
Necrosis is a form of cell injury which results in the premature death of cells in living tissue by autolysis. The term "necrosis" came about in the mid-19th century and is commonly attributed to German pathologist Rudolf Virchow in, who is often regarded as one of the founders of modern pathology. Necrosis is caused by factors external to the cell or tissue, such as infection, or trauma which result in the unregulated digestion of cell components. In contrast, apoptosis is a naturally occurring programmed and targeted cause of cellular death. While apoptosis often provides beneficial effects to the organism, necrosis is almost always detrimental and can be fatal.
Thrombosis is the formation of a blood clot inside a blood vessel, obstructing the flow of blood through the circulatory system. When a blood vessel is injured, the body uses platelets (thrombocytes) and fibrin to form a blood clot to prevent blood loss. Even when a blood vessel is not injured, blood clots may form in the body under certain conditions. A clot, or a piece of the clot, that breaks free and begins to travel around the body is known as an embolus.

Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) is the most common type of primary liver cancer in adults and is currently the most common cause of death in people with cirrhosis. HCC is the third leading cause of cancer-related deaths worldwide.

Disseminated intravascular coagulation (DIC) is a condition in which blood clots form throughout the body, blocking small blood vessels. Symptoms may include chest pain, shortness of breath, leg pain, problems speaking, or problems moving parts of the body. As clotting factors and platelets are used up, bleeding may occur. This may include blood in the urine, blood in the stool, or bleeding into the skin. Complications may include organ failure.
Interventional radiology (IR) is a medical specialty that performs various minimally-invasive procedures using medical imaging guidance, such as x-ray fluoroscopy, computed tomography, magnetic resonance imaging, or ultrasound. IR performs both diagnostic and therapeutic procedures through very small incisions or body orifices. Diagnostic IR procedures are those intended to help make a diagnosis or guide further medical treatment, and include image-guided biopsy of a tumor or injection of an imaging contrast agent into a hollow structure, such as a blood vessel or a duct. By contrast, therapeutic IR procedures provide direct treatment—they include catheter-based medicine delivery, medical device placement, and angioplasty of narrowed structures.

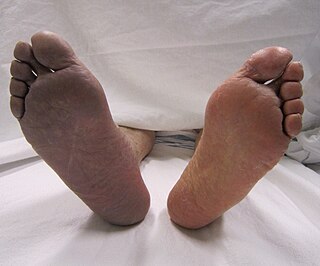
Ischemia or ischaemia is a restriction in blood supply to any tissue, muscle group, or organ of the body, causing a shortage of oxygen that is needed for cellular metabolism. Ischemia is generally caused by problems with blood vessels, with resultant damage to or dysfunction of tissue i.e. hypoxia and microvascular dysfunction. It also implies local hypoxia in a part of a body resulting from constriction. Ischemia causes not only insufficiency of oxygen, but also reduced availability of nutrients and inadequate removal of metabolic wastes. Ischemia can be partial or total blockage. The inadequate delivery of oxygenated blood to the organs must be resolved either by treating the cause of the inadequate delivery or reducing the oxygen demand of the system that needs it. For example, patients with myocardial ischemia have a decreased blood flow to the heart and are prescribed with medications that reduce chronotrophy and ionotrophy to meet the new level of blood delivery supplied by the stenosed vasculature so that it is adequate.
Infarction is tissue death (necrosis) due to inadequate blood supply to the affected area. It may be caused by artery blockages, rupture, mechanical compression, or vasoconstriction. The resulting lesion is referred to as an infarct (from the Latin infarctus, "stuffed into").
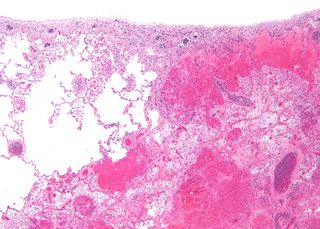
Liquefactive necrosis is a type of necrosis which results in a transformation of the tissue into a liquid viscous mass. Often it is associated with focal bacterial or fungal infections, and can also manifest as one of the symptoms of an internal chemical burn. In liquefactive necrosis, the affected cell is completely digested by hydrolytic enzymes, resulting in a soft, circumscribed lesion consisting of pus and the fluid remains of necrotic tissue. Dead leukocytes will remain as a creamy yellow pus. After the removal of cell debris by white blood cells, a fluid filled space is left. It is generally associated with abscess formation and is commonly found in the central nervous system.

Cerebral infarction is the pathologic process that results in an area of necrotic tissue in the brain. It is caused by disrupted blood supply (ischemia) and restricted oxygen supply (hypoxia), most commonly due to thromboembolism, and manifests clinically as ischemic stroke. In response to ischemia, the brain degenerates by the process of liquefactive necrosis.

High-intensity focused ultrasound (HIFU) is a non-invasive therapeutic technique that uses non-ionizing ultrasonic waves to heat or ablate tissue. HIFU can be used to increase the flow of blood or lymph or to destroy tissue, such as tumors, via thermal and mechanical mechanisms. Given the prevalence and relatively low cost of ultrasound generation mechanisms, The premise of HIFU is that it is expect a non-invasive and low-cost therapy that can at minimum outperform operating room care.

A bowel resection or enterectomy is a surgical procedure in which a part of an intestine (bowel) is removed, from either the small intestine or large intestine. Often the word enterectomy is reserved for the sense of small bowel resection, in distinction from colectomy, which covers the sense of large bowel resection. Bowel resection may be performed to treat gastrointestinal cancer, bowel ischemia, necrosis, or obstruction due to scar tissue, volvulus, and hernias. Some patients require ileostomy or colostomy after this procedure as alternative means of excretion. Complications of the procedure may include anastomotic leak or dehiscence, hernias, or adhesions causing partial or complete bowel obstruction. Depending on which part and how much of the intestines are removed, there may be digestive and metabolic challenges afterward, such as short bowel syndrome.
Myocytolysis refers to a state of significant damage to cardiac myocytes, muscle cells of the heart, caused by myocardial strain. It was first described in medical literature by Schlesinger and Reiner in 1955. It is considered a type of cellular necrosis. Two types of myocytolysis have been defined: coagulative and colliquative.

Liver cancer is cancer that starts in the liver. Liver cancer can be primary or secondary. Liver metastasis is more common than that which starts in the liver. Liver cancer is increasing globally.

Fat necrosis is a form of necrosis that is caused by the action of lipases on adipocytes.

A limb infarction is an area of tissue death of an arm or leg. It may cause skeletal muscle infarction, avascular necrosis of bones, or necrosis of a part of or an entire limb.
Myocardial infarction complications may occur immediately following a heart attack, or may need time to develop. After an infarction, an obvious complication is a second infarction, which may occur in the domain of another atherosclerotic coronary artery, or in the same zone if there are any live cells left in the infarct.

Sonodynamic therapy (SDT) is a noninvasive treatment, often used for tumor irradiation, that utilizes a sonosensitizer and the deep penetration of ultrasound to treat lesions of varying depths by reducing target cell number and preventing future tumor growth. Many existing cancer treatment strategies cause systemic toxicity or cannot penetrate tissue deep enough to reach the entire tumor; however, emerging ultrasound stimulated therapies could offer an alternative to these treatments with their increased efficiency, greater penetration depth, and reduced side effects. Sonodynamic therapy could be used to treat cancers and other diseases, such as atherosclerosis, and diminish the risk associated with other treatment strategies since it induces cytotoxic effects only when externally stimulated by ultrasound and only at the cancerous region, as opposed to the systemic administration of chemotherapy drugs.

Necroptosis is a programmed form of necrosis, or inflammatory cell death. Conventionally, necrosis is associated with unprogrammed cell death resulting from cellular damage or infiltration by pathogens, in contrast to orderly, programmed cell death via apoptosis. The discovery of necroptosis showed that cells can execute necrosis in a programmed fashion and that apoptosis is not always the preferred form of cell death. Furthermore, the immunogenic nature of necroptosis favors its participation in certain circumstances, such as aiding in defence against pathogens by the immune system. Necroptosis is well defined as a viral defense mechanism, allowing the cell to undergo "cellular suicide" in a caspase-independent fashion in the presence of viral caspase inhibitors to restrict virus replication. In addition to being a response to disease, necroptosis has also been characterized as a component of inflammatory diseases such as Crohn's disease, pancreatitis, and myocardial infarction.

Osteoradionecrosis (ORN) is a serious complication of radiation therapy in cancer treatment where radiated bone becomes necrotic and exposed. ORN occurs most commonly in the mouth during the treatment of head and neck cancer, and can arise over 5 years after radiation. Common signs and symptoms include pain, difficulty chewing, trismus, mouth-to-skin fistulas and non-healing ulcers.
Interventional oncology is a subspecialty field of interventional radiology that deals with the diagnosis and treatment of cancer and cancer-related problems using targeted minimally invasive procedures performed under image guidance. Interventional oncology has developed to a separate pillar of modern oncology and it employs X-ray, ultrasound, computed tomography (CT) or magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) to help guide miniaturized instruments to allow targeted and precise treatment of solid tumours located in various organs of the human body, including but not limited to the liver, kidneys, lungs, and bones. Interventional oncology treatments are routinely carried out by interventional radiologists in appropriate settings and facilities.















