CXorf49 is a protein, which in humans is encoded by the gene chromosome X open reading frame 49(CXorf49).
Chromosome 16 open reading frame 95 (C16orf95) is a gene which in humans encodes the protein C16orf95. It has orthologs in mammals, and is expressed at a low level in many tissues. C16orf95 evolves quickly compared to other proteins.

PRR29 is a protein encoded by the PRR29 gene located in humans on chromosome 17 at 17q23.

Glutamate Rich Protein 2 is a protein in humans encoded by the gene ERICH2. This protein is expressed heavily in male tissues specifically in the testes, and proteins are specifically found in the nucleoli fibrillar center and the vesicles of these testicular cells. The protein has multiple protein interactions which indicate that it may play a role in histone modification and proper histone functioning.

Chromosome 8 open reading frame 58 is an uncharacterised protein that in humans is encoded by the C8orf58 gene. The protein is predicted to be localized in the nucleus.
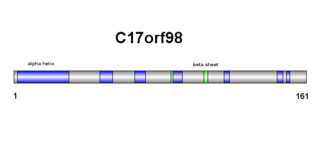
C17orf98 is a protein which in humans is coded by the gene c17orf98. The protein is derived from Homo sapiens chromosome 17. The C17orf98 gene consists of a 6,302 base sequence. Its mRNA has three exons and no alternative splice sites. The protein has 154 amino acids, with no abnormal amino acid levels. C17orf98 has a domain of unknown function (DUF4542) and is 17.6kDa in weight. C17orf98 does not belong to any other families nor does it have any isoforms. The protein has orthologs with high percent similarity in mammals and reptiles. The protein has additional distantly related orthologs across the metazoan kingdom, culminating with the sponge family.

Chromosome 16 open reading frame 46 is a protein of yet to be determined function in Homo sapiens. It is encoded by the C16orf46 gene with NCBI accession number of NM_001100873. It is a protein-coding gene with an overlapping locus.

Chromosome 19 open reading frame 44 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the C19orf44 gene. C19orf44 is an uncharacterized protein with an unknown function in humans. C19orf44 is non-limiting implying that the protein exists in other species besides human. The protein contains one domain of unknown function (DUF) that is highly conserved throughout its orthologs. This protein is most highly expressed in the testis and ovary, but also has significant expression in the thyroid and parathyroid. Other names for this protein include: LOC84167.

LOC101059915 is a protein, which in humans is encoded by the LOC101059915 gene. It is located on the X chromosome and has restricted expression in the testis.

Chromosome 4 open reading frame 51 (C4orf51) is a protein which in humans is encoded by the C4orf51 gene.

Cilia- and flagella-associated protein 299 (CFAP299), is a protein that in humans is encoded by the CFAP299 gene. CFAP299 is predicted to play a role in spermatogenesis and cell apoptosis.
Chromosome 1 open reading frame (C1orf167) is a protein which in humans is encoded by the C1orf167 gene. The NCBI accession number is NP_001010881. The protein is 1468 amino acids in length with a molecular weight of 162.42 kDa. The mRNA sequence was found to be 4689 base pairs in length.

Small integral membrane protein 11 is a protein which in humans is encoded by the SMIM11 gene.

C1orf122 is a gene in the human genome that encodes the cytosolic protein ALAESM.. ALAESM is present in all tissue cells and highly up-regulated in the brain, spinal cord, adrenal gland and kidney. This gene can be expressed up to 2.5 times the average gene in its highly expressed tissues. Although the function of C1orf122 is unknown, it is predicted to be used for mitochondria localization.

C12orf24 is a gene in humans that encodes a protein known as FAM216A. This gene is primarily expressed in the testis and brain, but has constitutive expression in 25 other tissues. FAM216A is an intracellular protein that has been predicted to reside within the nucleus of cells. The exact function of C12orf24 is unknown. FAM216A is highly expressed in Sertoli cells of the testis as well as different stage spermatids.
Chromosome 4 open reading frame 54 is a protein that in humans is coded by the c4orf54 gene. This gene is also known as FOPV and LOC285556. This protein is mostly expressed in the nucleus of muscle cells. Orthologs are found in vertebrates but not invertebrates.
Chromosome 4 open reading frame 50 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the C4orf50 gene. The protein localizes in the nucleus. C4orf50 has orthologs in vertebrates but not invertebrates

C13orf42 is a protein which, in humans, is encoded by the gene chromosome 13 open reading frame 42 (C13orf42). RNA sequencing data shows low expression of the C13orf42 gene in a variety of tissues. The C13orf42 protein is predicted to be localized in the mitochondria, nucleus, and cytosol. Tertiary structure predictions for C13orf42 indicate multiple alpha helices.

Chromosome 13 Open Reading Frame 46 is a protein which in humans is encoded by the C13orf46 gene. In humans, C13orf46 is ubiquitously expressed at low levels in tissues, including the lungs, stomach, prostate, spleen, and thymus. This gene encodes eight alternatively spliced mRNA transcript, which produce five different protein isoforms.

Chromosome 5 Open Reading Frame 47, or C5ORF47, is a protein which, in humans, is encoded by the C5ORF47 gene. It also goes by the alias LOC133491. The human C5ORF47 gene is primarily expressed in the testis.

















