
Rabelera holostea, known as greater stitchwort, greater starwort, and addersmeat, is a perennial herbaceous flowering plant in the family Caryophyllaceae. It was formerly placed in the genus Stellaria, as Stellaria holostea, but was transferred to the genus Rabelera in 2019 based on phylogenetic analyses. It is the only species in the genus Rabelera. Greater stitchwort is native to Western and Central Europe, including the British Isles.

Gentianella amarella, the autumn gentian, autumn dwarf gentian, or autumn felwort, is a short biennial plant flowering plant in the gentian family, Gentianaceae. It is found throughout Northern Europe, the western and northern United States, and Canada.

Carex vesicaria is an essentially Holarctic species of sedge known as bladder sedge, inflated sedge, and blister sedge. It has been used to insulate footwear in Norway and among the Sami people, and for basketry in North America.

Ribes hirtellum is a species of gooseberry commonly known as wild gooseberry or swamp gooseberry. It is native to Canada and the northern United States. Cultivated gooseberries are derived from this species and from Ribes uva-crispa.

Carex cryptolepis, known as northeastern sedge, is a North American species of sedge first described by Kenneth Mackenzie in 1914.

Carex hirsutella, the hairy green sedge or fuzzy wuzzy sedge, is a species of North American sedge that was first described by Kenneth Mackenzie in 1923. It ranges from Texas, throughout most of the central and eastern United States, north to Ontario and Quebec.

Carex swanii, known as Swan's sedge or downy green sedge, is a species of flowering plant in the family Cyperaceae. It is native to eastern North America.

Leucospora multifida, known variously as Obi-Wan conobea, narrow-leaved paleseed, cliff conobea, cut-leaved conobea, or much-cleft conobea, is an annual herb in the plantain family, Plantaginaceae, and the only species in the North American genus Leucospora.

Carex flexuosa, commonly called flexuous white-edge sedge, or Rudge's white-edge sedge, is a species of flowering plant in the sedge family, Cyperaceae. It is native to the eastern North America, where it is found in eastern Canada, the northeastern and midwestern United States, and southward in the Appalachian Mountains. Its natural habitat is in upland forests, rock outcrops, and Appalachian balds. It is typically found in areas with acidic soil.

Vaccinium fuscatum, the black highbush blueberry, is a species of flowering plant in the heath family (Ericaceae). It is native to North America, where it is found in Ontario, Canada and the eastern United States. Its typical natural habitat is wet areas such as bogs, pocosins, and swamps.

Hydrophyllum canadense, known as bluntleaf waterleaf, broadleaf waterleaf, or Canada waterleaf, is a flowering plant in the borage family, Boraginaceae. It is native to the eastern United States and Canada.
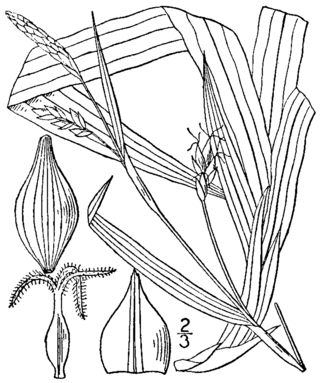
Carex careyana, commonly known as Carey's sedge, is a species of sedge found in the eastern United States and Ontario, Canada.

Platanthera dilatata, known as tall white bog orchid, bog candle, or boreal bog orchid is a species of orchid, a flowering plant in the family Orchidaceae, native to North America. It was first formally described in 1813 by Frederick Traugott Pursh as Orchis dilatata.
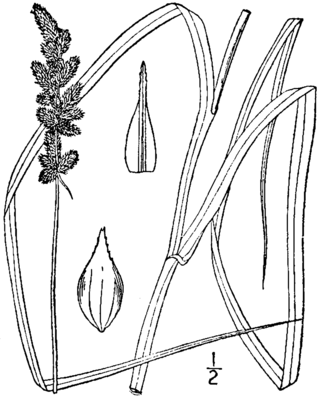
Carex annectens, sometimes called yellow-fruited fox sedge, is a species of sedge native to most of the eastern United States and southeastern Canada. It is common in prairies and high-water table fallow fields. In the Chicago area, its coefficient of conservatism is 3, and in Michigan, it is only 1, indicating its relatively low fidelity to high quality habitats.

Symphyotrichum ciliolatum, commonly known as Lindley's aster and fringed blue aster, is a perennial herb native to Canada and the northern United States. It is also known as ciliolate wood aster and northern heart-leaved aster. The common name Lindley's aster honours John Lindley who first described the species in 1834.

Solidago sect. Ptarmicoidei is a section of flowering plants in the genus Solidago. They are sometimes considered a separate genus: Oligoneuron. Like related species they are known as goldenrods. This section contains seven species of perennial herbs, all native to North America. They are distinguished from other goldenrods by their corymbiform flowerheads, which are flat or rounded in profile and about as broad as tall or broader, for which they are sometimes called flat-topped goldenrods.

Scirpus atrovirens, known as dark-green bulrush, is a perennial sedge native to wetlands of eastern Canada and the United States. It is sometimes called dark green bulsedge, black bulrush, or green bulrush.

Carex lupulina, known as hop sedge or common hop sedge, is a species of sedge native to most of eastern North America.

Oxypolis is a small genus of North American flowering plants in the carrot family known as cowbane, water dropwort, dropwort, hog-fennel, and pig-potato. As of 2020, Kew's Plants of the World Online accepts four species in the genus Oxypolis:
Carex peckii, Peck's sedge, Peck's oak sedge, or white-tinged sedge, is a species of sedge native to Canada and the United States.





















