Moroccan music varies greatly between geographic regions and social groups. It is influenced by musical styles including Arab, Berber, Andalusi, Mediterranean, Saharan, West African, and others.

Essaouira, known until the 1960s as Mogador, is a port city in the western Moroccan region of Marrakesh-Safi, on the Atlantic coast. It has 77,966 inhabitants as of 2014.

Safi or Asfi is a city in western Morocco on the Atlantic Ocean. It is the capital of Asfi Province. It recorded a population of 308,508 in the 2014 Moroccan census. The city was occupied by the Portuguese Empire from 1488 to 1541, was the center of Morocco's weaving industry, and became a fortaleza of the Portuguese Crown in 1508. Safi is the main fishing port for the country's sardine industry, and also exports phosphates, textiles and ceramics. During the Second World War, Safi was the site of Operation Blackstone, one of the landing sites for Operation Torch.

The Regraga are a subgroup within the larger Masmuda Berber tribal confederacy of Morocco. They historically played a pivotal role in the cultural and religious landscape of the Chiadma region along the Atlantic coast, situated between Safi and Essaouira. The Regraga are noted for their spiritual practices and their annual pilgrimage, known locally as the Moussem, which spans 39 days and begins each year at the spring equinox.
Émile-Félix Gautier or Gauthier was a French geographer.
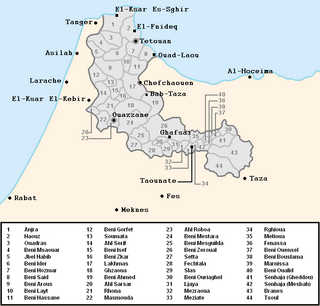
The Jebala are a tribal confederation inhabiting an area in northwest Morocco from the town of Ketema to the west. The Jbala region thus occupies the western part of the Rif mountains. The Jbala has a population of 1,284,000 and is divided into over 40 tribes, today known as "rural communes", and adjacent to them are a small group of nine tribes called the Ghmara (غمارة), who inhabit the territory between the line of mountain peaks to the north of Chefchaouen and the Mediterranean Sea. In addition to tribal heterogeneity, this region is also geographically diverse. High mountains are interspersed with hills and flatlands, and local inhabitants settle in both the high mountains and valleys. In addition to the rainy climate, which influences the way the inhabitants build their houses as well as their special agricultural practices, there are also numerous cultural characteristics that contribute to an emphasised sense of identity and make the Jbala people clearly distinguishable from their neighbours from the eastern part of the Rif Mountains where the climate is more arid, and from the former shepherds from the Atlantic coast (‘Arab). There are only a few cities in the country of the Jbala, and its population remains mostly rural. During the Middle Ages, chroniclers and historians knew the Jbala under their original name, Ghomara.

Fantasia is a traditional exhibition of horsemanship in the Maghreb performed during cultural festivals and for Maghrebi wedding celebrations. It is present in Algeria, Libya, Mali, Mauritania, Morocco, Niger and Tunisia. It is attested in the ancient Numidian times during which it was practiced by the Numidian cavalry. Historian Carlos Henriques Pereira stated that the North African fantasia also called barud is a modern watered down version of a Numidian military technique.
Charles Henri Marie Flahault was a French botanist, among the early pioneers of phytogeography, phytosociology, and forest ecology. The word relevé for a plant community sample is his invention.

The Val d'Anniviers is a Swiss Alpine valley, situated in the district of Sierre in Valais, which extends south of the Rhône Valley, on the northern slopes of the Pennine Alps. The valley was home to six municipalities: Ayer, Chandolin, Grimentz, Saint-Jean, Saint-Luc and Vissoie. The citizens of those municipalities agreed on November 26, 2006, to merge into one, which was named Anniviers. The merger took place in January 2009.
Maghrebis or Maghrebians are the inhabitants of the Maghreb region of North Africa. It is a modern Arabic term meaning "Westerners", denoting their location in the western part of the Arab world. Maghrebis are predominantly of Arab and Berber origins.

Jean-Bernard Racine was a professor of geography at the Institute of Geography, Faculty of Geosciences and Environment of the University of Lausanne (UNIL) and at HEC Lausanne Business School. Racine received his first PhD in geography from the University of Aix-en-Provence (1965) and his State PhD in geography (1973) from the University of Nice. Jean-Bernard Bernard was a professor at the University of Sherbrooke between 1965 and 1969, and at the University of Ottawa from 1969 to 1973.

Castelo Real was a Portuguese castle established in Mogador, now Essaouira in Morocco, by the Portuguese in 1506.

Tadla is a historical and geographical region of Morocco, located in the center of the country, north of the High Atlas mountain range and west of the Middle Atlas. It is the region of origin of the eponymous collection of tribal, semi-nomadic pastoralist population, the Tadla tribes.

Mayombe is a geographic area on the western coast of Africa occupied by low mountains extending from the mouth of the Congo River in the south to the Kouilou-Niari River to the north. The area includes parts of the Democratic Republic of the Congo, Angola, the Republic of the Congo and Gabon. In the Democratic Republic of the Congo, Mayombe is part of the north-western province of Kongo Central on the right bank of the River Congo, and contains the cities and towns of Lukula, Seke Banza, Kangu and Tshela.

Onésime Reclus was a French geographer who specialized in the relations between France and its colonies.

Jean Daniel François Schrader, better known as Franz Schrader, was a French mountaineer, geographer, cartographer and landscape painter, born in Bordeaux. He made an important contribution to the mapping of the Pyrenees and was highly considered among the pyreneists.
Christian Garnier (1872–1898) was a French geographer and linguist best known for developing a systematic transcription method for geographical names. At the age of 14, he became the youngest member of the Société de Géographie in Paris. He went on to write several books dealing with select topics of linguistic and geographical interest. Garnier died in 1898 at the age of 26 and was posthumously awarded the Prix Volney. In 1925, the Société de Géographie created the Christian Garnier Prize for contributions to the study of geography.

Louis Vivien, called Vivien de Saint-Martin, was a 19th-century French geographer.

Maximilien Sorre, known as Max Sorre, was a French geographer whose work was mainly in the areas of biological and human geography.

Following the spread of Islam, Algeria experienced three major waves of Arab migration that significantly altered its demographics and culture. The first wave occurred in the 7th century, with Arab political and trading elites settling mainly in large cities following the Muslim conquest of the Maghreb. This was followed by the large-scale migration of Bedouin tribes, including Banu Hilal, Banu Sulaym, and Banu Ma'qil in the 11th century, who settled in rural areas, especially the plains. Around the same time, Arabs from al-Andalus (Moors) also migrated, further contributing to the Arabization of the country. Gabriel Martinez described these Andalusian Arabs as the "watchdogs" of the Arabic language.
















