
Copepods are a group of small crustaceans found in nearly every freshwater and saltwater habitat. Some species are planktonic, some are benthic, a number of species have parasitic phases, and some continental species may live in limnoterrestrial habitats and other wet terrestrial places, such as swamps, under leaf fall in wet forests, bogs, springs, ephemeral ponds, puddles, damp moss, or water-filled recesses of plants (phytotelmata) such as bromeliads and pitcher plants. Many live underground in marine and freshwater caves, sinkholes, or stream beds. Copepods are sometimes used as biodiversity indicators.

Tantulocarida is a highly specialised group of parasitic crustaceans that consists of about 33 species, treated as a class in superclass Multicrustacea. They are typically ectoparasites that infest copepods, isopods, tanaids, amphipods and ostracods.

The Cyclopoida are an order of small crustaceans from the subclass Copepoda. Like many other copepods, members of Cyclopoida are small, planktonic animals living both in the sea and in freshwater habitats. They are capable of rapid movement. Their larval development is metamorphic, and the embryos are carried in paired or single sacs attached to first abdominal somite.

Calanus is a genus of marine copepod in the family Calanidae. The genus was split in 1974, with some species being placed in a new genus, Neocalanus. The following species are recognised:

Ectinosomatidae is a family of the Harpacticoida, a huge group of crustaceans belonging to the subclass Copepoda. Like most of their relatives, they are usually benthic inhabitants of marine environments. Ectinosomatidae commonly inhabit sediment and fragments of dead corals or glass sponges, and occasionally algae and bryozoans, in the deep oceans. In the epifaunal species, the first leg pair is often modified to allow the animals a better grip on the substrate.

Acartiidae is a family of calanoid copepods distinguishable by the rostral margin not being extended. They are epipelagic, planktonic animals, not being found below a depth of 500 metres (1,600 ft). There are over 100 described species distributed throughout the world's oceans, mainly in temperate areas.
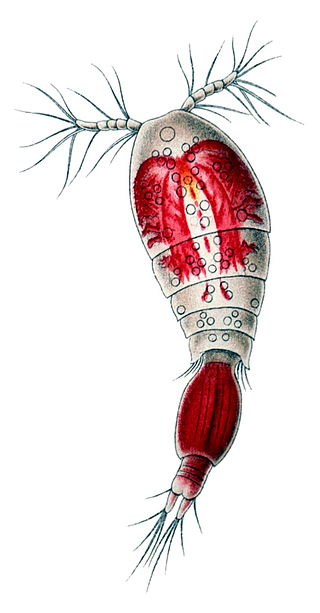
Oncaeidae is a family of copepods, containing the following genera:

Acartia is a genus of marine calanoid copepods. They are epipelagic, estuarine, zooplanktonic found throughout the oceans of the world, primarily in temperate regions.

Calocalanus is a genus of copepods, the only genus in the family Calocalanidae:

Cyclops bicuspidatus is a planktonic species of copepod found throughout the world, except Australia, and characteristic of the Great Lakes of North America. It is a deep water species found throughout the year with peak abundance occurring in May or June. Males grow up to 0.8–1.0 millimetre (0.031–0.039 in) long, while females are larger at 0.9–1.6 mm (0.035–0.063 in).
Centropagidae is a family of copepods in the order Calanoida. Its members are particularly known as plankton in coastal waters and in fresh water in Australia and southern South America. They are also found on subantarctic islands and in lakes in Antarctica.
Phaennidae is a family of planktonic copepods, found in pelagic or benthopelagic waters. It contains the following genera:

Pontella is a marine copepod genus in the family Pontellidae. It is an organism that bears three lenses in the eye. The outer has a parabolic surface, countering the effects of spherical aberration while allowing a sharp image to be formed.

Copilia is a genus of copepods in the family Sapphirinidae. The eyes in members of this genus have two lenses, arranged like those in a telescope.

Temoridae is a family of copepods, containing the following genera:
Augaptilidae is a family of copepods.
Centropages is a genus of copepods in the family Centropagidae with 34 known marine species.
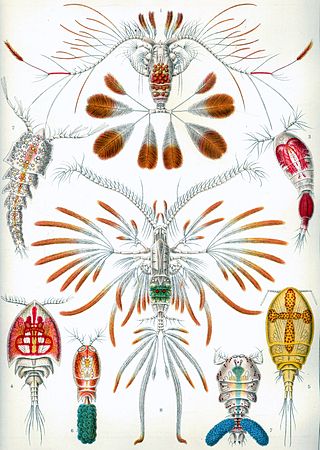
Artotrogidae is a family of copepods in the order Siphonostomatoida.
Neocalanus is a genus of marine copepods. They are a dominant component of the open water ecosystems of the northern Pacific Ocean. Neocalanus are large copepods, reaching body lengths of more than 8 mm (0.31 in) in Neocalanus plumchrus.

Euchaetidae is a family of marine copepods. The family is cosmopolitan and occurs in all the oceans, including the Southern and Arctic Oceans. Euchaetidae are medium to large-sized copepods.














