Illustrations of usage
- A 1965 Federal Bureau of Investigation surveillance photograph
- A heavily redacted page from the lawsuit American Civil Liberties Union v. Ashcroft
- The censor bar as used by Google in the SOPA and PIPA online protests
- Censor bars applied to a model
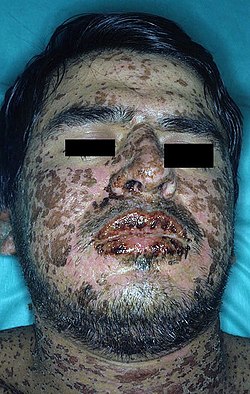
- Censor bars applied to a patient with Stevens–Johnson syndrome
- Censor bars used to anonymise a woman with familial dysautonomia
- The Turkish Wikipedia logo with a censor bar covering the text, used from April 2017 to January 2020 when Turkish authorities blocked online access to Wikipedia in all languages across Turkey
- A portion of the redacted affidavit used to obtain a search warrant for former U.S. President Donald Trump's Mar-a-Lago home and resort, with the signature block blacked out