
The Cyperaceae are a family of graminoid (grass-like), monocotyledonous flowering plants known as sedges. The family is large, with some 5,500 known species described in about 90 genera, the largest being the "true sedges" genus Carex with over 2,000 species.

Cymbidium, commonly known as boat orchids, is a genus of evergreen flowering plants in the orchid family Orchidaceae. Orchids in this genus are epiphytic, lithophytic, terrestrial or rarely leafless saprophytic herbs usually with pseudobulbs. There are usually between three and twelve leaves arranged in two ranks on each pseudobulb or shoot and lasting for several years. From one to a large number of flowers are arranged on an unbranched flowering stem arising from the base of the pseudobulb. The sepals and petals are all free from and similar to each other. The labellum is significantly different from the other petals and the sepals and has three lobes. There are about fifty-five species and sixteen further natural hybrids occurring in the wild from tropical and subtropical Asia to Australia. Cymbidiums are well known in horticulture and many cultivars have been developed.

Carex is a vast genus of more than 2,000 species of grass-like plants in the family Cyperaceae, commonly known as sedges. Other members of the family Cyperaceae are also called sedges, however those of genus Carex may be called true sedges, and it is the most species-rich genus in the family. The study of Carex is known as caricology.

Carex riparia, the greater pond sedge, is a species of sedge found across Europe and Asia. It grows in a variety of wet habitats, and can be a dominant species in some swamps. It is Britain's largest Carex, growing up to 130 cm tall, with glaucous leaves up to 160 cm long. It hybridises with a number of other Carex species, including the closely related Carex acutiformis – the lesser pond sedge. A variegated cultivar is grown as an ornamental grass.

Carex hirta, the hairy sedge or hammer sedge, is a species of sedge native across Europe. It has characteristic hairy leaves and inflorescences, and is the type species of the genus Carex.

Carex binervis, the green-ribbed sedge, is a European species of sedge with an Atlantic distribution. It is found from Fennoscandia to the Iberian Peninsula, and occurs in heaths, moorland and other damp, acidic environments. It typically grows to a height of 15–120 cm (6–50 in), and has inflorescences comprising one male and several female spikes, each up to 45 mm (1.8 in) long. The utricles have two conspicuous green veins, which give rise to both the scientific name and the common name of the species. In the vegetative state, it closely resembles C. bigelowii, a species that usually grows at higher altitude. C. binervis was first described by James Edward Smith in 1800, and is classified in Carex sect. Spirostachyae; several hybrids with other Carex species are known.

Carex panicea, commonly known as carnation sedge, is a plant species in the sedge family, Cyperaceae. It is known as grass-like sedge and can be found in Northern and Western Europe, and also in north-eastern North America. The plant produces fruits which are 3–4 millimetres (0.12–0.16 in) long, are egg shaped and spiked. Both male and female species leaves are pale blue on both sides.

Carex sylvatica is a species of sedge found in deciduous woodlands across Europe. It typically reaches 60 cm (24 in) tall, and has an inflorescence made up of 3–5 pendent female spikes and a single male spike. It is also used as a garden plant, and has been introduced to North America and New Zealand.

Carex kobomugi is a species of sedge, known as the Japanese sedge or Asiatic sand sedge, that lives in sandy coastal areas of eastern Asia, and has become an invasive species in the north-eastern United States.

Carex pumila, commonly known as strand sedge or spreading sedge, is a species of sedge of the family Cyperaceae.

Carex novae-angliae, the New England sedge, is a Carex species that is native to North America.
Liu Guodao, is a Chinese agrobiologist.

Carex juniperorum, the juniper sedge, is a perennial flowering plant native to North America, first described by botanist William J. Crins in 1993. C. juniperorum is in the Cyperaceae (sedge) family, and is closely related to C. jamesii and C. willdenowii. It is commonly called juniper sedge as it is often seen growing in areas with red cedar, though the presence of cedar is not necessarily a requirement for it to grow.
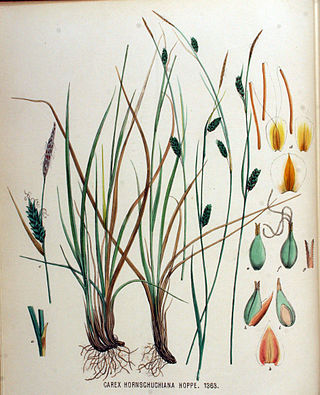
Carex hostiana, the tawny sedge, is a species of flowering plant in the genus Carex, native to Europe and northeast Canada, and extinct in Massachusetts. It is a member of the Carex flava species complex.

Carex tristachya, called the shiny-spike sedge, is a species of flowering plant in the genus Carex, native to south-central and southeast China, Korea, Japan, the Ryukyus, the Philippines, Borneo, and New Guinea. Its seeds are dispersed by ants.

Carex breviscapa is a tussock-forming perennial in the family Cyperaceae. It is native to eastern parts of the south east Asia and north eastern Australia

Carex gravida, also known as heavy-fruited sedge, heavy sedge or long-awned bracted sedge, is a tussock-forming species of perennial sedge in the family Cyperaceae. It is native to southern parts of Canada and parts of the United States.

Carex dickinsii, also known as Dickins' sedge or chao xian tai cao in pinyin, is a tussock-forming species of perennial sedge in the family Cyperaceae. It is native to parts of Japan, Taiwan and south-eastern China.
Carex phacota, the lentoid sedge, is a species of flowering plant in the family Cyperaceae. It is native to parts of the Indian Subcontinent, Southeast Asia, most of Malesia, New Guinea, central and southern China, Hainan, Taiwan, Korea, the Ryukyus, and Japan. A pioneer species adapted to disturbances such as fire and landslides, it is typically found in wet grasslands, ditches, the banks of streams, and the sides of roads, and is categorized by the IUCN as Least Concern.
















