
The Endangered Species Act of 1973 is the primary law in the United States for protecting imperiled species. Designed to protect critically imperiled species from extinction as a "consequence of economic growth and development untempered by adequate concern and conservation", the ESA was signed into law by President Richard Nixon on December 28, 1973. The Supreme Court of the United States described it as "the most comprehensive legislation for the preservation of endangered species enacted by any nation". The purposes of the ESA are two-fold: to prevent extinction and to recover species to the point where the law's protections are not needed. It therefore "protect[s] species and the ecosystems upon which they depend" through different mechanisms. For example, section 4 requires the agencies overseeing the Act to designate imperiled species as threatened or endangered. Section 9 prohibits unlawful ‘take,’ of such species, which means to "harass, harm, hunt..." Section 7 directs federal agencies to use their authorities to help conserve listed species. The Act also serves as the enacting legislation to carry out the provisions outlined in The Convention on International Trade in Endangered Species of Wild Fauna and Flora (CITES). The Supreme Court found that "the plain intent of Congress in enacting" the ESA "was to halt and reverse the trend toward species extinction, whatever the cost." The Act is administered by two federal agencies, the United States Fish and Wildlife Service (FWS) and the National Marine Fisheries Service (NMFS). FWS and NMFS have been delegated by the Act with the authority to promulgate any rules and guidelines within the Code of Federal Regulations (CFR) to implement its provisions.

The conservation status of a group of organisms indicates whether the group still exists and how likely the group is to become extinct in the near future. Many factors are taken into account when assessing conservation status: not simply the number of individuals remaining, but the overall increase or decrease in the population over time, breeding success rates, and known threats. Various systems of conservation status exist and are in use at international, multi-country, national and local levels as well as for consumer use.

The black toad, also known as the Inyo toad or Deep Springs toad, is a true toad that lives only in scattered oases in the Deep Springs Valley of Inyo County, California. In fact, its original scientific name, Bufo exsul, means "exiled toad," which refers to its species' isolation in a tiny spot in the high desert wilderness of the Californian Great Basin.

The California red-legged frog is a species of frog found in California (USA) and northern Baja California (Mexico). It was formerly considered a subspecies of the northern red-legged frog. The frog is an IUCN near-threatened species as of 2021, has a NatureServe conservation status of imperiled as of 2015, and is a federally listed threatened species of the United States that is protected by law.

The National Wildlife Refuge System in the United States has a long and distinguished history.

The California Department of Fish and Wildlife (CDFW), formerly known as the California Department of Fish and Game (CDFG), is a state agency under the California Natural Resources Agency. The Department of Fish and Wildlife manages and protects the state's wildlife, wildflowers, trees, mushrooms, algae (kelp) and native habitats (ecosystems). The department is responsible for regulatory enforcement and management of related recreational, commercial, scientific, and educational uses. The department also prevents illegal poaching.

A species of special concern is a protective legal designation assigned by the California Department of Fish and Wildlife (CDFW) to wildlife species that are at risk.
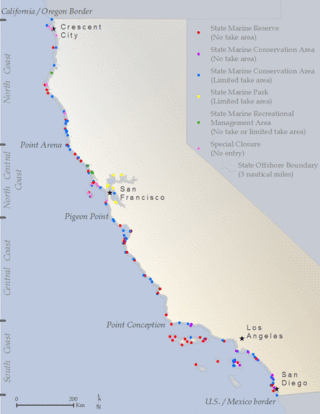
The Marine Life Protection Act (MLPA) was passed in 1999 and is part of the California Fish and Game Code. The MLPA requires California to reevaluate all existing marine protected areas (MPAs) and potentially design new MPAs that together form a statewide network. The MLPA has clear guidance associated with the development of this MPA network. MPAs are developed on a regional basis with MLPA and MPA-specific goals in mind and are evaluated over time to assess their effectiveness in meeting these goals. The five main goals of the Marine Life Protection Act are to maintain the diversity of marine ecosystems, conserve its populations, better educate people on human-marine life interactions, protect habitats, and effectively enforce MPAs. The establishment of this policy is an important step in expanding science-based management and decision making regarding policies.

The Loch Lomond Vernal Pool Ecological Reserve is a nature reserve of 8.22 acres (33,300 m2) in the community of Loch Lomond in Lake County, California. It is one of 119 ecological reserves managed by the California Department of Fish and Game (CDFG). The ecological reserve system was authorized by the state legislature in 1968 for the purpose of conservation and protection of rare plants, animals and habitats.

An endangered species is a species that is very likely to become extinct in the near future, either worldwide or in a particular political jurisdiction. Endangered species may be at risk due to factors such as habitat loss, poaching and invasive species. The International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN) Red List lists the global conservation status of many species, and various other agencies assess the status of species within particular areas. Many nations have laws that protect conservation-reliant species which, for example, forbid hunting, restrict land development, or create protected areas. Some endangered species are the target of extensive conservation efforts such as captive breeding and habitat restoration.

Manatees are large marine mammals that inhabit slow rivers, canals, saltwater bays, estuaries, and coastal areas. They are a migratory species, inhabiting the Florida waters during the winter and moving as far north as Virginia and into the Chesapeake Bay, sometimes seen as far north as Baltimore, Maryland and as far west as Texas in the warmer summer months. Manatees are calm herbivores that spend most of their time eating, sleeping, and traveling. They have a lifespan of about 60 years with no known natural enemies. Some of their deaths are the result of human activity. In the past, manatees were exploited for their meat, fat, and hides.

The Endangered Species Conservation Act of 1969 was an expansion of the Endangered Species Preservation Act of 1966 which authorized the United States Secretary of the Interior to develop a comprehensive list of species or subspecies of animals threatened with worldwide extinction. It also prohibited the importation from any foreign country any animal-whole or in part, any product, or any egg belonging to a species on that list. Limited exceptions for scientific, educational, zoological, or propagational purposes and for certain cases of commercial "economic hardship" were allowed under strict permitting procedures.

Wildlife smuggling or trafficking involves the illegal gathering, transportation, and distribution of animals and their derivatives. This can be done either internationally or domestically. "Wildlife smuggling is estimated at $7.8bn to $10bn a year, according to the U.S. State Department. The U.S. State Department also lists wildlife trafficking as the third most valuable illicit commerce in the world." The illegal nature of such activities makes determining the amount of money involved incredibly difficult. When considered with illegal timber and fisheries, wildlife trafficking is a major illegal trade along with narcotics, human trafficking, and counterfeit products.

The northern Rocky Mountain wolf, also known as the northern Rocky Mountain timber wolf, is a subspecies of gray wolf native to the northern Rocky Mountains. It is a light-colored, medium to large-sized subspecies with a narrow, flattened frontal bone. The subspecies was initially listed as Endangered on March 9, 1978, but had the classification removed in the year 2000 due to the effects of the Northern Rocky Mountain Wolf Recovery Plan. On August 6, 2010, the northern Rocky Mountain wolf was ordered to be returned under Endangered Species Act protections by U.S. District Judge Donald Molloy in a decision overturning a previous ruling by the U.S. Fish and Wildlife Service. They were later removed on August 31, 2012 from the list because of Idaho, Montana, and Wyoming meeting the population quotas for the species to be considered stable. This wolf is recognized as a subspecies of Canis lupus in the taxonomic authority Mammal Species of the World (2005).

An exotic pet is a pet which is relatively rare or unusual to keep, or is generally thought of as a wild species rather than as a domesticated pet. The definition varies by culture, location, and over time—as animals become firmly enough established in the world of animal fancy, they may no longer be considered exotic.

Sierra Club v. Babbitt, 15 F. Supp. 2d 1274, is a United States District Court for the Southern District of Alabama case in which the Sierra Club and several other environmental organizations and private citizens challenged the United States Fish and Wildlife Service (FWS). Plaintiffs filed action seeking declaratory injunctive relief regarding two incidental take permits (ITPs) issued by the FWS for the construction of two isolated high-density housing complexes in habitat of the endangered Alabama beach mouse. The District Court ruled that the FWS must reconsider its decision to allow high-density development on the Alabama coastline that might harm the endangered Alabama beach mouse. The District Court found that the FWS violated both the Endangered Species Act (ESA) and the National Environmental Policy Act (NEPA) by permitting construction on the dwindling beach mouse habitat.
In 1970 California became one of the first states in the U.S. to implement an act that conserves and protects endangered species and their environments. The California Endangered Species Act (CESA) declares that "all native species of fishes, amphibians, reptiles, birds, mammals, and plants, and their habitats, threatened with extinction and those experiencing a significant decline which, if not halted, would lead to a threatened or endangered designation, will be protected or preserved."

Hollenbeck Canyon Wildlife Area is located near Jamul and Dulzura in California. The former cattle ranch was designated a wildlife area in 2001, and forms a wildlife corridor between Otay Mountain Wilderness and Jamul Mountains under the protection of the California Department of Fish and Wildlife. The approximately 6,100-acre area is open to the public for activities including hunting, equestrian use, hiking, mountain-biking, and (hunting) dog training.

The Santa Clara Valley Habitat Conservation Plan (SCVHCP), also known as the Santa Clara Valley Habitat Plan, is an initiative issued in 2012 by the County of Santa Clara, the City of San José, the City of Morgan Hill, the City of Gilroy, the Santa Clara Valley Water District (SCVWD), and the Santa Clara Valley Transportation Authority (VTA). These governmental agencies are collectively called the "Local Partners" in regards to the Santa Clara Valley Habitat Conservation Plan. The plan's goal is to protect and encourage the growth of endangered species in Santa Clara County. It is a 50-year plan, costing an estimated $660 million as of 2012.
















