The Verbenaceae are a family — the verbena family or vervain family — of mainly tropical flowering plants. It contains trees, shrubs, and herbs notable for heads, spikes, or clusters of small flowers, many of which have an aromatic smell.

The Texas tortoise, is a species of tortoise in the family Testudinidae. The species G. berlandieri is one of six species of tortoises that are native to North America.
Jean-Louis Berlandier was a French-Mexican naturalist, physician, and anthropologist.

The Rio Grande leopard frog is a species of aquatic frog native to the southern United States in Texas and New Mexico, and south through Mexico and Central America. It is also sometimes referred to as the Mexican leopard frog. The epithet berlandieri is in honor of the naturalist Jean Louis Berlandier, who worked for the Mexican government on one of the first biological surveys of Texas.

Chenopodium berlandieri, also known by the common names pitseed goosefoot, huauzontle, lamb's quarters, and lambsquarters is an annual herbaceous plant in the family Amaranthaceae.

Senegalia berlandieri is a shrub native to the Southwestern United States and northeast Mexico that belongs to the Mimosoid clade of Fabaceae. It grows 1 to 5 metres tall, with blossoms that are spherical and white, occurring from February through April. The berlandieri epithet comes from the name of Jean-Louis Berlandier, a French naturalist who studied wildlife native to Texas and Mexico. S. berlandieri contains a wide variety of alkaloids and has been known to cause toxic reactions in domestic animals such as goats.

The Gulf Coast jaguarundi is a population of the jaguarundi. Two of these populations—the Gulf Coast jaguarundi and the Sinaloan jaguarundi—are considered endangered and were put on the endangered list on June 14, 1976. These cats are placed under the family Felidae and the subfamily Felinae because of their small size. As of 2017, the Cat Classification Taskforce of the Cat Specialist Group does not recognise any subspecies of jaguarundi.

Esenbeckia is a genus of flowering plants in the rue family, Rutaceae. All species in the genus are native to the Americas, with the highest diversity in South America. They are commonly known as jopoy, the Mayan word for E. berlandieri, or gasparillo (Spanish).

The Tamaulipan mezquital is a deserts and xeric shrublands ecoregion in the southern United States and northeastern Mexico. It covers an area of 141,500 km2 (54,600 sq mi), encompassing a portion of the Gulf Coastal Plain in southern Texas, northern Tamaulipas, northeastern Coahuila, and part of Nuevo León.

Jatropha cathartica is a species of flowering plant in the spurge family, Euphorbiaceae, that is native to Texas in the United States and Coahuila, Nuevo León and Tamaulipas in northeastern Mexico. Common names include jicamilla (Spanish) and Berlandier's nettlespurge.

Karwinskia humboldtiana, commonly known as coyotillo, cacachila or Humboldt coyotillo, is a species of flowering shrub or small tree in the family Rhamnaceae. It is native to southern and western Texas in the United States as well as much of Mexico. The seeds and leaves of this plant contain the quinones eleutherin and 7-methoxyeleutherin and chrysophanol and β-amyrin in the fruits that are toxic to humans and livestock. The toxins typically induce paralysis, which is often followed by death. However, it often takes days or even weeks after consumption for the symptoms to manifest.

Ebenopsis ebano is a species of flowering plant in the pea family, Fabaceae, that is native to the coastal plain of southern Texas in the United States and eastern Mexico. It is commonly known as Texas ebony or ebano.

Citharexylum is a genus of flowering plants in the verbena family, Verbenaceae. It contains shrub and tree species commonly known as fiddlewoods or zitherwoods. They are native to the Americas, ranging from southern Florida and Texas in the United States to Argentina. The highest diversity occurs in Mexico and the Andes. The generic name is derived from the Greek words κιθάρα (kithara), meaning "lyre", and ξύλον (xylon), meaning "wood," referring to the use of the wood in the sounding boards of string instruments. Several species, especially C. caudatum and C. spinosum, are cultivated as ornamentals.
- Citharexylum affineD.Don - from northern Mexico to Nicaragua
- Citharexylum alainiiMoldenke - Dominican Republic
- Citharexylum albicauleTurcz. - Cuba
- Citharexylum altamiranumGreenm. - northeastern Mexico
- Citharexylum andinumMoldenke - Bolivia, Jujuy Province of Argentina
- Citharexylum argutedentatumMoldenke - Peru
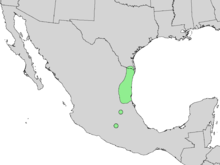
- Citharexylum berlandieriB.L. Rob. - from Texas to Oaxaca - Berlandier's fiddlewood, Tamaulipan fiddlewood
- Citharexylum bourgeauanumGreenm. - Veracruz, Oaxaca
- Citharexylum brachyanthum(A.Gray ex Hemsl.) A.Gray - Texas, Coahuila, Nuevo León - Boxthorn fiddlewood, Mexican fiddlewood
- Citharexylum bullatumMoldenke - Colombia
- Citharexylum calvumMoldenke - Quintana Roo
- Citharexylum caudatumL. - southern Mexico, West Indies, Central America, Colombia, Peru - Juniper berry
- Citharexylum chartaceumMoldenke - Peru, Ecuador
- Citharexylum cooperiStandl. - Costa Rica, Panama, Guatemala
- Citharexylum costaricenseMoldenke - Costa Rica, Nicaragua, Honduras
- Citharexylum crassifoliumGreenm - Chiapas, Belize, Guatemala, Honduras
- Citharexylum daniraeLeón de la Luz & F.Chiang - Revillagigedo Islands of Baja California
- Citharexylum decorumMoldenke - Colombia, Venezuela
- Citharexylum dentatumD.Don - Peru
- Citharexylum discolorTurcz. - Cuba, Hispaniola
- Citharexylum donnell-smithiiGreenm. - Oaxaca, Chiapas, Central America
- Citharexylum dryanderaeMoldenke - Colombia, Venezuela, Peru, Ecuador
- Citharexylum ekmaniiMoldenke - Cuba
- Citharexylum ellipticumMoc. & Sessé ex D.Don - Veracruz, Campeche, Tabasco; naturalized in Cuba + Cayman Islands
- Citharexylum endlichiiMoldenke - northeastern Mexico
- Citharexylum flabellifoliumS.Watson - Sonora, Baja California
- Citharexylum flexuosum(Ruiz & Pav.) D.Don - Bolivia, Peru
- Citharexylum fulgidumMoldenke - Veracruz, northeastern Mexico
- Citharexylum gentryiMoldenke - Ecuador
- Citharexylum glabrum(S.Watson) Greenm - Oaxaca
- Citharexylum glazioviiMoldenke - eastern Brazil
- Citharexylum grandiflorumAymard & Rueda - Ecuador
- Citharexylum guatemalense(Moldenke) D.N.Gibson - Guatemala, Nicaragua
- Citharexylum herreraeMansf. - Peru
- Citharexylum hexangulareGreenm. - from northern Mexico to Costa Rica
- Citharexylum hidalgenseMoldenke - Mexico
- Citharexylum hintoniiMoldenke - México State
- Citharexylum hirtellumStandl. - from Veracruz to Panama
- Citharexylum ilicifoliumKunth - Bolivia, Peru, Ecuador
- Citharexylum iltisiiMoldenke - Peru
- Citharexylum × jamaicenseMoldenke - Jamaica, Haiti, Puerto Rico (C. caudatum × C. spinosum)
- Citharexylum joergensenii(Lillo) Moldenke - Argentina, Bolivia
- Citharexylum karsteniiMoldenke - Colombia, Venezuela
- Citharexylum kerberiGreenm. - Veracruz
- Citharexylum kobuskianumMoldenke - Peru
- Citharexylum krukoviiMoldenke - eastern Brazil
- Citharexylum kunthianumMoldenke - Colombia, Venezuela, Ecuador
- Citharexylum laetumHiern - southern Brazil
- Citharexylum laurifoliumHayek - Bolivia, Peru
- Citharexylum lemsiiMoldenke - Guanacaste Province in Costa Rica
- Citharexylum × leonisMoldenke - Cuba (C. caudatum × C. tristachyum)
- Citharexylum ligustrifolium(Thur. ex Decne.) Van Houtte - Mexico
- Citharexylum lojenseMoldenke - Ecuador
- Citharexylum lucidumCham. & Schltdl. - Mexico
- Citharexylum lycioidesD.Don - Mexico
- Citharexylum macradeniumGreenm. - Panama, Costa Rica
- Citharexylum macrochlamysPittier - Panama, Colombia
- Citharexylum macrophyllumPoir. - Colombia, Venezuela, Ecuador, Guianas, northwestern Brazil
- Citharexylum matheanumBorhidi & Kereszty - Cuba
- Citharexylum matudaeMoldenke - Chiapas
- Citharexylum mexicanumMoldenke - Veracruz, Puebla, Oaxaca
- Citharexylum microphyllum(DC.) O.E.Schulz - Hisipaniola
- Citharexylum mirifoliumMoldenke - Colombia, Venezuela
- Citharexylum mocinoiD.Don - Mexico, Central America
- Citharexylum montanumMoldenke - Colombia, Ecuador
- Citharexylum montevidense(Spreng.) Moldenke - Brazil, Argentina, Paraguay, Uruguay
- Citharexylum myrianthumCham. - Brazil, Argentina, Paraguay
- Citharexylum obtusifoliumKuhlm - Espírito Santo
- Citharexylum oleinum Moldenke - Mexico
- Citharexylum ovatifoliumGreenm. - Mexico
- Citharexylum pachyphyllumMoldenke - Peru
- Citharexylum pernambucenseMoldenke - eastern Brazil
- Citharexylum poeppigiiWalp. - Colombia, Venezuela, Ecuador, Bolivia, Peru, Brazil
- Citharexylum punctatumGreenm. - Bolivia, Peru
- Citharexylum quercifoliumHayek - Peru
- Citharexylum quitenseSpreng. - Ecuador
- Citharexylum racemosumSessé & Moc. - Mexico
- Citharexylum reticulatumKunth - Ecuador, Peru
- Citharexylum rigidum(Briq.) Moldenke - Paraguay, southern Brazil
- Citharexylum rimbachiiMoldenke - Ecuador
- Citharexylum roseiGreenm. - Mexico
- Citharexylum roxanaeMoldenke - Baja California
- Citharexylum scabrumMoc. & Sessé ex D.Don - northern Mexico
- Citharexylum schottiiGreenm. - southern Mexico, Central America
- Citharexylum schulziiUrb. & Ekman - Hispaniola
- Citharexylum sessaeiD.Don - Mexico
- Citharexylum shreveiMoldenke - Sonora
- Citharexylum solanaceumCham. - southern Brazil
- Citharexylum spinosumL. – Spiny fiddlewood - West Indies, Panama, Venezuela, the Guianas; naturalized in India, Mozambique, Fiji, Bermuda
- Citharexylum stenophyllumUrb. & Ekman - Haiti
- Citharexylum steyermarkiiMoldenke - Veracruz, Chiapas, Guatemala
- Citharexylum suberosumLoes. ex Moldenke - Cuba
- Citharexylum subflavescensS.F.Blake - Colombia, Venezuela, Ecuador, Peru
- Citharexylum subthyrsoideumPittier - Colombia, Venezuela
- Citharexylum subtruncatumMoldenke - northwestern Brazil
- Citharexylum sulcatumMoldenke - Colombia
- Citharexylum svensoniiMoldenke - Ecuador
- Citharexylum teclenseStandl. - El Salvador
- Citharexylum ternatumMoldenke - Cuba
- Citharexylum tetramerumBrandegee - Valle de Tehuacán-Cuicatlán in Mexico
- Citharexylum tristachyumTurcz. – Threespike Fiddlewood - Cuba, Jamaica, Leeward Islands
- Citharexylum uleiMoldenke - Colombia, Peru, northwestern Brazil
- Citharexylum vallenseMoldenke - Colombia
- Citharexylum venezuelenseMoldenke - Venezuela
- Citharexylum weberbaueriHayek - Peru

Diospyros texana is a species of persimmon that is native to central, south and west Texas and southwest Oklahoma in the United States, and eastern Chihuahua, Coahuila, Nuevo León, and Tamaulipas in northeastern Mexico. Common names include Texas persimmon, Mexican persimmon and the more ambiguous "black persimmon". It is known in Spanish as chapote, chapote manzano, or chapote prieto, all of which are derived from the Nahuatl word tzapotl. That word also refers to several other fruit-bearing trees.
Esenbeckia runyonii is a species of flowering tree in the citrus family, Rutaceae, that is native to northeastern Mexico, with a small, disjunct population in the Lower Rio Grande Valley of Texas in the United States. Common names include Limoncillo and Runyon's Esenbeckia. The specific epithet honors Robert Runyon, a botanist and photographer from Brownsville, Texas, who collected the type specimen from a stand of four trees discovered by Harvey Stiles on the banks of Resaca del Rancho Viejo, Texas, in 1929. Conrad Vernon Morton of the Smithsonian Institution received the plant material and formally described the species in 1930. Some consider it a synonym of E. berlandieriBaill. ex Hemsl..

Lippia graveolens, a species of flowering plant in the verbena or vervain family, Verbenaceae, is native to the southwestern United States, Mexico, and Central America as far south as Nicaragua. Common names include: Mexican oregano, redbrush lippia, orégano cimarrón, scented lippia, and scented matgrass. The specific epithet is derived from two Latin words: gravis, meaning 'heavy', and oleo, meaning 'oil'. It is a shrub or small tree, reaching 1–2.7 m (3.3–8.9 ft) in height. Fragrant white or yellowish flowers can be found on the plant throughout the year, especially after rains.

Citharexylum spinosum is a species of flowering plant in the family Verbenaceae that is native to southern Florida in the United States, the Caribbean, Guyana, Suriname, and Venezuela. Common names include Florida fiddlewood and spiny fiddlewood.

Lycium berlandieri is a species of flowering plant in the nightshade family known by the common name Berlandier's wolfberry. It is native to Mexico and the south-western United States from Arizona to Texas.
Berlandieri, a word referring to French naturalist Jean-Louis Berlandier, may refer to:

Aconophora compressa is a species of insect in the treehopper family, Membracidae. It is known by the common names lantana bug, lantana treehopper, lantana stemsucking treehopper, and lantana sap-sucking bug.