
Beta blockers, also spelled β-blockers, are a class of medications that are predominantly used to manage abnormal heart rhythms (arrhythmia), and to protect the heart from a second heart attack after a first heart attack. They are also widely used to treat high blood pressure, although they are no longer the first choice for initial treatment of most patients.

Propranolol, sold under the brand name Inderal among others, is a medication of the beta blocker class. It is used to treat high blood pressure, a number of types of irregular heart rate, thyrotoxicosis, capillary hemangiomas, performance anxiety, and essential tremors, as well to prevent migraine headaches, and to prevent further heart problems in those with angina or previous heart attacks. It can be taken orally or by intravenous injection. The formulation that is taken orally comes in short-acting and long-acting versions. Propranolol appears in the blood after 30 minutes and has a maximum effect between 60 and 90 minutes when taken orally.
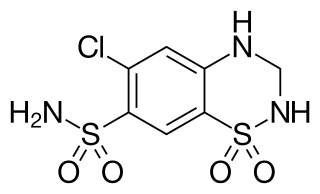
Hydrochlorothiazide, sold under the brand name Hydrodiuril among others, is a diuretic medication used to treat hypertension and swelling due to fluid build-up. Other uses include treating diabetes insipidus and renal tubular acidosis and to decrease the risk of kidney stones in those with a high calcium level in the urine. Hydrochlorothiazide is taken by mouth and may be combined with other blood pressure medications as a single pill to increase effectiveness. Hydrochlorothiazide is a thiazide medication which inhibits reabsorption of sodium and chloride ions from the distal convoluted tubules of the kidneys, causing a natriuresis. This initially increases urine volume and lowers blood volume. It is believed to reduce peripheral vascular resistance.
Antihypertensives are a class of drugs that are used to treat hypertension. Antihypertensive therapy seeks to prevent the complications of high blood pressure, such as stroke, heart failure, kidney failure and myocardial infarction. Evidence suggests that reduction of the blood pressure by 5 mmHg can decrease the risk of stroke by 34% and of ischaemic heart disease by 21%, and can reduce the likelihood of dementia, heart failure, and mortality from cardiovascular disease. There are many classes of antihypertensives, which lower blood pressure by different means. Among the most important and most widely used medications are thiazide diuretics, calcium channel blockers, ACE inhibitors, angiotensin II receptor antagonists (ARBs), and beta blockers.

Esophageal varices are extremely dilated sub-mucosal veins in the lower third of the esophagus. They are most often a consequence of portal hypertension, commonly due to cirrhosis. People with esophageal varices have a strong tendency to develop severe bleeding which left untreated can be fatal. Esophageal varices are typically diagnosed through an esophagogastroduodenoscopy.
Atenolol is a beta blocker medication primarily used to treat high blood pressure and heart-associated chest pain. Atenolol, however, does not seem to improve mortality in those with high blood pressure. Other uses include the prevention of migraines and treatment of certain irregular heart beats. It is taken orally or by intravenous injection. It can also be used with other blood pressure medications.

Sotalol, sold under the brand name Betapace among others, is a medication used to treat and prevent abnormal heart rhythms. Evidence does not support a decreased risk of death with long term use. It is taken by mouth or given by injection into a vein.

Chlortalidone, also known as chlorthalidone, is a thiazide-like diuretic drug used to treat high blood pressure, swelling, diabetes insipidus, and renal tubular acidosis. Because chlortalidone is reliably effective in most patients with high blood pressure, it is considered a preferred initial treatment. It is also used to prevent calcium-based kidney stones. It is taken by mouth. Effects generally begin within three hours and last for up to three days. Long-term treatment with chlortalidone is more effective than hydrochlorothiazide for prevention of heart attack or stroke.

Losartan, sold under the brand name Cozaar among others, is a medication used to treat high blood pressure (hypertension). It is in the angiotensin receptor blocker (ARB) family of medication, and is considered protective of the kidneys. Besides hypertension, it is also used in diabetic kidney disease, heart failure, and left ventricular enlargement. It comes as a tablet that is taken by mouth. It may be used alone or in addition to other blood pressure medication. Up to six weeks may be required for the full effects to occur.
Alpha-1 blockers constitute a variety of drugs that block the effect of catecholamines on alpha-1-adrenergic receptors. They are mainly used to treat benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH), hypertension and post-traumatic stress disorder. Alpha-1 adrenergic receptors are present in vascular smooth muscle, the central nervous system, and other tissues. When alpha blockers bind to these receptors in vascular smooth muscle, they cause vasodilation.
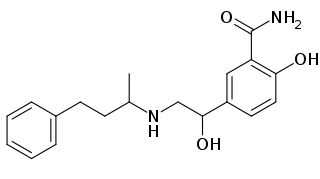
Labetalol is a medication used to treat high blood pressure and in long term management of angina. This includes essential hypertension, hypertensive emergencies, and hypertension of pregnancy. In essential hypertension it is generally less preferred than a number of other blood pressure medications. It can be given by mouth or by injection into a vein.
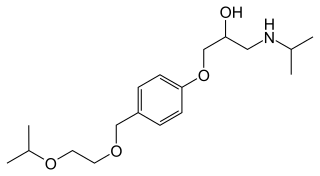
Bisoprolol, sold under the brand name Zebeta among others, is a beta blocker medication used for heart diseases. This includes tachyarrhythmias, high blood pressure, chest pain from not enough blood flow to the heart, and heart failure. It is taken by mouth.
Atenolol/chlorthalidone, also known as co-tenidone, is a combination medication used to treat high blood pressure. It is made up of atenolol, a beta-blocker and chlortalidone, a diuretic. It is not recommended as an initial treatment but may be used in those who are taking atenolol and chlortalidone individually. It is taken by mouth.

Perindopril is a medication used to treat high blood pressure, heart failure, or stable coronary artery disease.

Nebivolol is a beta blocker used to treat high blood pressure and heart failure. As with other β-blockers, it is generally a less preferred treatment for high blood pressure. It may be used by itself or with other blood pressure medication. It is taken by mouth.

An adrenergic antagonist is a drug that inhibits the function of adrenergic receptors. There are five adrenergic receptors, which are divided into two groups. The first group of receptors are the beta (β) adrenergic receptors. There are β1, β2, and β3 receptors. The second group contains the alpha (α) adrenoreceptors. There are only α1 and α2 receptors. Adrenergic receptors are located near the heart, kidneys, lungs, and gastrointestinal tract. There are also α-adreno receptors that are located on vascular smooth muscle.
Co-amilozide (BAN) is a non-proprietary combination of amiloride and hydrochlorothiazide. Co-amilozide is used in the treatment of hypertension and congestive heart failure with the tendency of the thiazide to cause low potassium levels (hypokalaemia) offset by the potassium-sparing effects of amiloride.
Arotinolol is a medication in the class of mixed alpha/beta blockers. It also acts as a β3 receptor agonist. A 1979 publication suggests arotinolol as having first been described in the scientific literature by Sumitomo Chemical as "β-adrenergic blocking, antiarrhythmic compound S-596".

Antiarins are cardiac glycoside poisons produced by the upas tree. There are two forms, α-antiarin and β-antiarin.

β adrenergic receptor antagonists were initially developed in the 1960s, for the treatment of angina pectoris but are now also used for hypertension, congestive heart failure and certain arrhythmias. In the 1950s, dichloroisoproterenol (DCI) was discovered to be a β-antagonist that blocked the effects of sympathomimetic amines on bronchodilation, uterine relaxation and heart stimulation. Although DCI had no clinical utility, a change in the compound did provide a clinical candidate, pronethalol, which was introduced in 1962.













