In biochemistry, hydrolases constitute a class of enzymes that commonly function as biochemical catalysts that use water to break a chemical bond:

Chenodeoxycholic acid is a bile acid. Salts of this carboxylic acid are called chenodeoxycholates. Chenodeoxycholic acid is one of the main bile acids. It was first isolated from the bile of the domestic goose, which gives it the "cheno" portion of its name.
In enzymology, a 2,6-dioxo-6-phenylhexa-3-enoate hydrolase (EC 3.7.1.8) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a taurine-transporting ATPase (EC 3.6.3.36) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction.
The enzyme α-amino-acid esterase (EC 3.1.1.43) catalyzes the reaction
In enzymology, a bile-acid-CoA hydrolase (EC 3.1.2.26) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
The enzyme choloyl-CoA hydrolase (EC 3.1.2.27) catalyzes the reaction
The enzyme sterol esterase (EC 3.1.1.13) catalyzes the reaction
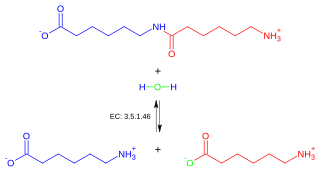
In enzymology, a 6-aminohexanoate-dimer hydrolase (EC 3.5.1.46) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction N-(6-aminohexanoyl)-6-aminohexanoate + H2O 2 6-aminohexanoate. Thus, the two substrates of this enzyme are N-(6-aminohexanoyl)-6-aminohexanoate and H2O, whereas its product is two molecules of 6-aminohexanoate.
In enzymology, a carboxymethylhydantoinase (EC 3.5.2.4) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a choloylglycine hydrolase (EC 3.5.1.24) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, an imidazolonepropionase (EC 3.5.2.7) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a maleimide hydrolase (EC 3.5.2.16) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a mandelamide amidase (EC 3.5.1.86) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction

In enzymology, a methenyltetrahydrofolate cyclohydrolase (EC 3.5.4.9) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a N-acyl-D-amino-acid deacylase (EC 3.5.1.81) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, Nα-benzyloxycarbonylleucine hydrolase (EC 3.5.1.64) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a N-benzyloxycarbonylglycine hydrolase (EC 3.5.1.58) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a pantothenase (EC 3.5.1.22) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
Bile salt hydrolases (BSH) are microbial enzymes that deconjugate primary bile acids. They catalyze the first step of bile acid metabolism and maintain the bile acid pool for further modification by the microbiota. BSH enzymes play a role in a range of host and microbe functions including host physiology, immunity, and protection from pathogens.




