
Clostridium is a genus of anaerobic, Gram-positive bacteria. Species of Clostridium inhabit soils and the intestinal tract of animals, including humans. This genus includes several significant human pathogens, including the causative agents of botulism and tetanus. It also formerly included an important cause of diarrhea, Clostridioides difficile, which was reclassified into the Clostridioides genus in 2016.

Clostridium acetobutylicum, ATCC 824, is a commercially valuable bacterium sometimes called the "Weizmann Organism", after Jewish Russian-born biochemist Chaim Weizmann. A senior lecturer at the University of Manchester, England, he used them in 1916 as a bio-chemical tool to produce at the same time, jointly, acetone, ethanol, and n-butanol from starch. The method has been described since as the ABE process,, yielding 3 parts of acetone, 6 of n-butanol, and 1 of ethanol. Acetone was used in the important wartime task of casting cordite. The alcohols were used to produce vehicle fuels and synthetic rubber.

Butanol may be used as a fuel in an internal combustion engine. It is more similar to gasoline than it is to ethanol. A C4-hydrocarbon, butanol is a drop-in fuel and thus works in vehicles designed for use with gasoline without modification. Both n-butanol and isobutanol have been studied as possible fuels. Both can be produced from biomass (as "biobutanol" ) as well as from fossil fuels (as "petrobutanol"). The chemical properties depend on the isomer (n-butanol or isobutanol), not on the production method.
Acetivibrio thermocellus is an anaerobic, thermophilic bacterium. A. thermocellus has garnered research interest due to its cellulolytic and ethanologenic abilities, being capable of directly converting a cellulosic substrate into ethanol by consolidated bioprocessing. This makes it useful in converting biomass into a usable energy source. The degradation of the cellulose is carried out in the bacterium by a large extracellular cellulase system called a cellulosome, which contains nearly 20 catalytic subunits. The cellulase system of the bacterium significantly differs from fungal cellulases due to its high activity on crystalline cellulose, being able to completely solubilize crystalline sources of cellulose, such as cotton. However, there are some shortfalls in applying the organism to practical applications due to it having low ethanol yield, at least partially due to branched fermentation pathways that produce acetate, formate, and lactate along with ethanol. There is also evidence of inhibition due to the presence of hydrogen and due to agitation. Some recent research has been directed to optimizing the ethanol-producing metabolic pathway in hopes of creating more efficient biomass conversion.
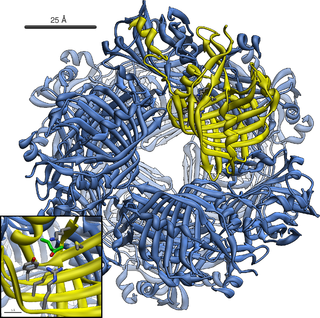
Acetoacetate decarboxylase is an enzyme involved in both the ketone body production pathway in humans and other mammals, and solventogenesis in bacteria. Acetoacetate decarboxylase plays a key role in solvent production by catalyzing the decarboxylation of acetoacetate, yielding acetone and carbon dioxide.

Enterobacter cloacae is a clinically significant Gram-negative, facultatively-anaerobic, rod-shaped bacterium.
Klebsiella aerogenes, previously known as Enterobacter aerogenes, is a Gram-negative, oxidase-negative, catalase-positive, citrate-positive, indole-negative, rod-shaped bacterium. Capable of motility via peritrichous flagella, the bacterium is approximately 1–3 microns in length.
Clostridium tyrobutyricum is a rod-shaped, Gram-positive bacterium that grows under anaerobic conditions and produces butyric acid, acetic acid and hydrogen gas as the major fermentation products from glucose and xylose.

Acetone–butanol–ethanol (ABE) fermentation, also known as the Weizmann process, is a process that uses bacterial fermentation to produce acetone, n-butanol, and ethanol from carbohydrates such as starch and glucose. It was developed by chemist Chaim Weizmann and was the primary process used to produce acetone, which was needed to make cordite, a substance essential for the British war industry during World War I.
Clostridium ljungdahlii is an anaerobic, rod-shaped, motile, endospore-forming, gram-positive bacterium. It is named after the biochemist Lars G. Ljungdahl. When originally harvested from the waste matter of animals, it tended to produce acetate with respect to ethanol, but a major undertaking to increase the ethanol-to-acetate ratio was initiated. A 1993 publication by researchers from the University of Arkansas, in cooperation with Oak Ridge National Laboratories, showed results from a series of continuous reactor studies caused a major change in the bacterium's preference for ethanol production, which increased from <0.1 g/L to 1.8 g/L in a continuous stirred tank reactor.
Bacillus pumilus is a Gram-positive, aerobic, spore-forming bacillus commonly found in soil.
Caldicellulosiruptor bescii is a species of thermophilic, anaerobic cellulolytic bacteria. It was isolated from a geothermally heated freshwater pool in the Valley of Geysers on the Kamchatka Peninsula in Russia in 1990. The species was originally named Anaerocellum thermophilum, but reclassified in 2010, based on genomic data.
Moorella thermoautotrophica, previously known as Clostridium thermoautotrophicum, is a rod-shaped, endospore-forming bacterium belonging to the phylum Bacillota. It is thermophilic, strictly anaerobic and acetogenic, and was isolated from a hot spring in Yellowstone National Park USA.
Thiomonas intermedia is a Gram-negative, aerobic, moderately acidophilic bacterium from the genus Thiomonas, which has the ability to oxidise sulfur compounds. Thiomonas intermedia was isolated from an sewage pipe in Hamburg.
Syntrophococcus sucromutans is a Gram-negative strictly anaerobic chemoorganotrophic Bacillota. These bacteria can be found forming small chains in the habitat where it was first isolated, the rumen of cows. It is the type strain of genus Syntrophococcus and it has an uncommon one-carbon metabolic pathway, forming acetate from formate as a product of sugar oxidation.
Clostridium saccharoperbutylacetonicum is an indole and notably butanol-producing bacterium, with the type strain N1-4 (HMT). Its genome has been sequenced.
Clostridium saccharobutylicum is an indole and notably acetone, butanol and ethanol-producing bacterium, with type strain DSM 13864T. Its genome has been sequenced.
Clostridium pasteurianum is a bacterium discovered in 1890 by the Russian microbiologist Sergei Winogradsky. It was the first free living (non-symbiotic) micro-organism discovered that could fix free nitrogen from the air.

Streptomyces puniceus is a bacterium species from the genus of Streptomyces which has been isolated from soil. Streptomyces puniceus produces vinactane and viomycin.
Clostridium carboxidivorans is a Gram-positive anaerobic, spore-forming and motile bacterium from the genus Clostridium which has been isolated from an agricultural lagoon in Oklahoma in the United States.







