
The bassoon is a woodwind instrument in the double reed family that plays music written in the bass and tenor clefs, and occasionally the treble. Appearing in its modern form in the 19th century, the bassoon figures prominently in orchestral, concert band, and chamber music literature. It is known for its distinctive tone colour, wide range, variety of character, and agility. The modern bassoon exists in two forms; Buffet and Heckel systems. One who plays a bassoon of either system is called a bassoonist.

A brass instrument is a musical instrument that produces sound by sympathetic vibration of air in a tubular resonator in sympathy with the vibration of the player's lips. Brass instruments are also called labrosones, literally meaning "lip-vibrated instruments".

The cello ( CHEL-oh; plural celli or cellos) or violoncello ( VY-ə-lən-CHEL-oh; Italian pronunciation: [vjolonˈtʃɛllo]) is a bowed (and occasionally plucked) string instrument of the violin family. Its four strings are usually tuned in perfect fifths: from low to high, C2, G2, D3 and A3. Each string is an octave lower than the viola's four strings. Music for the cello is generally written in the bass clef, with tenor clef and treble clef used for higher-range passages.

The double bass, also known simply as the bass, is the largest and lowest-pitched bowed string instrument in the modern symphony orchestra.

The French horn is a brass instrument made of tubing wrapped into a coil with a flared bell. The double horn in F/B♭ is the horn most often used by players in professional orchestras and bands. A musician who plays a horn is known as a horn player or hornist.

The guitar is a fretted musical instrument that usually has six strings. It is typically played with both hands by strumming or plucking the strings with either a guitar pick or the fingers/fingernails of one hand, while simultaneously fretting with the fingers of the other hand. The sound of the vibrating strings is projected either acoustically, by means of the hollow chamber of the guitar, or through an electrical amplifier and a speaker.
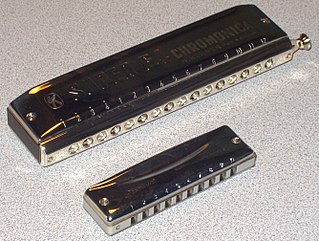
The harmonica, also known as a French harp or mouth organ, is a free reed wind instrument used worldwide in many musical genres, notably in blues, American folk music, classical music, jazz, country, and rock. The many types of harmonica include diatonic, chromatic, tremolo, octave, orchestral, and bass versions. A harmonica is played by using the mouth to direct air into or out of one holes along a mouthpiece. Behind each hole is a chamber containing at least one reed. A harmonica reed is a flat, elongated spring typically made of brass, stainless steel, or bronze, which is secured at one end over a slot that serves as an airway. When the free end is made to vibrate by the player's air, it alternately blocks and unblocks the airway to produce sound.

The violin, sometimes known as a fiddle, is a wooden string instrument in the violin family. Most violins have a hollow wooden body. It is the smallest and highest-pitched instrument (soprano) in the family in regular use. The violin typically has four strings, usually tuned in perfect fifths with notes G3, D4, A4, E5, and is most commonly played by drawing a bow across its strings. It can also be played by plucking the strings with the fingers (pizzicato) and, in specialized cases, by striking the strings with the wooden side of the bow.

String instruments, stringed instruments, or chordophones are musical instruments that produce sound from vibrating strings when the performer plays or sounds the strings in some manner.

The cornett, cornetto, or zink is an early wind instrument that dates from the Medieval, Renaissance and Baroque periods, popular from 1500 to 1650. It was used in what are now called alta capellas or wind ensembles. It is not to be confused with the trumpet-like cornet.

The vibraphone is a musical instrument in the struck idiophone subfamily of the percussion family. It consists of tuned metal bars and is usually played by holding two or four soft mallets and striking the bars. People who play the vibraphone are called vibraphonists or vibraharpists.

A mute is a device fitted to a musical instrument to alter the sound produced: by affecting the timbre, reducing the volume, or most commonly both. The use of a mute is usually indicated in musical notation by the Italian direction con sordino and removed with the direction senza sordino or via sordino. The spelling sordino is standard in musical notation, but in Italian, the proper spelling is sordina.

The morin khuur, also known as the horsehead fiddle, is a traditional Mongolian bowed stringed instrument. It is one of the most important musical instruments of the Mongol people, and is considered a symbol of the Mongolian nation. The morin khuur is one of the Masterpieces of the Oral and Intangible Heritage of Humanity identified by UNESCO.

Gamelan gong kebyar is a style or genre of Balinese gamelan music of Indonesia. Kebyar means "to flare up or burst open", and refers to the explosive changes in tempo and dynamics characteristic of the style. It is the most popular form of gamelan in Bali, and its best known musical export.

The kaval is a chromatic end-blown flute traditionally played throughout the Balkans and Anatolia. The kaval is primarily associated with mountain shepherds.

The davul, tapan, atabal or tabl is a large double-headed drum that is played with mallets. It has many names depending on the country and region. These drums are commonly used in the music of Middle East. These drums have both a deep bass sound and a thin treble sound due to their construction and playing style, where different heads and sticks are used to produce different sounds on the same drum.

A flamenco guitar is a guitar similar to a classical guitar but with thinner tops and less internal bracing. It usually has nylon strings, as opposed to steel. Usually, it has a livelier sound compared to the classical guitar. It is used in toque, the guitar-playing part of the art of flamenco.

A horn is any of a family of musical instruments made of a tube, usually made of metal and often curved in various ways, with one narrow end into which the musician blows, and a wide end from which sound emerges. In horns, unlike some other brass instruments such as the trumpet, the bore gradually increases in width through most of its length—that is to say, it is conical rather than cylindrical. In jazz and popular-music contexts, the word may be used loosely to refer to any wind instrument, and a section of brass or woodwind instruments, or a mixture of the two, is called a horn section in these contexts.

Mechanical music technology is the use of any device, mechanism, machine or tool by a musician or composer to make or perform music; to compose, notate, play back or record songs or pieces; or to analyze or edit music. The earliest known applications of technology to music was prehistoric peoples' use of a tool to hand-drill holes in bones to make simple flutes. Ancient Egyptians developed stringed instruments, such as harps, lyres and lutes, which required making thin strings and some type of peg system for adjusting the pitch of the strings. Ancient Egyptians also used wind instruments such as double clarinets and percussion instruments such as cymbals. In Ancient Greece, instruments included the double-reed aulos and the lyre. Numerous instruments are referred to in the Bible, including the horn, pipe, lyre, harp, and bagpipe. During Biblical times, the cornet, flute, horn, organ, pipe, and trumpet were also used. During the Middle Ages, hand-written music notation was developed to write down the notes of religious Plainchant melodies; this notation enabled the Catholic church to disseminate the same chant melodies across its entire empire.

The midwinter horn, in Dutch midwinterhoorn and in various dialects of German Middewinterhorn, Mittewinterhorn, Mirrewinterhorn, Midwinterhorn and Mittwinterhorn, also known as the dewertshorn and adventshorn, is a wooden natural trumpet traditionally blown at the Christmas season in areas of the Netherlands and nearby parts of North Germany.





















