
The bassoon is a musical instrument in the woodwind family, which plays in the tenor and bass ranges. It is composed of six pieces, and is usually made of wood. It is known for its distinctive tone color, wide range, versatility, and virtuosity. It is a non-transposing instrument and typically its music is written in the bass and tenor clefs, and sometimes in the treble. There are two forms of modern bassoon: the Buffet and Heckel systems. It is typically played while sitting using a seat strap, but can be played while standing if the player has a harness to hold the instrument. Sound is produced by rolling both lips over the reed and blowing direct air pressure to cause the reed to vibrate. Its fingering system can be quite complex when compared to those of other instruments. Appearing in its modern form in the 19th century, the bassoon figures prominently in orchestral, concert band, and chamber music literature, and is occasionally heard in pop, rock, and jazz settings as well. One who plays a bassoon is called a bassoonist.

A percussion instrument is a musical instrument that is sounded by being struck or scraped by a beater including attached or enclosed beaters or rattles struck, scraped or rubbed by hand or struck against another similar instrument. Excluding zoomusicological instruments and the human voice, the percussion family is believed to include the oldest musical instruments. In spite of being a very common term to designate instruments, and to relate them to their players, the percussionists, percussion is not a systematic classificatory category of instruments, as described by the scientific field of organology. It is shown below that percussion instruments may belong to the organological classes of idiophone, membranophone, aerophone and chordophone.

The trumpet is a brass instrument commonly used in classical and jazz ensembles. The trumpet group ranges from the piccolo trumpet—with the highest register in the brass family—to the bass trumpet, pitched one octave below the standard B♭ or C trumpet.
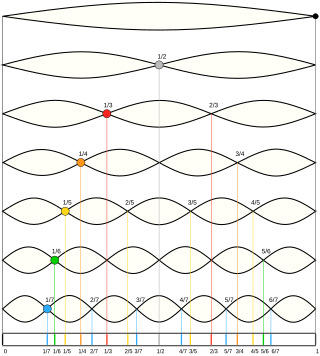
In physics, acoustics, and telecommunications, a harmonic is a sinusoidal wave with a frequency that is a positive integer multiple of the fundamental frequency of a periodic signal. The fundamental frequency is also called the 1st harmonic; the other harmonics are known as higher harmonics. As all harmonics are periodic at the fundamental frequency, the sum of harmonics is also periodic at that frequency. The set of harmonics forms a harmonic series.

An overtone is any resonant frequency above the fundamental frequency of a sound. In other words, overtones are all pitches higher than the lowest pitch within an individual sound; the fundamental is the lowest pitch. While the fundamental is usually heard most prominently, overtones are actually present in any pitch except a true sine wave. The relative volume or amplitude of various overtone partials is one of the key identifying features of timbre, or the individual characteristic of a sound.

A carillon ( KARR-ə-lon, kə-RIL-yən) is a pitched percussion instrument that is played with a keyboard and consists of at least 23 bells. The bells are cast in bronze, hung in fixed suspension, and tuned in chromatic order so that they can be sounded harmoniously together. They are struck with clappers connected to a keyboard of wooden batons played with the hands and pedals played with the feet. Often housed in bell towers, carillons are usually owned by churches, universities, or municipalities. They can include an automatic system through which the time is announced and simple tunes are played throughout the day.

The triangle is a musical instrument in the percussion family, classified as an idiophone in the Hornbostel-Sachs classification system. Triangles are made from a variety of metals including aluminum, beryllium copper, brass, bronze, iron, and steel. The metal is bent into a triangular shape with one open end. The instrument is usually held by a loop of some form of thread or wire at the top curve, to enable the triangle to vibrate and it is struck with a metal rod called a "beater". The triangle theoretically has indefinite pitch, and produces a plurality of overtones when struck with an appropriate beater.

Conducting is the art of directing a musical performance, such as an orchestral or choral concert. It has been defined as "the art of directing the simultaneous performance of several players or singers by the use of gesture." The primary duties of the conductor are to interpret the score in a way that reflects the specific indications in that score, set the tempo, ensure correct entries by ensemble members, and "shape" the phrasing where appropriate. Conductors communicate with their musicians primarily through hand gestures, usually with the aid of a baton, and may use other gestures or signals such as facial expression and eye contact. A conductor usually supplements their direction with verbal instructions to their musicians in rehearsal.

Campanology is the scientific and musical study of bells. It encompasses the technology of bells – how they are founded, tuned and rung – as well as the history, methods, and traditions of bellringing as an art.

The cowbell is an idiophone hand percussion instrument used in various styles of music, such as Latin and rock. It is named after the similar bell used by herdsmen to keep track of the whereabouts of cows. The instrument initially and traditionally has been metallic; however, contemporarily, some variants are made of synthetic materials.

A bell is a directly struck idiophone percussion instrument. Most bells have the shape of a hollow cup that when struck vibrates in a single strong strike tone, with its sides forming an efficient resonator. The strike may be made by an internal "clapper" or "uvula", an external hammer, or—in small bells—by a small loose sphere enclosed within the body of the bell.
A handbell is a bell designed to be rung by hand. To ring a handbell, a ringer grasps the bell by its slightly flexible handle – traditionally made of leather, but often now made of plastic – and moves the arm to make the hinged clapper strike the inside of the bell. An individual handbell can be used simply as a signal to catch people's attention or summon them together, but handbells are also often heard in tuned sets.

Marching percussion instruments are percussion instruments specially designed to be played while moving. This is achieved by attaching the drum(s) to a special harness worn by the drummer, although not all marching bands use such harnesses and instead use traditional baldrics to sling their drums.

An experimental musical instrument is a musical instrument that modifies or extends an existing instrument or class of instruments, or defines or creates a new class of instrument. Some are created through simple modifications, such as cracked cymbals or metal objects inserted between piano strings in a prepared piano. Some experimental instruments are created from household items like a homemade mute for brass instruments such as bathtub plugs. Other experimental instruments are created from electronic spare parts, or by mixing acoustic instruments with electric components.

The 3rd bridge is an extended playing technique used on the electric guitar and other string instruments that allows a musician to produce distinctive timbres and overtones that are unavailable on a conventional string instrument with two bridges. The timbre created with this technique is close to that of gamelan instruments like the bonang and similar Indonesian types of pitched gongs.
A third bridge can be devised by inserting a rigid preparation object between the strings and the body or neck of the instrument, effectively dividing the string into distinct vibrating segments.

A tabla is a pair of hand drums from the Indian subcontinent. Since the 18th century, it has been the principal percussion instrument in Hindustani classical music, where it may be played solo, as an accompaniment with other instruments and vocals, or as a part of larger ensembles. It is frequently played in popular and folk music performances in India, Bangladesh, Afghanistan, Pakistan, Nepal and Sri Lanka. The tabla is an essential instrument in the bhakti devotional traditions of Hinduism and Sikhism, such as during bhajan and kirtan singing. It is one of the main qawwali instruments used by Sufi musicians. The instrument is also featured in dance performances such as Kathak. Tabla is a rhythmic instrument.

A chime bar or resonator bell is a percussion instrument consisting of a tuned metal bar similar to a glockenspiel bar, with each bar mounted on its own wooden resonator. Chime bars are played with mallets again similar to a glockenspiel.

An unpitched percussion instrument is a percussion instrument played in such a way as to produce sounds of indeterminate pitch, or an instrument normally played in this fashion.

A tifa totobuang is a music ensemble from the Maluku Islands, related to the kulintang orchestra. It consists of a set of a double row of gong chimes known as the totobuang and a set of tifa drums. It can also include a large gong.


















