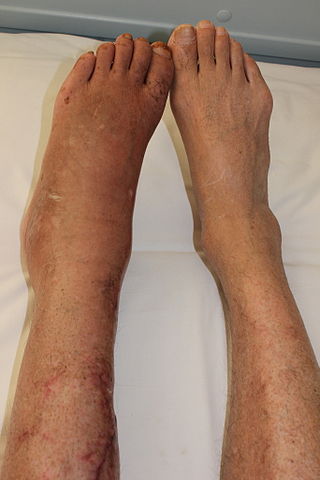
Complex regional pain syndrome (CRPS) is any of several painful conditions that are characterized by a continuing regional pain that is seemingly disproportionate in time or degree to the usual course of any known trauma or other lesion. Usually starting in a limb, it manifests as pain, swelling, limited range of motion, and/or changes to the skin and bones. It may initially affect one limb and then spread throughout the body; 35% of affected people report symptoms throughout their whole bodies. Two types exist: reflex sympathetic dystrophy (RSD) and causalgia. Having both types is possible.
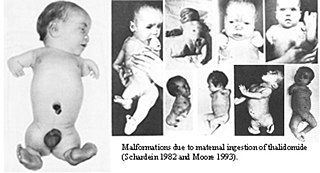
Phocomelia is a condition that involves malformations of human arms and legs. Although many factors can cause phocomelia, the prominent roots come from the use of the drug thalidomide and from genetic inheritance.

Adducted thumb syndrome recessive form is a rare disease affecting multiple systems causing malformations of the palate, thumbs, and upper limbs. The name Christian syndrome derives from Joe. C. Christian, the first person to describe the condition. Inheritance is believed to be autosomal recessive, caused by mutation in the CHST14 gene.

Tetraplegia, also known as quadriplegia, is defined as the dysfunction or loss of motor and/or sensory function in the cervical area of the spinal cord. A loss of motor function can present as either weakness or paralysis leading to partial or total loss of function in the arms, legs, trunk, and pelvis; paraplegia is similar but affects the thoracic, lumbar, and sacral segments of the spinal cord and arm function is spared. The paralysis may be flaccid or spastic. A loss of sensory function can present as an impairment or complete inability to sense light touch, pressure, heat, pinprick/pain, and proprioception. In these types of spinal cord injury, it is common to have a loss of both sensation and motor control.

Compartment syndrome is a condition in which increased pressure within one of the body's anatomical compartments results in insufficient blood supply to tissue within that space. There are two main types: acute and chronic. Compartments of the leg or arm are most commonly involved.
Alien hand syndrome (AHS) or Dr. Strangelove syndrome is a category of conditions in which a person experiences their limbs acting seemingly on their own, without conscious control over the actions. There are a variety of clinical conditions that fall under this category, which most commonly affects the left hand. There are many similar terms for the various forms of the condition, but they are often used inappropriately. The affected person may sometimes reach for objects and manipulate them without wanting to do so, even to the point of having to use the controllable hand to restrain the alien hand. Under normal circumstances however, given that intent and action can be assumed to be deeply mutually entangled, the occurrence of alien hand syndrome can be usefully conceptualized as a phenomenon reflecting a functional "disentanglement" between thought and action.

A phantom limb is the sensation that an amputated or missing limb is still attached. Approximately 80–100% of individuals with an amputation experience sensations in their amputated limb. However, only a small percentage will experience painful phantom limb sensation. These sensations are relatively common in amputees and usually resolve within two to three years without treatment. Research continues to explore the underlying mechanisms of phantom limb pain (PLP) and effective treatment options.
Periodic limb movement disorder (PLMD) is a sleep disorder where the patient moves limbs involuntarily and periodically during sleep, and has symptoms or problems related to the movement. PLMD should not be confused with restless legs syndrome (RLS). RLS is characterized by a voluntary response to an urge to move legs due to discomfort. PLMD on the other hand is involuntary, and the patient is often unaware of these movements altogether. Periodic limb movements (PLMS) occurring during daytime period can be found but are considered as a symptom of RLS. Only PLMS during sleep can suggest a diagnosis of PLMD.

Stiff-person syndrome (SPS), also known as stiff-man syndrome (SMS), is a rare neurologic disorder of unclear cause characterized by progressive rigidity and stiffness. The stiffness primarily affects the truncal muscles and is superimposed by spasms, resulting in postural deformities. Chronic pain, impaired mobility, and lumbar hyperlordosis are common symptoms.

Bartter syndrome (BS) is a rare inherited disease characterised by a defect in the thick ascending limb of the loop of Henle, which results in low potassium levels (hypokalemia), increased blood pH (alkalosis), and normal to low blood pressure. There are two types of Bartter syndrome: neonatal and classic. A closely associated disorder, Gitelman syndrome, is milder than both subtypes of Bartter syndrome.
Klüver–Bucy syndrome is a syndrome resulting from bilateral lesions of the medial temporal lobe. Klüver–Bucy syndrome may present with compulsive eating, hypersexuality, insertion of inappropriate objects in the mouth (hyperorality), visual agnosia, and docility. Klüver–Bucy syndrome is more commonly found in rhesus monkeys, where the condition was first documented, than in humans. Pathology on the syndrome is still controversial with Norman Geschwind's theory and Muller theory offering different explanations for the condition. Treatment for Klüver–Bucy syndrome is minimal with no current cure.

Holt–Oram syndrome is an autosomal dominant disorder that affects bones in the arms and hands and often causes heart problems. The syndrome may include an absent radial bone in the forearm, an atrial septal defect in the heart, or heart block. It affects approximately 1 in 100,000 people.

Amelia is the birth defect of lacking one or more limbs. It can also result in a shrunken or deformed limb. The term may be modified to indicate the number of legs or arms missing at birth, such as tetra-amelia for the absence of all four limbs. A related term is meromelia, which is the partial absence of a limb or limbs. The term is from Greek ἀ- "lack of" plus μέλος "limb"

Dysmelia is a congenital disorder of a limb resulting from a disturbance in embryonic development.
T-box refers to a group of transcription factors involved in embryonic limb and heart development. Every T-box protein has a relatively large DNA-binding domain, generally comprising about a third of the entire protein that is both necessary and sufficient for sequence-specific DNA binding. All members of the T-box gene family bind to the "T-box", a DNA consensus sequence of TCACACCT.
T-box transcription factor TBX5, is a protein that in humans is encoded by the TBX5 gene.
Congenital limb deformities are congenital musculoskeletal disorders which primarily affect the upper and lower limbs.

Hanhart syndrome is a broad classification of congenital disorders that cause an undeveloped tongue and malformed extremities and fingers. There exist 5 types of Hanhart syndrome, with the severity and nature of the condition rangeing widely on a case-by-case basis. Hanhart syndrome is classified as a rare disease, with only 30 known cases having ever been diagnosed. Early hypotheses believed that the disease was caused by genetic conditions, with a more recent hypothesis demonstrating that the disease is caused by hemorrhagic lesions during prenatal development.

Constriction ring syndrome (CRS) is a congenital disorder with unknown cause. Because of the unknown cause there are many different, and sometimes incorrect names. It is a malformation due to intrauterine bands or rings that give deep grooves in, most commonly, distal extremities like fingers and toes. In rare cases the constriction ring can form around other parts of the fetus and cause amputation or even intrauterine death. The anatomy proximal to the site of constriction is developmentally normal. CRS can be associated with other malformations with club foot being most common. The precise configuration of the bands, lymphedema, and character of the amputations are not predictable and vary with each individual patient. Also more than one extremity is usually affected, and it is rare for only one ring to present as an isolated malformation with no other manifestation of this syndrome.














