Charles-Édouard Jeanneret, known as Le Corbusier, was a Swiss-French architect, designer, painter, urban planner and writer, who was one of the pioneers of what is now regarded as modern architecture. He was born in Switzerland to French speaking Swiss parents, and acquired French nationality by naturalization on 19 September 1930. His career spanned five decades, in which he designed buildings in Europe, Japan, India, as well as North and South America. He considered that "the roots of modern architecture are to be found in Viollet-le-Duc".
A roof is the top covering of a building, including all materials and constructions necessary to support it on the walls of the building or on uprights, providing protection against rain, snow, sunlight, extremes of temperature, and wind. A roof is part of the building envelope.

Modern architecture, also called modernist architecture, was an architectural movement and style that was prominent in the 20th century, between the earlier Art Deco and later postmodern movements. Modern architecture was based upon new and innovative technologies of construction ; the principle functionalism ; an embrace of minimalism; and a rejection of ornament.

The Unité d'habitation is a modernist residential housing typology developed by Le Corbusier, with the collaboration of painter-architect Nadir Afonso. It formed the basis of several housing developments throughout Europe designed by Le Corbusier and sharing the same name.

In architecture, functionalism is the principle that buildings should be designed based solely on their purpose and function. An international functionalist architecture movement emerged in the wake of World War I, as part of the wave of Modernism. Its ideas were largely inspired by a desire to build a new and better world for the people, as broadly and strongly expressed by the social and political movements of Europe after the extremely devastating world war. In this respect, functionalist architecture is often linked with the ideas of socialism and modern humanism.
Albert Frey was a Swiss-born architect who established a style of modernist architecture centered on Palm Springs, California, United States, that came to be known as "desert modernism".

Notre-Dame du Haut is a Roman Catholic chapel in Ronchamp, France. Built in 1955, it is one of the finest examples of the architecture of Franco-Swiss architect Le Corbusier. The chapel is a working religious building and is under the guardianship of the private foundation Association de l’Œuvre de Notre-Dame du Haut. It attracts 80,000 visitors each year. In 2016, it was inscribed on the UNESCO World Heritage List in along with sixteen other works by Le Corbusier, because of its importance to the development of modernist architecture.

Archibald Quincy Jones was a Los Angeles–based architect and educator known for innovative buildings in the modernist style and for urban planning that pioneered the use of greenbelts and green design.

Ranch is a domestic architectural style that originated in the United States. The ranch-style house is noted for its long, close-to-the-ground profile, and wide open layout. The style fused modernist ideas and styles with notions of the American Western period of wide open spaces to create a very informal and casual living style. While the original ranch style was informal and basic in design, ranch-style houses built in the United States from around the early 1960s increasingly had more dramatic features such as varying roof lines, cathedral ceilings, sunken living rooms, and extensive landscaping and grounds.
Emerson Stewart Williams, FAIA was a prolific Palm Springs, California-based architect whose distinctive modernist buildings, in the Mid-century modern style, significantly shaped the Coachella Valley's architectural landscape and legacy.

Mid-century modern (MCM) is a movement in interior design, product design, graphic design, architecture and urban development that was present in all the world, but more popular in North America, Brazil and Europe from roughly 1945 to 1970 during the United States's post-World War II period.

Joseph Leopold Eichler was a 20th-century post-war American real estate developer known for developing distinctive residential subdivisions of mid-century modern style tract housing in California. He was one of the influential advocates of bringing modern architecture from custom residences and large corporate buildings to general public availability. His company and developments remain in the Greater San Francisco Bay Area and Greater Los Angeles.

Alexander Construction Company was a Palm Springs, California, residential development company that built over 2,200 houses in the Coachella Valley of Riverside County, California, between 1955 and 1965.
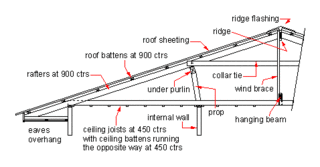
Domestic roof construction is the framing and roof covering which is found on most detached houses in cold and temperate climates. Such roofs are built with mostly timber, take a number of different shapes, and are covered with a variety of materials.
Paradise Palms is a Mid-Century Modern housing community in Las Vegas, Nevada located between downtown and the city's University District. It was designated as a historic overlay district in 2021, the first such recognition in Clark County. The planned community, Las Vegas' first, was the brain child of Irwin Molasky in 1960 who hired the architectural firm of Palmer & Krisel to build a community within walking distance to his Boulevard Mall and when completed drew entertainers, mobsters and other members of the city's social scene. A house originally owned by Fred Glusman subsequently featured stays by Cher, Don Rickles, Diana Ross and other Vegas entertainers. The original homes off Cayuga Parkway debuted in 1960 and were developed by Molasky and Adelson's Paradise Homes. In 1963, other builders were added to the community, including California-based Americana Homes, Tropical Estates by Vallee Development, Stellar Greens by D.L Bradley, Miranti Homes and Fontainebleau Estates by Eastern Enterprises.

A hip roof, hip-roof or hipped roof, is a type of roof where all sides slope downward to the walls, usually with a fairly gentle slope, with variants including tented roofs and others. Thus, a hipped roof has no gables or other vertical sides to the roof.
The Cité Frugès de Pessac(the Frugès Estate of Pessac), or Les Quartiers Modernes Frugès, is a housing development located in Pessac, a suburb of Bordeaux, France. It was commissioned by the industrialist Henri Frugès in 1924 as worker housing and designed by architects Le Corbusier and Pierre Jeanneret, who were responsible for the development's masterplan and individual buildings. It was intended as a testing ground for the ideas Le Corbusier had expressed in his 1922 manifesto Vers une Architecture and was his first attempt designing low-cost, mass-produced collective housing in his trademark aesthetic. Drawings of some of the buildings were subsequently included in the second edition of the text.

William Krisel was an American architect best known for his pioneering designs of mid-century residential and commercial architecture. Most of his designs are for affordable homes, especially tract housing, with a modern aesthetic.
Walter S. White (1917–2002) was an American modernist architect and industrial designer who worked in the Coachella Valley, CA in the 1950s and the Colorado Springs, CO area in the 1960s. White is noted for influencing innovative roofing and window systems in early Palm Desert, CA architecture.

Atherwood is a subdivision in Redwood City, California, that was built in 1950 by housing developer Joseph Eichler. It was one of Eichler's first developments working with an architect and his first major subdivision in San Mateo County. It consists of 64 original single family homes designed by architectural firm Anshen and Allen based on their AA-1 design. The Atherwood subdivision is accessed by Atherwood Avenue off of SR-84 and is located at the border of Atherton and Redwood City.