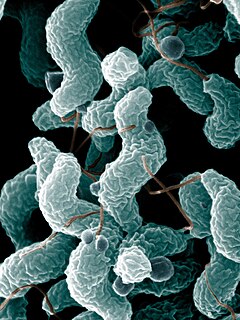
Campylobacter is a genus of Gram-negative bacteria. Campylobacter typically appear comma- or s-shaped, and are motile. Some Campylobacter species can infect humans, sometimes causing campylobacteriosis, a diarrhoeal disease in humans. Campylobacteriosis is usually self-limiting and antimicrobial treatment is often not required, except in severe cases or immunocompromised patients. The most known source for Campylobacter is poultry, but due to their diverse natural reservoir, Campylobacter spp. can also be transmitted via water. Other known sources of Campylobacter infections include food products, such as unpasteurised milk and contaminated fresh produce. Sometimes the source of infection can be direct contact with infected animals, which often carry Campylobacter asymptomatically. At least a dozen species of Campylobacter have been implicated in human disease, with C. jejuni (80–90%) and C. coli (5-10%) being the most common. C. jejuni is recognized as one of the main causes of bacterial foodborne disease in many developed countries. It is the number one cause of bacterial gastroentritis in Europe, with over 246,000 cases confirmed annually. C. jejuni infection can also cause bacteremia in immunocompromised individuals, while C. lari is a known cause of recurrent diarrhea in children. C. fetus can cause spontaneous abortions in cattle and sheep, and is an opportunistic pathogen in humans.

Staphylococcus haemolyticus is a member of the coagulase-negative staphylococci (CoNS). It is part of the skin flora of humans, and its largest populations are usually found at the axillae, perineum, and inguinal areas. S. haemolyticus also colonizes primates and domestic animals. It is a well-known opportunistic pathogen, and is the second-most frequently isolated CoNS. Infections can be localized or systemic, and are often associated with the insertion of medical devices. The highly antibiotic-resistant phenotype and ability to form biofilms make S. haemolyticus a difficult pathogen to treat. Its most closely-related species if Staphylococcus borealis.

Burkholderia pseudomallei is a Gram-negative, bipolar, aerobic, motile rod-shaped bacterium. It is a soil-dwelling bacterium endemic in tropical and subtropical regions worldwide, particularly in Thailand and northern Australia. Recently, there has been an expansion of the affected regions due to significant natural disasters and it can now be found in Southern China, Hong Kong, and countries in America. Although it is mainly a soil-dwelling bacteria, a study performed by Apinya Pumpuang and others showed that Burkholderia pseudomallei survived in distilled water for 16 years, demonstrating that it is capable of living in water if a specific environment is provided. It is resistant to variety of harsh conditions including nutrient deficiency, extreme temperature or PH scale. It infects humans and other animals most commonly livestock such as goats, pigs, and sheep. It happens less frequently in other animals, but is possible for them to get infected and causes the disease melioidosis. It is also capable of infecting plants in a labatory setting.

Etest is a way of determining antimicrobial sensitivity by placing a strip impregnated with antimicrobials onto an agar plate. A strain of bacterium or fungus will not grow near a concentration of antibiotic or antifungal if it is sensitive. For some microbial and antimicrobial combinations, the results can be used to determine a minimum inhibitory concentration (MIC). Etest is a proprietary system manufactured by bioMérieux. It is a laboratory test used in healthcare settings to help guide physicians by indicating what concentration of antimicrobial could successfully be used to treat patients' infections.
Campylobacter upsaliensis is a gram negative bacteria in the Campylobacter genus. C. upsaliensis is found worldwide, and is a common cause of campylobacteriosis in humans, as well as gastroenteritis in dogs. Human infections are primarily associated with raw or undercooked meat and contaminated water sources, however there is some zoonotic risk associated with the spread from dogs. C. upsaliensis primarily affects the gastrointestinal tract as it damages gastrointestinal epithelial cells. There are many methods for detecting C.upsaliensis including PCR and ELISA, however there is no current gold standard in detection techniques. Infection is typically self limiting, however there is antimicrobial therapy available.
mecA is a gene found in bacterial cells which allows them to be resistant to antibiotics such as methicillin, penicillin and other penicillin-like antibiotics.
Clostridium innocuum is an anaerobic, non-motile, gram-positive bacterium that reproduces by sporulation. While there are over 130 species of Clostridium, C. innocuum is the third most commonly isolated. Although it is not normally considered an aggressive human pathogen, it has been isolated in some disease processes. C. innocuum and other Clostridium line the oropharynx and gastrointestinal tract, and are considered normal gut flora.

Staphylococcus hyicus is a Gram-positive, facultatively anaerobic bacterium in the genus Staphylococcus. It consists of clustered cocci and forms white circular colonies when grown on blood agar. S. hyicus is a known animal pathogen. It causes disease in poultry, cattle, horses, and pigs. Most notably, it is the agent that causes porcine exudative epidermitis, also known as greasy pig disease, in piglets. S. hyicus is generally considered to not be zoonotic, however it has been shown to be able to cause bacteremia and sepsis in humans.
Staphylococcus intermedius is a Gram-positive, catalase positive member of the bacterial genus Staphylococcus consisting of clustered cocci. Strains of this species were originally isolated from the anterior nares of pigeons, dogs, cats, mink, and horses. Many of the isolated strains show coagulase activity. Clinical tests for detection of methicillin-resistant S. aureus may produce false positives by detecting S. intermedius, as this species shares some phenotypic traits with methicillin-resistant S. aureus strains. It has been theorized that S. intermedius has previously been misidentified as S. aureus in human dog bite wound infections, which is why molecular technologies such as MALDI-TOF and PCR are preferred in modern veterinary clinical microbiology laboratories for their more accurate identifications over biochemical tests. S. intermedius is largely phenotypically indiscriminate from Staphylococcus pseudintermedius and Staphylococcus delphini, and therefore the three organisms are considered to be included in the more general 'Staphylococcus intermedius group'.
Escherichia fergusonii is a Gram-negative, rod-shaped species of bacterium. Closely related to the well-known species Escherichia coli, E. fergusonii was first isolated from samples of human blood. The species is named for American microbiologist William W. Ferguson.
Campylobacter concisus is a Gram-negative, highly fastidious, mesophilic bacterium that grows under both anaerobic and microaerobic conditions with the presence of hydrogen significantly aiding growth. Motile, with either unipolar or bipolar flagella, the organisms have a characteristic spiral/corkscrew appearance and are oxidase-positive. Although the human oral cavity is the natural colonization site of the bacterium, C. concisus may also colonize the intestinal tract of some individuals. In particular, several studies have reported higher intestinal prevalence of C. concisus in patients with IBD compared to healthy controls, which has led to current speculation of the bacterium's implication in the induction of Crohn's disease.
Campylobacter mucosalis was initially isolated in 1974 by Lawson and Rowland from the lesions of porcine intestinal adenomatosis. Isolated species were gram-negative, microaerophilic and curve shaped. These organisms resembled Campylobacter sputorum in their morphological and phenotypic characteristics and were given the name Campylobacter sputorum subsp. mucosalis. A study, using DNA homology experiments, found that Campylobacter sputorum subsp. mucosalis is a distinct species and is not a subspecies of C. sputorum. Thus, its name was changed to Campylobacter mucosalis.
Campylobacter lari is a species of nalidixic acid-resistant, thermophilic, microaerophilic bacteria first isolated from human faeces. It shows anaerobic growth in the presence of trimethylamine N-oxide hydrochloride. Its type strain is NCTC 11352. It is commonly found in sea gulls. In humans, it has been involved in cases of enteritis, severe abdominal pain and terminal bacteremia.
Yersinia intermedia is a Gram-negative species of bacteria which uses rhamnose, melibiose, and raffinose. Its type strain is strain 3953. It has been found in fish, and contains several biotypes. It is not considered of clinical relevance, being isolated from humans in a routine manner.

Achromobacter xylosoxidans is a Gram-negative, aerobic, oxidase and catalase-positive, motile bacterium with peritrichous flagella, from the genus Achromobacter. It is generally found in wet environments. Achromobacter xylosoxidans can cause infections such as bacteremia, especially in patients with cystic fibrosis. In 2013, the complete genome of an A. xylosoxidans strain from a patient with cystic fibrosis was sequenced.
Campylobacter lanienae is a species of Campylobacter found in humans and other animals. Like other Campylobacter species, it is rod-shaped, non-glucose-fermenting, oxidase- and catalase-positive, Gram-negative and motile.
Staphylococcus schleiferi is a Gram-positive, cocci-shaped bacterium of the family Staphylococcaceae. It is facultatively anaerobic, coagulase-variable, and can be readily cultured on blood agar where the bacterium tends to form opaque, non-pigmented colonies and beta (β) hemolysis. There exists two subspecies under the species S. schleiferi: Staphylococcus schleiferi subsp. schleiferi and Staphylococcus schleiferi subsp. coagulans.
Staphylococcus pseudintermedius is a gram positive coccus bacteria of the genus Staphylococcus found worldwide. It is primarily a pathogen for domestic animals, but has been known to affect humans as well.S. pseudintermedius is an opportunistic pathogen that secretes immune modulating virulence factors, has many adhesion factors, and the potential to create biofilms, all of which help to determine the pathogenicity of the bacterium. Diagnoses of Staphylococcus pseudintermedius have traditionally been made using cytology, plating, and biochemical tests. More recently, molecular technologies like MALDI-TOF, DNA hybridization and PCR have become preferred over biochemical tests for their more rapid and accurate identifications. This includes the identification and diagnosis of antibiotic resistant strains.
Acinetobacter schindleri is a species of bacteria. It is potentially pathogenic. Its type strain is LUH 5832T.

Corynebacterium striatum is a bacterium that is a member of the Corynebacterium genus. It is classified as non-diphtheritic. The bacterium is a gram-positive prokaryote that assumes a 'club-like' morphology, more formally known as a corynebacteria structure. It is non-lipophilic and undergoes aerobic respiration and is also a facultative anaerobe it is catalase negative and oxidase positive glucose and sucrose fermenter.






