Related Research Articles
In computing, a code page is a character encoding and as such it is a specific association of a set of printable characters and control characters with unique numbers. Typically each number represents the binary value in a single byte.
ISO/IEC 8859-6:1999, Information technology — 8-bit single-byte coded graphic character sets — Part 6: Latin/Arabic alphabet, is part of the ISO/IEC 8859 series of ASCII-based standard character encodings, first edition published in 1987. It is informally referred to as Latin/Arabic. It was designed to cover Arabic. Only nominal letters are encoded, no preshaped forms of the letters, so shaping processing is required for display. It does not include the extra letters needed to write most Arabic-script languages other than Arabic itself.

Code page 850 is a code page used under DOS operating systems in Western Europe. Depending on the country setting and system configuration, code page 850 is the primary code page and default OEM code page in many countries, including various English-speaking locales, whilst other English-speaking locales default to the hardware code page 437.

Code page 437 is the character set of the original IBM PC. It is also known as CP437, OEM-US, OEM 437, PC-8, or DOS Latin US. The set includes all printable ASCII characters as well as some accented letters (diacritics), Greek letters, icons, and line-drawing symbols. It is sometimes referred to as the "OEM font" or "high ASCII", or as "extended ASCII".
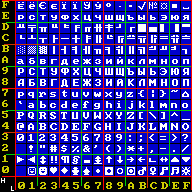
Code page 866 is a code page used under DOS and OS/2 in Russia to write Cyrillic script. It is based on the "alternative code page" developed in 1984 in IHNA AS USSR and published in 1986 by a research group at the Academy of Science of the USSR. The code page was widely used during the DOS era because it preserves all of the pseudographic symbols of code page 437 and maintains alphabetic order of Cyrillic letters. Initially this encoding was only available in the Russian version of MS-DOS 4.01 (1990), but with MS-DOS 6.22 it became available in any language version.
Code page 852 is a code page used under DOS to write Central European languages that use Latin script.
Code page 865 is a code page used under DOS in Denmark and Norway to write Nordic languages.
Code page 860 is a code page used under DOS in Portugal to write Portuguese and it is also suitable to write Spanish and Italian. In Brazil, however, the most widespread codepage – and that which DOS in Brazilian Portuguese used by default – was code page 850.
Code page 863 is a code page used under DOS in Canada to write French although it lacks the letters Æ, æ, Œ, œ, Ÿ and ÿ.

Code page 737 is a code page used under DOS to write the Greek language. It was much more popular than code page 869 although it lacks the letters ΐ and ΰ.
Code page 861 is a code page used under DOS in Iceland to write the Icelandic language.
Code page 862 is a code page used under DOS in Israel for Hebrew.

Unified Hangul Code (UHC), or Extended Wansung, also known under Microsoft Windows as Code Page 949, is the Microsoft Windows code page for the Korean language. It is an extension of Wansung Code to include all 11172 non-partial Hangul syllables present in Johab. This corresponds to the pre-composed syllables available in Unicode 2.0 and later.
The programming language APL uses a number of symbols, rather than words from natural language, to identify operations, similarly to mathematical symbols. Prior to the wide adoption of Unicode, a number of special-purpose EBCDIC and non-EBCDIC code pages were used to represent the symbols required for writing APL.
In computing, a hardware code page (HWCP) refers to a code page supported natively by a hardware device such as a display adapter or printer. The glyphs to present the characters are stored in the alphanumeric character generator's resident read-only memory and are thus not user-changeable. They are available for use by the system without having to load any font definitions into the device first. Startup messages issued by a PC's System BIOS or displayed by an operating system before initializing its own code page switching logic and font management and before switching to graphics mode are displayed in a computer's default hardware code page.
Code page 856, is a code page used under DOS for Hebrew in Israel.

The Atari ST character set is the character set of the Atari ST personal computer family including the Atari STE, TT and Falcon. It is based on code page 437, the original character set of the IBM PC.
The GEM character set is the character set of Digital Research's graphical user interface GEM on Intel platforms. It is based on code page 437, the original character set of the IBM PC.
Ventura International is an 8-bit character encoding created by Ventura Software for use with Ventura Publisher. Ventura International is based on the GEM character set, but ¢ and ø are swapped and ¥ and Ø are swapped so that it is more similar to code page 437. There is also the PCL Ventura International, which is used for communication with PCL printers. PCL Ventura International is based on HP Roman-8. Both have the same character set, but a different encoding.

DEC Special Graphics is a 7-bit character set developed by Digital Equipment Corporation. This was used very often to draw boxes on the VT100 video terminal and the many emulators, and used by bulletin board software. The designation escape sequence ESC ( 0 switched the codes for lower-case ASCII letters to draw this set, and the sequence ESC ( B switched back. IBM calls it Code page 1090.
References
- ↑ "IBM i Globalization: Code pages". Archived from the original on 2012-07-16.
- ↑ "Code Page 01057" (PDF). Archived from the original (PDF) on 8 July 2015. Retrieved 31 January 2019.
- ↑ "Code Page 00437" (PDF). Archived (PDF) from the original on 8 July 2015. Retrieved 31 January 2019.