Windows-1258 is a code page used in Microsoft Windows to represent Vietnamese texts. It makes use of combining diacritical marks.
KOI8-R is an 8-bit character encoding, derived from the KOI-8 encoding by the programmer Andrei Chernov in 1993 and designed to cover Russian, which uses a Cyrillic alphabet. KOI8-R was based on Russian Morse code, which was created from a phonetic version of Latin Morse code. As a result, Russian Cyrillic letters are in pseudo-Roman order rather than the normal Cyrillic alphabetical order. Although this may seem unnatural, if the 8th bit is stripped, the text is partially readable in ASCII and may convert to syntactically correct KOI-7. For example, "Код Обмена Информацией" in KOI8-R becomes kOD oBMENA iNFORMACIEJ.
KOI8-U is an 8-bit character encoding, designed to cover Ukrainian, which uses a Cyrillic alphabet. It is based on KOI8-R, which covers Russian and Bulgarian, but replaces eight box drawing characters with four Ukrainian letters Ґ, Є, І, and Ї in both upper case and lower case.
Windows-1251 is an 8-bit character encoding, designed to cover languages that use the Cyrillic script such as Russian, Ukrainian, Belarusian, Bulgarian, Serbian Cyrillic, Macedonian and other languages.

Code page 850 is a code page used under DOS operating systems in Western Europe. Depending on the country setting and system configuration, code page 850 is the primary code page and default OEM code page in many countries, including various English-speaking locales, whilst other English-speaking locales default to the hardware code page 437.

Code page 855 is a code page used under DOS to write Cyrillic script.
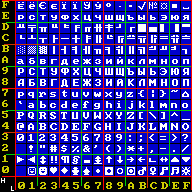
Code page 866 is a code page used under DOS and OS/2 in Russia to write Cyrillic script. It is based on the "alternative code page" developed in 1984 in IHNA AS USSR and published in 1986 by a research group at the Academy of Science of the USSR. The code page was widely used during the DOS era because it preserves all of the pseudographic symbols of code page 437 and maintains alphabetic order of Cyrillic letters. Initially this encoding was only available in the Russian version of MS-DOS 4.01 (1990), but with MS-DOS 6.22 it became available in any language version.
Windows-1255 is a code page used under Microsoft Windows to write Hebrew. It is an almost compatible superset of ISO-8859-8 – most of the symbols are in the same positions, but Windows-1255 adds vowel-points and other signs in lower positions.
Mac OS Cyrillic is a character encoding used on Apple Macintosh computers to represent texts in the Cyrillic script.
Mac OS Central European is a character encoding used on Apple Macintosh computers to represent texts in Central European and Southeastern European languages that use the Latin script. This encoding is also known as Code Page 10029. IBM assigns code page/CCSID 1282 to this encoding. This codepage contains diacritical letters that ISO 8859-2 does not have, and vice versa.
Code page 720 is a code page used under DOS to write Arabic in Egypt, Iraq, Jordan, Saudi Arabia, and Syria. The Windows (ANSI) code page for Arabic is Windows-1256.
MacGreek encoding or Macintosh Greek encoding is used in Apple Macintosh computers to represent texts in the Greek language that uses the Greek script. This encoding is registered as IBM code page/CCSID 1280 and Windows code page 10006.
Mac OS Romanian is a character encoding used on Apple Macintosh computers to represent the Romanian language. It is a derivative of Mac OS Roman.
KOI8-RU is an 8-bit character encoding, designed to cover Russian, Ukrainian, and Belarusian which use a Cyrillic alphabet. It is closely related to KOI8-R, which covers Russian and Bulgarian, but replaces ten box drawing characters with five Ukrainian and Belarusian letters Ґ, Є, І, Ї, and Ў in both upper case and lower case. It is even more closely related to KOI8-U, which does not include Ў but otherwise makes the same letter replacements. The additional letter allocations are matched by KOI8-E, except for Ґ which is added to KOI8-F.
Nikisoft-681 Cyrillic is an 8-bit character encoding, designed to cover languages that use the Cyrillic script such as Russian, Ukrainian, Belarusian, Bulgarian, Serbian Cyrillic, Macedonian and other languages. In Bulgarian, extended support is added for Ѝ to render the corrections well-maintained. Sample: