
Amaranthaceae is a family of flowering plants commonly known as the amaranth family, in reference to its type genus Amaranthus. It includes the former goosefoot family Chenopodiaceae and contains about 165 genera and 2,040 species, making it the most species-rich lineage within its parent order, Caryophyllales.

The Chenopodioideae are a subfamily of the flowering plant family Amaranthaceae in the APG III system, which is largely based on molecular phylogeny, but were included – together with other subfamilies – in the family Chenopodiaceae in the Cronquist system.

Chenopodium is a genus of numerous species of perennial or annual herbaceous flowering plants known as the goosefoots, which occur almost anywhere in the world. It is placed in the family Amaranthaceae in the APG II system; older classification systems, notably the widely used Cronquist system, separate it and its relatives as Chenopodiaceae, but this leaves the rest of the Amaranthaceae polyphyletic. However, among the Amaranthaceae, the genus Chenopodium is the namesake member of the subfamily Chenopodioideae.

Chenopodiastrum murale, is a species of plant in the family Amaranthaceae known by the common names nettle-leaved goosefoot, Australian-spinach, salt-green, and sowbane. This plant is native to Europe and parts of Asia and northern Africa, but it is widespread worldwide, particularly in tropical and subtropical areas due to the ease of it being introduced. It is a common weed of fields and roadsides.

Chenopodium candolleanum, commonly known as seaberry saltbush, is a shrub in the subfamily Chenopodioideae of the family Amaranthaceae, native to Australia.
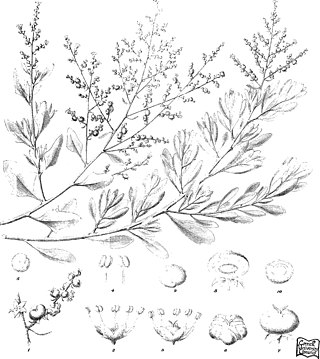
Chenopodium baccatum, commonly known as berry saltbush, is a species of shrub endemic to Western Australia.
Chenopodium benthamii is a species of shrub endemic to midwest Western Australia.

Blitum californicum is a species of flowering plant in the amaranth family known by the common names California goosefoot and (ambiguously) "Indian lettuce".

Oxybasis chenopodioides, is a species of flowering plant in the family Amaranthaceae known by the common name low goosefoot.

Spinacia is a flowering plant genus in the subfamily Chenopodioideae of the family Amaranthaceae. The most common member is spinach.

Chenopodium nutans, known by its common name of climbing saltbush or nodding saltbush, is a climbing groundcover native to Australia.

Dysphania is a plant genus in the family Amaranthaceae, distributed worldwide from the tropics and subtropics to warm-temperate regions.

Oxybasis glauca, common name oak-leaved goosefoot, is a species of goosefoot plant native to Europe. It has been introduced and become an invasive weed in North America. This invader of European origin also appears in trampled communities in North Korea.

Chenopodium parabolicum, commonly known as fragrant saltbush or mealy saltbush, is a shrub in the family Amaranthaceae. The species is native to Australia.

Chenopodiastrum is a genus of herbaceous flowering plants in the family Amaranthaceae. The genus was formally described in 2012. The 5 species occur in Eurasia, North Africa, and North America.

Blitum is a genus of flowering plants in the amaranth family Amaranthaceae, subfamily Chenopodioideae. It is closely related to genus Spinacia. Its 12 species were traditionally placed in the genera Chenopodium, Monolepis, or Scleroblitum. The species of genus Blitum occur in Asia, Europe, North Africa, the Americas, and Australia.

Oxybasis is a flowering plant genus from the subfamily Chenopodioideae of the family Amaranthaceae. It was first described in 1841, and newly used since 2012 for five species that were traditionally grouped into genus Chenopodium. They occur in Europe, Asia, North Africa and America.

Lipandra polysperma, common name manyseed goosefoot, is the only species of the monotypic plant genus Lipandra from the subfamily Chenopodioideae of the family Amaranthaceae.

Atripliceae are a tribe of the subfamily Chenopodioideae belonging to the plant family Amaranthaceae. Atriplex is the largest genus of the tribe. Species of Atripiceae are ecologically important in steppe and semi-desert climates.

Chenopodium spinescens is a species of plant in the family Amaranthaceae and is endemic to all mainland states and territories of Australia where it is known as Rhagodia spinescens.
















