
The Exocoetidae are a family of marine ray-finned fish in the order Beloniformes, known colloquially as flying fish or flying cod. About 64 species are grouped in seven genera. While they cannot fly in the same way a bird does, flying fish can make powerful, self-propelled leaps out of the water where their long wing-like fins enable gliding for considerable distances above the water's surface. The main reason for this behavior is thought to be to escape from underwater predators, which include swordfish, mackerel, tuna, and marlin, among others, though their periods of flight expose them to attack by avian predators such as frigate birds.

The red-tailed tropicbird is a seabird native to tropical parts of the Indian and Pacific Oceans. One of three closely related species of tropicbird (Phaethontidae), it was described by Pieter Boddaert in 1783. Superficially resembling a tern in appearance, it has almost all-white plumage with a black mask and a red bill. The sexes have similar plumage. As referenced in the common name, adults have red tail streamers that are about twice their body length. Four subspecies are recognised, but there is evidence of clinal variation in body size—with smaller birds in the north and larger in the south—and hence no grounds for subspecies.

Cheilopogon is a genus of flyingfishes. They are found worldwide except the Antarctic and Arctic oceans.
The Australasian flying fish, Cheilopogon pinnatibarbatus melanocercus, is a subspecies of flyingfish of the family Exocoetidae, found off New South Wales of Australia, and around New Zealand, in surface waters. The Australasian flying fish feeds mainly on plankton and small crustaceans.

Cheilopogon pinnatibarbatus japonicus is a subspecies of flyingfish of the family Exocoetidae, found in the seas around Japan. Its length is up to 50 cm.

The California flying fish, Cheilopogon pinnatibarbatus californicus, is a subspecies of Bennett's flying fish, Cheilopogon pinnatibarbatus. Prior to the 1970s, the California flying fish was known as a distinct species, with the scientific classification Cypselurus californicus. The California flying fish is one of 40 distinct classifications of flying fish. It is the largest member of the flying fish family, growing up to 19 inches (48 cm) in length. It is a marine species found in the Eastern Pacific Ocean, from Oregon to Baja California. As with all other flying fish, the California can not actually fly, it launches itself into the air, using its specially adapted fins to glide along the surface. The California flying fish spends most of its time in the open ocean but comes close to shore at night to forage and lay eggs in the protection of kelp beds.

The bluelashed butterflyfish, also known as the eclipse butterflyfish, archer butterflyfish or Bennett's butterflyfish, is a species of marine ray-finned fish, a butterflyfish belonging to the family Chaetodontidae, It is found in the Indo-Pacific.

The mirrorwing flyingfish is a flying fish of the family Exocoetidae. It was first described by the French zoologist, Achille Valenciennes in a 22-volume work titled Histoire naturelle des poissons, which was a collaboration with Georges Cuvier.

The Atlantic flyingfish is a flying fish in the family Exocoetidae. The flyingfish fauna is made up of 16 total species, 6 of which belong to the genus Cheilopogon, including C. melanurus. The Atlantic flyingfish is also in the order Beloniformes and class Actinopterygii. It was first described by the French zoologist, Achille Valenciennes in a 22-volume work entitled Histoire naturelle des poissons, which was a collaboration with fellow zoologist Georges Cuvier.

Fodiator is a genus of flying fishes. It is the only genus in the subfamily Fodiatorinae.

The sailfin flying fish is a member of the flying fish family (Exocoetidae). As is typical of other members of its family, this species has the ability to jump out of the water and glide on hypertrophied fins in order to evade predators. It is considered a “two-winged” flying fish, meaning that it only has enlarged pectoral fins, as opposed to “four-winged” flying fish, which have both enlarged pectoral and pelvic fins.

Cheilopogon nigricans, the blacksail flyingfish, also known as African flyingfish, or leaping flyingfish, is a flying fish in the family Exocoetidae. It is an oceanodromous, plankton-eating marine fish which has commercial value.

Fodiator acutus, the sharpchin flyingfish, is a species of flying fish in the genus Fodiator endemic to the northeast Pacific Ocean and the eastern Atlantic Ocean.
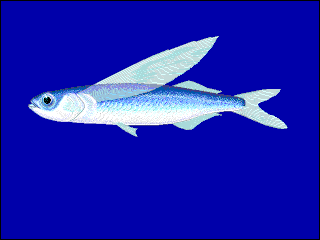
Exocoetus volitans, commonly known as the tropical two-wing flyingfish or blue flyingfish, is a species of ray-finned fish native to tropical and subtropical seas. It can glide above the surface of the sea to escape predators.

Exocoetus obtusirostris, commonly known as the oceanic two-wing flyingfish or the blunt-snouted flyingfish, is a species of ray-finned fish native to the tropical and subtropical western Atlantic Ocean. It has the ability to glide above the surface of the water to escape from predators.

Hirundichthys rondeletii, the black wing flyingfish, is a species of flying fish from the family Exocoetidae which is found throughout the tropical and subtropical waters of the Atlantic, Pacific and Indian Oceans.
Exocoetus peruvianus, commonly known as the Peruvian flyingfish, is a species of ray-finned fish endemic to the tropical southeast Pacific Ocean in the waters off Peru and Ecuador.
Cheilopogon papilio, the butterfly flyingfish, is a species of ray-finned fish within the family Exocoetidae, distributed in the eastern Pacific off the coasts of Mexico in Baja California and the Revillagigedos Islands, as well as some areas off Costa Rica and Panama. Other common names of the species include the exocet papillon in French and volador mariposa in Spanish.

Cheilopogon heterurus, the Mediterranean flyingfish, is a fish in the flying fish family Exocoetidae.















