
Ŭiju County is a kun, or county, in North Pyongan Province, North Korea. The county has an area of 420 km², and a population of 110,018.

Manpo is a city of northwestern Chagang Province, North Korea. As of 2008, it had an estimated population of 116,760. It looks across the border to the city of Ji'an, Jilin province, China.

Kimhyŏngjik County is a kun of Ryanggang Province, North Korea. Formerly known as Huch'ang County, it was renamed in 1988 in honour of Kim Hyŏng-jik, the leader of the anti-Japanese liberation movement of Korea.

Changjin County is a mountainous county in South Hamgyong Province, North Korea.

Kimjŏngsuk County is a kun, or county, in Ryanggang province, North Korea, along the Yalu River.

Samsu County is a kun, or county, in Ryanggang province, North Korea. Prior to 1954, it was part of South Hamgyŏng province.
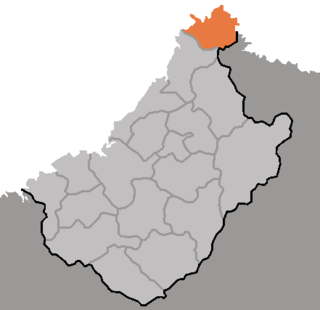
Chunggang County is a kun, or county, in northern Chagang province, North Korea. It was originally part of Huchang county in Ryanggang, and for that reason older sources still identify it as being part of Huchang. The county seat was originally known as Chunggangjin (중강진), but is now known as Chunggang ŭp. Chunggang looks across the Yalu River at China, and borders Ryanggang province to the south.

Ch'osan County is a kun, or county, in Chagang province, North Korea. It borders the People's Republic of China to the north.

Wiwŏn County is a kun, or county, in northern Chagang province, North Korea. It stands across the Yalu River from the People's Republic of China. It was originally part of North P'yŏngan province, but was annexed to Chagang in 1954. It borders Manp'o and Sijungto the north, Kanggye and Songgan to the east, Ch'onch'ŏn to the southeast, Kop'ung to the south and west, and Ch'osan to the west.
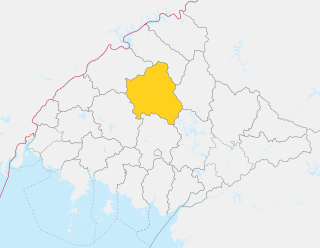
Taegwan County is a kun, or county, in northeastern North P'yŏngan province, North Korea. It lies in the province's interior, and is bounded by Tongch'ang on the east, Kusŏng and T'aech'ŏn to the south, Ch'ŏnma to the west, and Ch'angsŏng and Sakchu to the north. It was created in 1952 from portions of Sakchu county.

Ch'ŏnma County is a kun, or county, in northwestern North P'yŏngan province, North Korea. It borders Kusŏng city and Taegwan county to the east, Sonch'ŏn and Tongrim counties to the south, Ŭiju and P'ihyŏn counties to the west, and Sakchu county to the north. It was created in 1952 from parts of Kusŏng and Ŭiju.

Pakch'ŏn County is a kun, or county, in southern North P'yŏngan province, North Korea. It is bordered to the north by T'aech'ŏn, to the east and southeast by Nyŏngbyŏn, and to the west by Unjŏn counties. To the south, it looks across the Ch'ŏngch'ŏn River at Anju city and Mundŏk county in South P'yŏngan province. In 1952, 4 myŏn of Pakch'ŏn were split off to join Unjŏn county; since then, the county's administrative divisions have been revised in 1954, 1956, 1958, 1978, 1980, and 1982.

Phihyŏn County is a kun, or county, in northwestern North P'yŏngan province, North Korea. It is bounded to the north by Ŭiju, to the east by Chŏnma, to the south by Yŏmju and Tongrim, and to the west by Ryongchŏn and the large city of Sinŭiju. It was established as a separate county in 1952, and was subsequently reorganized in 1954, 1958, 1961, 1963, 1967 and 1978.
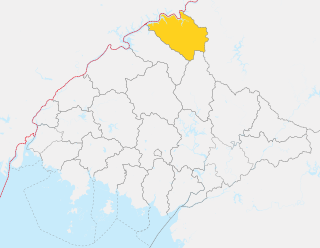
Pyŏktong County is a kun, or county, in northern North P'yŏngan province, North Korea. It lies in the valley of the Yalu River, and borders China to the north. Within North Korea, it is bounded by Tongch'ang to the south, Ch'angsŏng to the west, and Usi county in Chagang province to the east. It was separated from Usi in 1952, as part of a nationwide reorganization of local government.
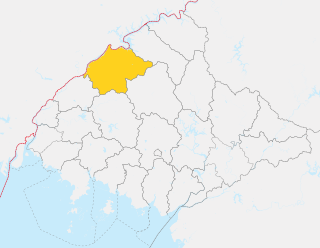
Sakju County is a kun, or county, in northern part of North P'yŏngan province, in North Korea. It lies along the Yalu River bordering the People's Republic of China to the north. Within North Korea, it borders Ch'angsŏng to the east, Ch'ŏnma and Taegwan to the south, and Ŭiju to the west.

T'aechŏn County or Thaechŏn County is a kun, or county, in central North P'yŏngan province, North Korea. It borders Taegwan and Tongch'ang to the north, Unsan and Nyŏngbyŏn to the east, Pakch'ŏn and Unjŏn to the south, and Kusŏng to the west.

Tongchang County is a kun, or county, in the northeast of the far western North Pyŏngan province, North Korea. It borders Pyŏktong and Chagang's Usi county to the north, Unsan and Songwŏn to the east, Thaechŏn to the south, and Changsŏng and Taegwan to the west.

Tongrim County is a kun, or county, in coastal southwestern North P'yŏngan province, North Korea. It borders P'ihyŏn and Ch'ŏnma to the north, Sŏnch'ŏn to the east, Ch'ŏlsan to the southwest and Yŏmju to the west. To the south, it looks out on the Yellow Sea.

Unjŏn County is a kun, or county, in North P'yŏngan province, North Korea. It borders T'aech'ŏn to the north, Pakch'ŏn to the east and southeast, and Chŏngju to the north. To the south, it looks out on the Yellow Sea. Unjŏn county was created in 1952 from portions of Pakch'ŏn county and Chŏngju city, and subsequently reorganized in 1954 and 1958.
Usi County is a kun, or county, in westernmost Chagang Province, North Korea. It looks across the Yalu River into the People's Republic of China. Within North Korea, it borders Chosan and Kopung to the east, Songwon to the south, and North Pyongan Province's Pyoktong county to the west. Originally part of Pyoktong, it was made a separate county in 1952 as part of a general reorganization of local government; in 1954, it was transferred from North Pyongan to Chagang.





















