Diseases
Oral and maxillofacial pathology can involve many different types of tissues of the head. Different disease processes affect different tissues within this region with various outcomes. A great many diseases involve the mouth, jaws and orofacial skin. The following list is a general outline of pathologies that can affect oral and maxillofacial region; some are more common than others. This list is by no means exhaustive.
Congenital
Cleft lip and palate
Cleft lip and palate is one of the most common occurring multi-factorial congenital disorder occurring in 1 in 500–1000 live births in several forms. [8] [9] [10] The most common form is combined cleft lip and palate and it accounts for approximately 50% of cases, whereas isolated cleft lip concerns 20% of the patients. [11]
People with cleft lip and palate malformation tend to be less social and report lower self-esteem, anxiety and depression related to their facial malformation. [12] [13] One of the major goals in the treatment of patients with cleft is to enhance social acceptance by surgical reconstruction.
A cleft lip is an opening of the upper lip, mainly due to the failure of fusion of the medial nasal processes with the palatal processes; a cleft palate is the opening of the soft and hard palate in the mouth, which is due to the failure of the palatal shelves to fuse together. [10]
The palate's main function is to demarcate the nasal and oral cavity, without which the patient will have problems with swallowing, eating and speech, thus affecting the quality of life and in some cases certain functions. [10]
Some examples include food going up into the nasal cavity during swallowing as the soft palate is not present to close the cavity during the process. Speech is also affected as the nasal cavity is a source of resonance during speech and failure to manipulate spaces in the cavities will result in the lack of ability to produce certain consonants in audible language. [10]
Macroglossia
Macroglossia is a rare condition, categorised by tongue enlargement which will eventually create a crenated border in relation to the embrasures between the teeth. [14]
Hereditary causes include vascular malformations, Down syndrome, Beckwith–Wiedemann syndrome, Duchenne muscular dystrophy, and Neurofibromatosis type I. [14]
Acquired causes include carcinoma, [14] lingual thyroid, [5] myxedema, [14] and amyloidosis. [14]
Consequences may include noisy breaths – airway obstruction in severe cases, drooling, difficulty eating, lisping speech, open bite, and protruding tongue, which may ulcerate and undergo necrosis. [14]
For mild cases, surgical treatment is not mandatory but if speech is affected, speech therapy may be useful. Reduction glossectomy may be required for severe cases. [14]
Ankyloglossia
Ankyloglossia (also known as tongue-tie) may decrease the mobility of the tongue tip [15] and is caused by an unusually short, thick lingual frenulum, a membrane connecting the underside of the tongue to the floor of the mouth. [16]
Stafne defect
Stafne defect, or lingual mandibular cortical defect, is a depression of the mandible, most commonly located on the lingual surface (the inside of the jawbone, near the tongue). [17]
Torus palatinus
Torus palatinus is a bony protrusion on the palate, usually present on the midline of the hard palate.[ citation needed ]
Torus mandibularis
Torus mandibularis is a bony growth in the mandible along the surface nearest to the tongue. Mandibular tori usually are present near the premolars and above the location on the mandible of the mylohyoid muscle attachment. [18]
Eagle syndrome
Eagle syndrome is a condition where there is an abnormal ossification of the stylohyoid ligament. This leads to an increase in the thickness and the length of the stylohyoid process and the ligament. Pain is felt due to the pressure applied to the internal jugular vein. Eagle syndrome occurs due to elongation of the styloid process or calcification of the stylohyoid ligament. However, the cause of the elongation has not been known clearly. It could occur spontaneously or could arise since birth. Usually normal stylohyoid process is 2.5–3 cm in length, if the length is longer than 3 cm, it is classified as an elongated stylohyoid process. [19]
Acquired
Infective

Bacterial
- (Plaque-induced) gingivitis—A common periodontal (gum) disease is gingivitis. Periodontal refers to the area the infection affects, which include the teeth, gums, and tissues surrounding the teeth. Bacteria cause inflammation of the gums which become red, swollen and can bleed easily. The bacteria along with mucus form a sticky colorless substance called plaque which harbours the bacteria. Plaque that is not removed by brushing and flossing hardens to form tartar that brushing does not clean. Smoking is a major risk factor. [20] Treatment of gingivitis is dependent on how severe and how far the disease has progressed. If the disease is not too severe it is possible to treat it with chlorhexidine rinse and brushing with fluoride toothpaste to kill the bacteria and remove the plaque, but once the infection has progressed antibiotics may be needed to kill the bacteria. [21]
- Periodontitis—When gingivitis is not treated it can advance to periodontitis, when the gums pull away from the teeth and form pockets that harbor the bacteria. Bacterial toxins and the body's natural defenses start to break down the bone and connective tissues. The tooth may eventually become loose and have to be removed.
- Scarlet fever is caused by a particular streptococci species, Streptococci Pyogenes, and is classified be a severe form of bacterial sore throat. The condition involves the release of pyrogenic and erythrogenic endotoxins from the immune system. [22] It starts as tonsilitis and pharyngitis before involving the soft palate and the tongue. It usually occurs in children where a fever occurs and an erythematous rash develops on the face and spreads to most part of the body. If not treated, late stages of this condition may include a furred, raw, red tongue. [22] Treatment options include penicillin and the prognosis is generally excellent. [4]
Viral
- Herpes simplex (infection with herpes simplex virus, or HSV) is very common in the mouth and lips. This virus can cause blisters and sores around the mouth (herpetic gingivostomatitis) and lips (herpes labialis). HSV infections tend to recur periodically. Although many people get infected with the virus, only 10% actually develop the sores. The sores may last anywhere from 3–10 days and are very infectious. Some people have recurrences either in the same location or at a nearby site. Unless the individual has an impaired immune system, e.g., owing to HIV or cancer-related immune suppression, [23] recurrent infections tend to be mild in nature and may be brought on by stress, sun, menstrual periods, trauma or physical stress. [24]
- Mumps of the salivary glands is a viral infection of the parotid glands. This results in painful swelling at the sides of the mouth in both adults and children, which leads to a sore throat, and occasionally pain in chewing. [22] The infection is quite contagious. Mumps is prevented through vaccination in infancy with the measles, mumps, and rubella (MMR) vaccination and subsequent boosters. There is no specific treatment for mumps except for hydration and painkillers with complete recovery ranging from 5–10 days. [22] Sometimes mumps can cause inflammation of the brain, pancreatitis, testicular swelling or hearing loss. [25]
Fungal

- Oral candidiasis is by far the most common fungal infection that occurs in the mouth. It usually occurs in immunocompromised individuals. Individuals who have undergone a transplant, HIV, cancer or use corticosteroids commonly develop candida of the mouth and oral cavity. Other risk factors are dentures and tongue piercing. The typical signs are a white patch that may be associated with burning, soreness, irritation or a white cheesy-like appearance. Once the diagnosis is made, candida can be treated with a variety of anti fungal drugs. [26]
Traumatic
- Chemical, thermal, mechanical or electrical trauma to the oral soft tissues can cause traumatic oral ulceration.
Autoimmune
This article may benefit from being shortened by the use of summary style. |
Sjögren syndrome is an autoimmune chronic inflammatory disorder characterised by some of the body's own immune cells infiltrating and destroying lacrimal and salivary glands (and other exocrine glands). There are two types of Sjögren syndrome: primary and secondary. In primary Sjögren syndrome (pSS) individuals have dry eyes (keratoconjunctivitis sicca) and a dry mouth (xerostomia). Based on a meta-analysis, the prevalence of pSS worldwide is estimated to 0.06%, with 90% of the patients being female. [27] In secondary Sjögren syndrome (sSS), individuals have a dry mouth, dry eyes and a connective tissue disorder such as rheumatoid arthritis (prevalence 7% in the UK), systemic lupus erythematosus (prevalence 6.5%–19%) and systemic sclerosis (prevalence 14%–20.5%). [28] Additional features and symptoms include:
- Erythema and lobulation of the tongue
- Oral discomfort
- Difficulty in swallowing and talking
- Altered taste
- Poor retention of dentures (if worn)
- Oral fungal and bacterial infections
- Salivary glands swelling
- Dryness of skin; nose; throat; vagina
- Peripheral neuropathies
- Pulmonary; thyroid; and renal disorders;
- Arthralgias and myalgias;
Tests used to diagnose Sjögren syndrome include:
- tear break-up time and Schirmer's tests
- a minor salivary gland biopsy taken from the lip
- blood tests
- salivary flow rate
There is no cure for Sjögren syndrome; however, there are treatments used to help with the associated symptoms.
- Eye care: artificial tears, moisture chamber spectacles, punctal plugs, pilocarpine medication
- Mouth care: increase oral intake, practice good oral hygiene, use sugar free gum (to increase saliva flow), regular use of mouth rinses, pilocarpine medication, reduce alcohol intake and smoking cessation. Saliva substitutes are also available as a spray, gel, gum or in the form of a medicated sweet
- Dry skin: creams, moisturising soaps
- Vaginal dryness: lubricant, oestrogen creams, hormonal replacement therapy
- Muscle and joint pains: Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs
Complications of Sjögren syndrome include ulcers that can develop on the surface of the eyes if the dryness is not treated. These ulcers can then cause more worrying issues such as loss of eyesight and life-long damage. Individuals with Sjögren syndrome have a slightly increased risk of developing non-Hodgkin lymphoma, a type of cancer. Other conditions such as peripheral neuropathy, Raynaud's phenomenon, kidney problems, underactive thyroid gland and irritable bowel syndrome have been linked to Sjögren syndrome. [29]
Inflammatory
Neoplastic
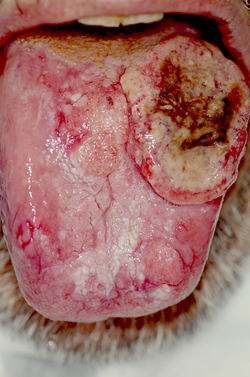
- Oral cancer may occur on the lips, tongue, gums, floor of the mouth or inside the cheeks. The majority of cancers of the mouth are squamous cell carcinoma. Oral cancers are usually painless in the initial stages or may appear like an ulcer. Causes of oral cancer include smoking, excessive alcohol consumption, exposure to sunlight (lip cancer), chewing tobacco, infection with human papillomavirus, and hematopoietic stem cell transplantation. [30] The earlier the oral cancer is diagnosed, the better the chances for full recovery. Persistent suspicious masses or ulcers on the mouth should always be examined. Diagnosis is usually made with a biopsy; treatment depends on the exact type of cancer, where it is situated, and extent of spreading.
Environmental
Unknown
There are many oral and maxillofacial pathologies which are not fully understood.
- Burning mouth syndrome (BMS) is a disorder where there is a burning sensation in the mouth that has no identifiable medical or dental cause. The disorder can affect anyone but tends to occur most often in middle-aged women. BMS has been hypothesized to be linked to a variety of factors such as the menopause, dry mouth (xerostomia) and allergies. BMS usually lasts for several years before disappearing for unknown reasons. Other features of this disorder include anxiety, depression and social isolation. There is no cure for this disorder and treatment includes use of hydrating agents, pain medications, vitamin supplements or the usage of antidepressants. [31]

- Aphthous stomatitis is a condition where ulcers (canker sores) appear on the inside of the mouth, lips and on tongue. Most small canker sores disappear within 10–14 days. Canker sores are most common in young and middle aged individuals. Sometimes individuals with allergies are more prone to these sores. Besides an awkward sensation, these sores can also cause pain or tingling or a burning sensation. Unlike herpes sores, canker sores are always found inside the mouth and are usually less painful.[ citation needed ] Good oral hygiene helps but topical corticosteroids may be necessary. [32]

- Migratory stomatitis is a condition that involves the tongue and other oral mucosa. The common migratory glossitis (geographic tongue) affects the anterior two thirds of the dorsal and lateral tongue mucosa of 1% to 2.5% of the population, with one report of up to 12.7% of the population. The tongue is often fissured, especially. in elderly individuals. In the American population, a lower prevalence was reported among Mexican Americans (compared with Caucasians and African Americans) and cigarette smokers. When other oral mucosa, beside the dorsal and lateral tongue, are involved, the term migratory stomatitis (or ectopic geographic tongue) is preferred. In this condition, lesions infrequently involve also the ventral tongue and buccal or labial mucosa. They are rarely reported on the soft palate and floor of the mouth. [33]