
Tantulocarida is a highly specialised group of parasitic crustaceans that consists of about 33 species, treated as a class in superclass Multicrustacea. They are typically ectoparasites that infest copepods, isopods, tanaids, amphipods and ostracods.

Siphonostomatoida is an order of copepods, containing around 75% of all the copepods that parasitise fishes. Their success has been linked to their possession of siphon-like mandibles and of a "frontal filament" to aid attachment to their hosts. Most are marine, but a few live in fresh water. There are 40 recognised families:

The Cyclopoida are an order of small crustaceans from the subclass Copepoda. Like many other copepods, members of Cyclopoida are small, planktonic animals living both in the sea and in freshwater habitats. They are capable of rapid movement. Their larval development is metamorphic, and the embryos are carried in paired or single sacs attached to first abdominal somite.

Calanidae is the largest taxonomic family of calanoid copepods. It includes the genus Calanus, which may be the most abundant metazoan genus on Earth.

Calanus is a genus of marine copepod in the family Calanidae. The genus was split in 1974, with some species being placed in a new genus, Neocalanus. The following species are recognised:
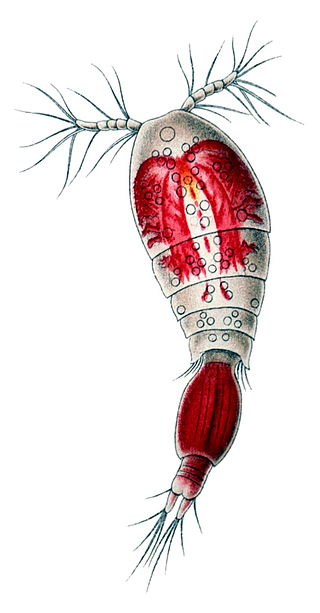
Oncaea is a genus of copepods. The genus contains bioluminescent species. Unlike other bioluminescent copepods, Oncaea have an internal (non-secreted) bioluminescence. Oncaea contains the following species:

Sapphirina, whose members are commonly known as sea sapphires, is a genus of parasitic copepods in the family Sapphirinidae.

Acartia is a genus of marine calanoid copepods. They are epipelagic, estuarine, zooplanktonic found throughout the oceans of the world, primarily in temperate regions.

Calocalanus is a genus of copepods, the only genus in the family Calocalanidae:
Centropagidae is a family of copepods. Its members are particularly known as plankton in coastal waters and in fresh water in Australia and southern South America. They are also found on subantarctic islands and in lakes in Antarctica.
Pontellidae is a family of copepods in the order Calanoida, containing the following genera:

Pontella is a marine copepod genus in the family Pontellidae. It is an organism that bears three lenses in the eye. The outer has a parabolic surface, countering the effects of spherical aberration while allowing a sharp image to be formed.

Copilia is a genus of copepods in the family Sapphirinidae. The eyes in members of this genus have two lenses, arranged like those in a telescope.

Misophrioida is an order of copepods, containing the following families:
Augaptilidae is a family of copepods.
Centropages is a genus of copepods in the family Centropagidae with 34 known marine species.
Neocalanus is a genus of marine copepods. They are a dominant component of the open water ecosystems of the northern Pacific Ocean. Neocalanus are large copepods, reaching body lengths of more than 8 mm (0.31 in) in Neocalanus plumchrus.

The clade Multicrustacea constitutes the largest superclass of crustaceans, containing approximately four-fifths of all described crustacean species, including crabs, lobsters, crayfish, shrimp, krill, prawns, woodlice, barnacles, copepods, amphipods, mantis shrimp and others. The largest branch of multicrustacea is the class Malacostraca.

Temora is a genus of copepods in the family Temoridae. The World Register of Marine Species lists the following species:
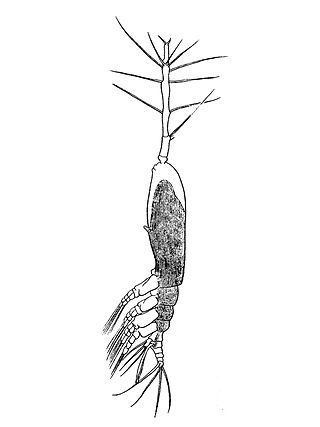
Monstrilla is a genus of copepods in the family Monstrillidae.















