Indian Standard Code for Information Interchange (ISCII) is a coding scheme for representing various writing systems of India. It encodes the main Indic scripts and a Roman transliteration. The supported scripts are: Bengali–Assamese, Devanagari, Gujarati, Gurmukhi, Kannada, Malayalam, Oriya, Tamil, and Telugu. ISCII does not encode the writing systems of India that are based on Persian, but its writing system switching codes nonetheless provide for Kashmiri, Sindhi, Urdu, Persian, Pashto and Arabic. The Persian-based writing systems were subsequently encoded in the PASCII encoding.
Mac OS Roman is a character encoding created by Apple Computer, Inc. for use by Macintosh computers. It is suitable for representing text in English and several other languages that use the Latin script. Mac OS Roman encodes 256 characters, the first 128 of which are identical to ASCII, with the remaining characters including mathematical symbols, diacritics, and additional punctuation marks. Mac OS Roman is an extension of the original Macintosh character set, which encoded only 217 characters. Full support for Mac OS Roman first appeared in System 6.0.4, released in 1989, and the encoding is still supported in current versions of macOS, though the standard character encoding is now UTF-8. Apple modified Mac OS Roman in 1998 with the release of Mac OS 8.5 by replacing the currency sign with the euro sign, but otherwise the encoding has been unchanged since its release.
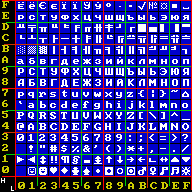
Code page 866 is a code page used under DOS and OS/2 in Russia to write Cyrillic script. It is based on the "alternative code page" developed in 1984 in IHNA AS USSR and published in 1986 by a research group at the Academy of Science of the USSR. The code page was widely used during the DOS era because it preserves all of the pseudographic symbols of code page 437 and maintains alphabetic order of Cyrillic letters. Initially this encoding was only available in the Russian version of MS-DOS 4.01 (1990), but with MS-DOS 6.22 it became available in any language version.
Mac OS Cyrillic is a character encoding used on Apple Macintosh computers to represent texts in the Cyrillic script.
Mac OS Central European is a character encoding used on Apple Macintosh computers to represent texts in Central European and Southeastern European languages that use the Latin script. This encoding is also known as Code Page 10029. IBM assigns code page/CCSID 1282 to this encoding. This codepage contains diacritical letters that ISO 8859-2 does not have, and vice versa.
Several 8-bit character sets (encodings) were designed for binary representation of common Western European languages, which use the Latin alphabet, a few additional letters and ones with precomposed diacritics, some punctuation, and various symbols. These character sets also happen to support many other languages such as Malay, Swahili, and Classical Latin.
Mac OS Icelandic is an obsolete character encoding that was used in Apple Macintosh computers to represent Icelandic text. It is largely identical to Mac OS Roman, except for the Icelandic special characters Ý, Þ and Ð which have replaced typography characters.
Mac OS Ukrainian is a character encoding used on Apple Macintosh computers prior to Mac OS 9 to represent texts in Cyrillic script which include the letters ‹Ґ› and ‹ґ›, including the Ukrainian alphabet.
MacGreek encoding or Macintosh Greek encoding is used in Apple Macintosh computers to represent texts in the Greek language that uses the Greek script. This encoding is registered as IBM code page/CCSID 1280 and Windows code page 10006.
Mac OS Romanian is a character encoding used on Apple Macintosh computers to represent the Romanian language. It is a derivative of Mac OS Roman.
Mac OS Croatian is a character encoding used on Apple Macintosh computers to represent Gaj's Latin alphabet. It is a derivative of Mac OS Roman. The three digraphs, Dž, Lj, and Nj, are not encoded.
Mac OS Sámi is a character encoding used on classic Mac OS to represent the Sámi languages and the Finnish Kalo language. While not used in any official Apple product, it has been used in various fonts designed to support Sámi languages under classic Mac OS, including those from Evertype. FreeDOS calls it code page 58630.
Mac OS Maltese/Esperanto, called MacOS Esperanto in older sources, is a character encoding for Esperanto, Maltese and Turkish created by Michael Everson on August 15 1997, based on the Mac OS Turkish encoding. It is used in his fonts, but not on official Mac OS fonts.
Macintosh Latin is an obsolete character encoding which was used by Kermit to represent text on the Apple Macintosh. It is a modification of Mac OS Icelandic to include all characters in ISO/IEC 8859-1, DEC MCS, the PostScript Standard Encoding, and a Dutch ISO 646 variant. Although Macintosh Latin is designed to be compatible with the standard Macintosh Mac OS Roman encoding for the shared subset of characters, the two should not be confused.
KOI8-T is an 8-bit single-byte extended ASCII character encoding adapting KOI8 to cover the Tajik Cyrillic alphabet. It was introduced by Michael Davis as an interim solution for representing Tajiki Cyrillic text in an interchangeable manner appropriate for use on the web, in an attempt to bridge the gap between existing non-interoperable font-specific encodings and the eventual wide adoption of Unicode. It is used by the GNU C Library as its default encoding for Tajik. FreeDOS calls it code page 62318.
Mac OS Inuit, also called Mac OS Inuktitut or InuitSCII, is an 8-bit, single byte, extended ASCII character encoding supporting the variant of Canadian Aboriginal syllabics used by the Inuktitut language. It was designed by Doug Hitch for the government of the Northwest Territories, and adopted by Michael Everson for his fonts.
The Macintosh Barents Cyrillic encoding is used in Apple Macintosh computers to represent texts in Kildin Sami, Komi, Mansi, and Nenets.
Mac OS Ogham is a character encoding for representing Ogham text on Apple Macintosh computers. It is a superset of the Irish Standard I.S. 434:1999 character encoding for Ogham, adding some punctuation characters from Mac OS Roman. It is not an official Mac OS Codepage.
Mac OS Armenian is an Armenian character encoding for Mac OS created by Michael Everson for use in his fonts. It is not an official Mac OS character set.
Mac OS Georgian is a character encoding for Mac OS created by Michael Everson for use in his fonts. It is not an official Mac OS character set.
