Related Research Articles

Mission La Purísima Concepción, or La Purísima Mission is a Spanish mission in Lompoc, California. It was established on December 8, 1787 by the Franciscan order. The original mission complex south of Lompoc was destroyed by an earthquake in 1812, and the mission was rebuilt at its present site a few miles to the northeast.
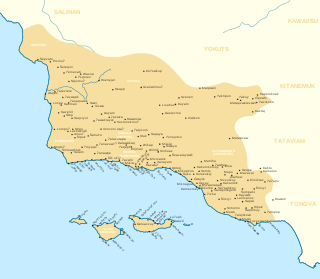
The Chumash are a Native American people of the central and southern coastal regions of California, in portions of what is now San Luis Obispo, Santa Barbara, Ventura and Los Angeles counties, extending from Morro Bay in the north to Malibu in the south. Their territory included three of the Channel Islands: Santa Cruz, Santa Rosa, and San Miguel; the smaller island of Anacapa was likely inhabited seasonally due to the lack of a consistent water source.

The Tongva are an Indigenous people of California from the Los Angeles Basin and the Southern Channel Islands, an area covering approximately 4,000 square miles (10,000 km2). In the precolonial era, the people lived in as many as 100 villages and primarily identified by their village rather than by a pan-tribal name. During colonization, the Spanish referred to these people as Gabrieleño and Fernandeño, names derived from the Spanish missions built on their land: Mission San Gabriel Arcángel and Mission San Fernando Rey de España. Tongva is the most widely circulated endonym among the people, used by Narcisa Higuera in 1905 to refer to inhabitants in the vicinity of Mission San Gabriel. Some direct lineal descendants of the people advocate the use of their ancestral name Kizh as an endonym.

The Channel Islands are an eight-island archipelago located within the Southern California Bight in the Pacific Ocean, off the coast of California. The four Northern Channel Islands are part of the Transverse Ranges geologic province, and the four Southern Channel Islands are part of the Peninsular Ranges province. Five of the islands are within the Channel Islands National Park, and the waters surrounding these islands make up Channel Islands National Marine Sanctuary. The Nature Conservancy was instrumental in establishing the Channel Islands National Marine Sanctuary. The islands were inhabited as early as 13,000 years ago, the earliest paleontological evidence of humans in North America. They are the easternmost islands in the Pacific Island group.

Chatsworth is a suburban neighborhood in the City of Los Angeles, California, in the San Fernando Valley.

The Tataviam are a Native American group in Southern California. The ancestral land of the Tataviam people includes northwest present-day Los Angeles County and southern Ventura County, primarily in the upper basin of the Santa Clara River, the Santa Susana Mountains, and the Sierra Pelona Mountains. They are distinct from the Kitanemuk and the Gabrielino-Tongva peoples.

Puvunga is an ancient village and sacred site of the Tongva nation, the Indigenous people of the Los Angeles Basin, and the Acjachemen, the Indigenous people of Orange County. The site is now located within California State University, Long Beach and the surrounding area. The Tongva know Puvunga as the "place of emergence" and it is where they believed "their world and their lives began." The site remains an important ceremonial site and ending to an annual pilgrimage for the Tongva, Acjachemen, and Chumash.

The Tongva Sacred Springs are a group of springs located on the campus of University High School in Los Angeles, California.

Santa Susana Pass State Historic Park is a California State Park of 670.68 acres (2.7141 km2) located in the city of Los Angeles, in Los Angeles County on the boundary between Ventura and Los Angeles counties, between the communities of Chatsworth and Simi Valley. Geologically, the park is located where the Simi Hills meet the Santa Susana Mountains. Here in the western part of the Transverse Ranges, the land is dominated by high, narrow ridges and deep canyons covered with an abundant variety of plant life. The park offers panoramic views of the rugged natural landscape as a striking contrast to the developed communities nearby. The park is also rich in archaeological, historical, and cultural significance.

The history of the San Fernando Valley from its exploration by the 1769 Portola expedition to the annexation of much of it by the City of Los Angeles in 1915 is a story of booms and busts, as cattle ranching, sheep ranching, large-scale wheat farming, and fruit orchards flourished and faded. Throughout its history, settlement in the San Fernando Valley was shaped by availability of reliable water supplies and by proximity to the major transportation routes through the surrounding mountains.

Hahamongna and Hahamog-na are historic Tongva villages located in the Verdugo Mountains of Southern California named after the local Tongva band's name Hahamog'na. The village sites are located in present-day Pasadena and Glendale in Los Angeles County, California. Hahamongna was one of the largest Tongva villages in the greater San Fernando Valley area, along with Cahuenga, Tujunga, and Siutcanga.
Satwiwa was a former Chumash village in the Santa Monica Mountains of Newbury Park, California. The current Satwiwa Native American Indian Culture Center is operated by the National Park Service in cooperation with the Friends of Satwiwa. Satwiwa has been inhabited by Chumash Indians for over 10,000 years. It is situated at the foothills of Boney Mountain, a sacred mountain for the Chumash.
Humaliwo was a Chumash village located in present-day Malibu, California. “Humaliwo” meant "where the surf sounds loudly." The village occupied a hill across from the lagoon in Malibu Lagoon State Beach. The neighboring Tongva referred to the village as Ongobehangna. The Humaliwo village was recorded on the National Register of Historic Places (NRHP) in 1976. Cultural remains are present at this site, consisting of numerous human burials, artifacts and other cultural materials. Sections of the site can be dated to 7,000 years old.

Genga, alternative spelling Gengaa and Kengaa, was a Tongva and Acjachemen village located on Newport Mesa overlooking the Santa Ana River in the Newport Beach and Costa Mesa, California area which included an open site now referred to as Banning Ranch. Archaeological evidence dates the village at over 9,000 years old. Villagers were recorded as Gebit in Spanish Mission records. The village may have been occupied as late as 1829 or 1830.
Pajbenga, alternative spelling Pagbigna and Pasbengna, was a Tongva village located at Santa Ana, California, near the El Refugio Adobe, which was the home of José Sepulveda. It was one of the main villages along the Santa Ana River, including Lupukngna, Genga, Totpavit, and Hutuknga. People from the village were recorded in mission records as Pajebet, Pajbet, Pajbebet, and Pajbepet.
Totpavit, alternative spellings Totabit and possibly Totavet, was a Tongva village located in what is now Olive, California. The village was located between the Santa Ana River and Santiago Creek. It was part of a series of villages along the Santa Ana River, including Genga, Pajbenga, and Hutuknga.

Achooykomenga is a former settlement that was located at the site of Mission San Fernando Rey de España before it was founded in 1797. Prior to the mission's founding, in the 1780s, it functioned as a shared native settlement for an agricultural rancho of Pueblo de Los Ángeles that was worked by Ventureño Chumash, Fernandeño (Tongva), and Tataviam laborers.
Comicranga was a coastal Tongva village located at what is now the area of Santa Monica, California. The village is also referred to as Comigranga, Comicraibit, Comicrabit, and possibly Coronababit. It is most notable as the home village of Bartolomea, or Victoria Reid after marriage, a respected Indigenous woman in Mexican California, who was the wife of Hugo Reid.

Geveronga was a Tongva village located at what is now Pico-Union, Los Angeles, California along the Los Angeles River. Part of the village area is also located on the campuses of the University of Southern California (USC) at its University Park Campus. The USC History Department provided a map of the general location of Geveronga in its land acknowledgement in 2021. People from the village were known as Geverovit.
Momonga was a Tongva village located at what is now Chatsworth, Los Angeles, California in the San Fernando Valley. The village may have been located in the area now referred to as Stoney Point. The village was located near the village of Ashaawanga, also associated with the Chatsworth area.
References
- ↑ Survey, University of California, Los Angeles Archaeological (1966). Annual Report - Archaeological Survey. Department of Anthropology, University of California. p. 144.
- 1 2 Southern California Quarterly. Historical Society of Southern California. 1997. p. 253.
- 1 2 "Villages | TONGVA PEOPLE" . Retrieved 2023-04-21.
- ↑ McLendon, Sally (1999). Cultural Affiliation and Lineal Descent of Chumash Peoples in the Channel Islands and the Santa Monica Mountains: Final Report. National Park Service. p. 11.
- ↑ John R., Johnson (June 2006). "Ethnohistoric Overview for the Santa Susana Pass State Historic Park Cultural Resources Inventory Project" (PDF). Southern Service Center: State of California Department of Parks and Recreation: 15.