
Atriplex is a plant genus of about 250 species, known by the common names of saltbush and orache. It belongs to the subfamily Chenopodioideae of the family Amaranthaceae s.l.. The genus is quite variable and widely distributed. It includes many desert and seashore plants and halophytes, as well as plants of moist environments. The generic name originated in Latin and was applied by Pliny the Elder to the edible oraches. The name saltbush derives from the fact that the plants retain salt in their leaves; they are able to grow in areas affected by soil salination.

Atriplex semibaccata, commonly known as Australian saltbush, berry saltbush, or creeping saltbush, is a species of flowering plant in the family Amaranthaceae and is endemic to Australia. It is a perennial herb native to Western Australia, South Australia, Queensland and New South Wales, but has been introduced into other states and to overseas countries. It flowers and fruits in spring, and propagates from seed when the fruit splits open. This species of saltbush is adapted to inconsistent rainfall, temperature and humidity extremes and to poor soil. It is used for rehabilitation, medicine, as a cover crop and for fodder. Its introduction to other countries has had an environmental and economic impact on them.

Atriplex cinerea, commonly known as grey saltbush, coast saltbush, barilla or truganini, is a plant species in the family Amaranthaceae. It occurs in sheltered coastal areas and around salt lakes in the Australian states of Western Australia, South Australia, Tasmania, Victoria and New South Wales. The species is also known to be present in the Waimea inlet in New Zealand, although has historically been found in Boulder Bank, D'Urville Island, and Palliser Bay.

Chenopodium candolleanum, commonly known as seaberry saltbush, is a shrub in the subfamily Chenopodioideae of the family Amaranthaceae, native to Australia.

Atriplex vesicaria, commonly known as bladder saltbush, is a species of flowering plant of the family Amaranthaceae and is endemic to arid and semi-arid inland regions of Australia. It is an upright or sprawling shrub with scaly leaves and separate male and female plants, the fruit often with a bladder-like appendage.
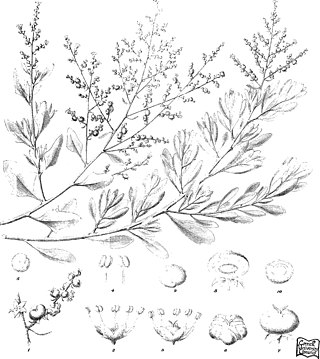
Chenopodium baccatum, commonly known as berry saltbush, is a species of shrub endemic to Western Australia.
Chenopodium benthamii is a species of shrub endemic to midwest Western Australia.

Enchylaena tomentosa, commonly known as barrier saltbush or ruby saltbush, is a small native shrub of Australia.

Atriplex nummularia is a species of saltbush from the family Amaranthaceae and is a large woody shrub known commonly as oldman saltbush. A. nummularia is native to Australia and occurs in each of the mainland states, thriving in arid and semi-arid inland regions.

Capparis anomala is a species of flowering plant, commonly called warrior bush or broom bush, which is native to Australia.

Cassinia arcuata, commonly known as drooping cassinia, biddy bush, Chinese scrub, sifton bush and Chinese shrub, is a species of flowering plant in the family Asteraceae and is endemic to Australia. It is a shrub, sometimes a small tree with sessile, linear leaves, and heads of up to two hundred brownish flowers arranged in pyramid-shaped panicles. In New South Wales, the species is known as Cassinia sifton. In disturbed areas, C. arcuata can become weedy.

Dodonaea microzyga, commonly known as brilliant hopbush, is a dioecious spreading shrub in the family Sapindaceae. It grows between 0.3 and 1.5 metres tall.

Chenopodium parabolicum, commonly known as fragrant saltbush or mealy saltbush, is a shrub in the family Amaranthaceae. The species is native to Australia.

Chenopodium spinescens is a species of plant in the family Amaranthaceae and is endemic to all mainland states and territories of Australia where it is known as Rhagodia spinescens.

Dissocarpus paradoxus is a shrub species of inland Australia, also known by the common names of cannonball burr or curious saltbush.

Atriplex holocarpa is a low-growing species of Atriplex (saltbush) found throughout arid regions of Australia. A. holocarpa is commonly known as pop saltbush, because its carpels pop when stepped upon.

Atriplex stipitata, commonly known as mallee saltbush, bitter saltbush and kidney saltbush, is a species of shrub in the family Amaranthaceae, found in all mainland states of Australia.

Atriplex sturtii, commonly known as saltbush, is an endangered species within the widespread genus Atriplex.A. sturtii is a native Australian shrub and grows in the Channel Country bioregion, also referred to as 'Corner Country'.

Atriplex angulata, commonly known as fan saltbush or angular saltbush, is a species of flowering plant in the family Amaranthaceae. It is an annual to short-lived perennial subshrub, native to Australia, distributed throughout drier parts of the mainland.

Maireana erioclada, commonly known as the rosy bluebush, is a common shrub endemic to Australia, belonging to the genus Maireana.

















